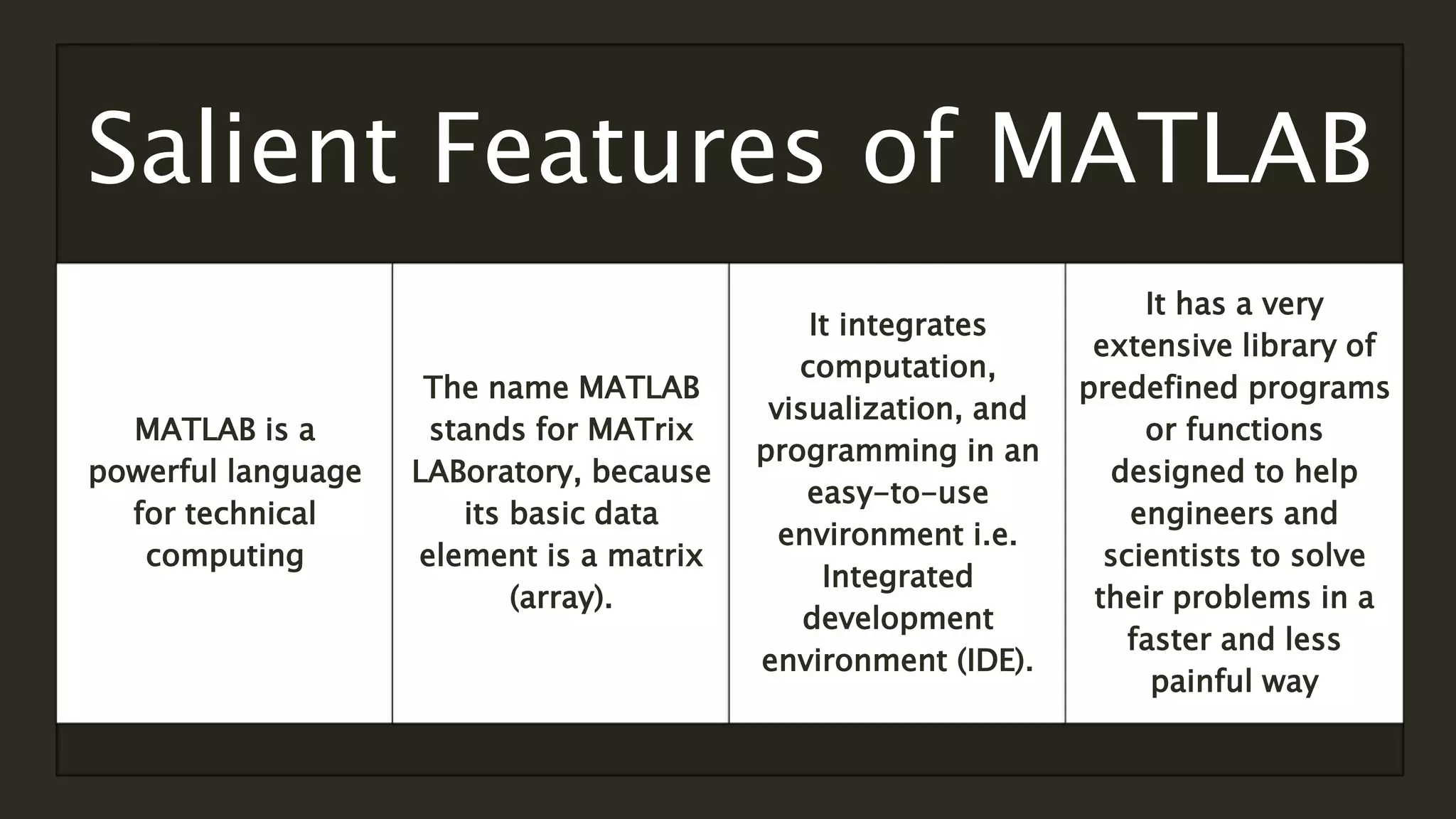
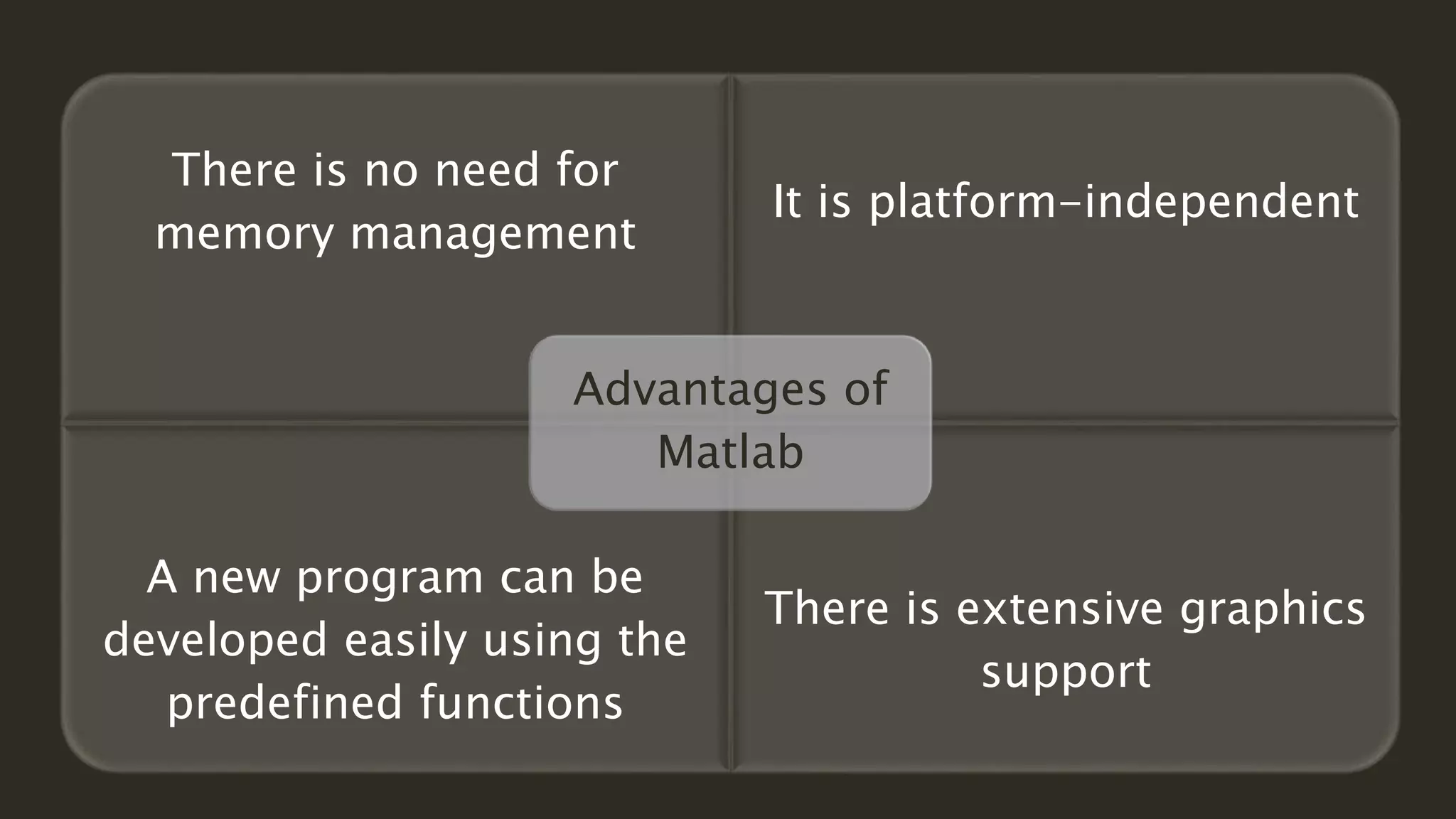
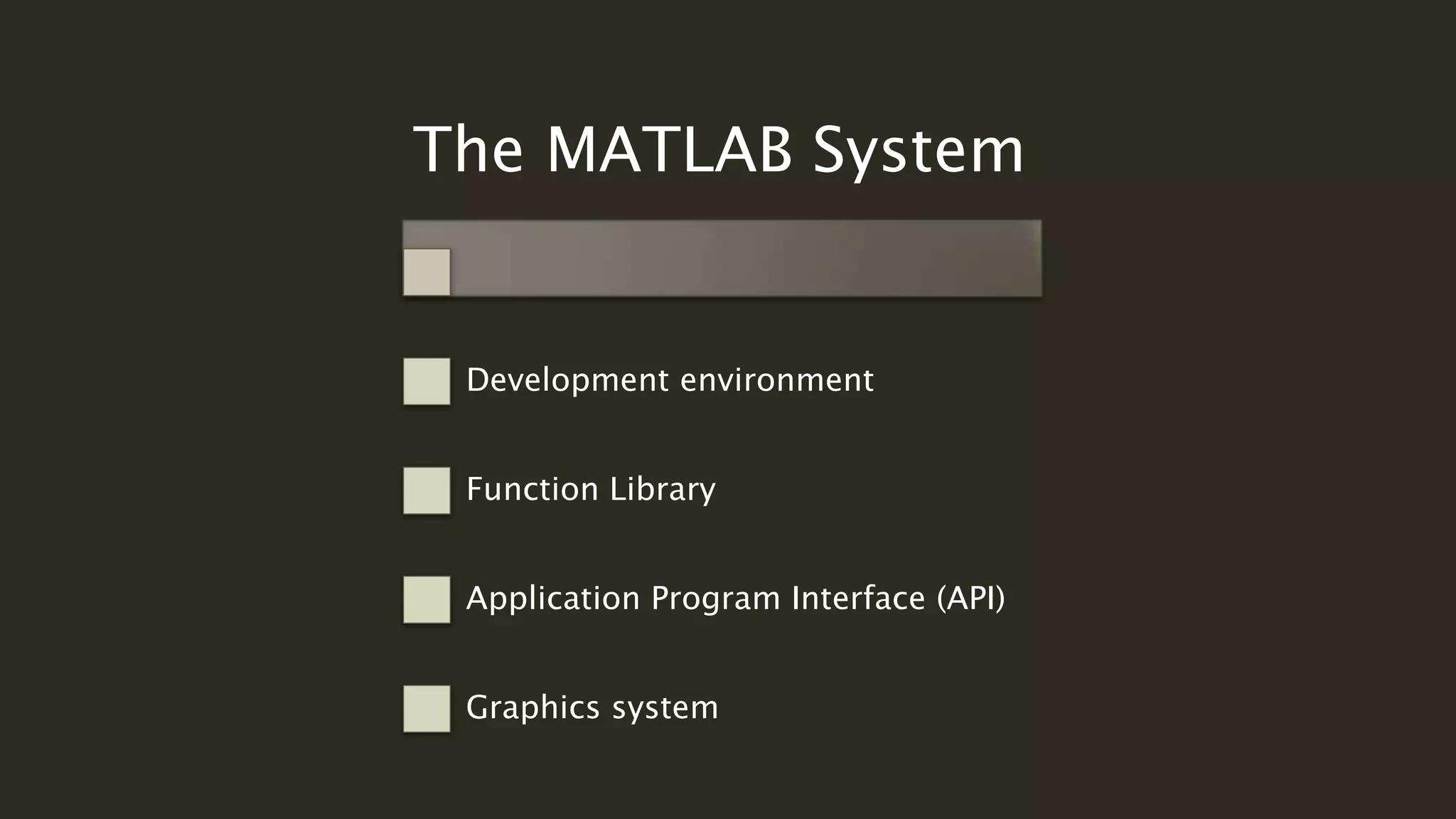
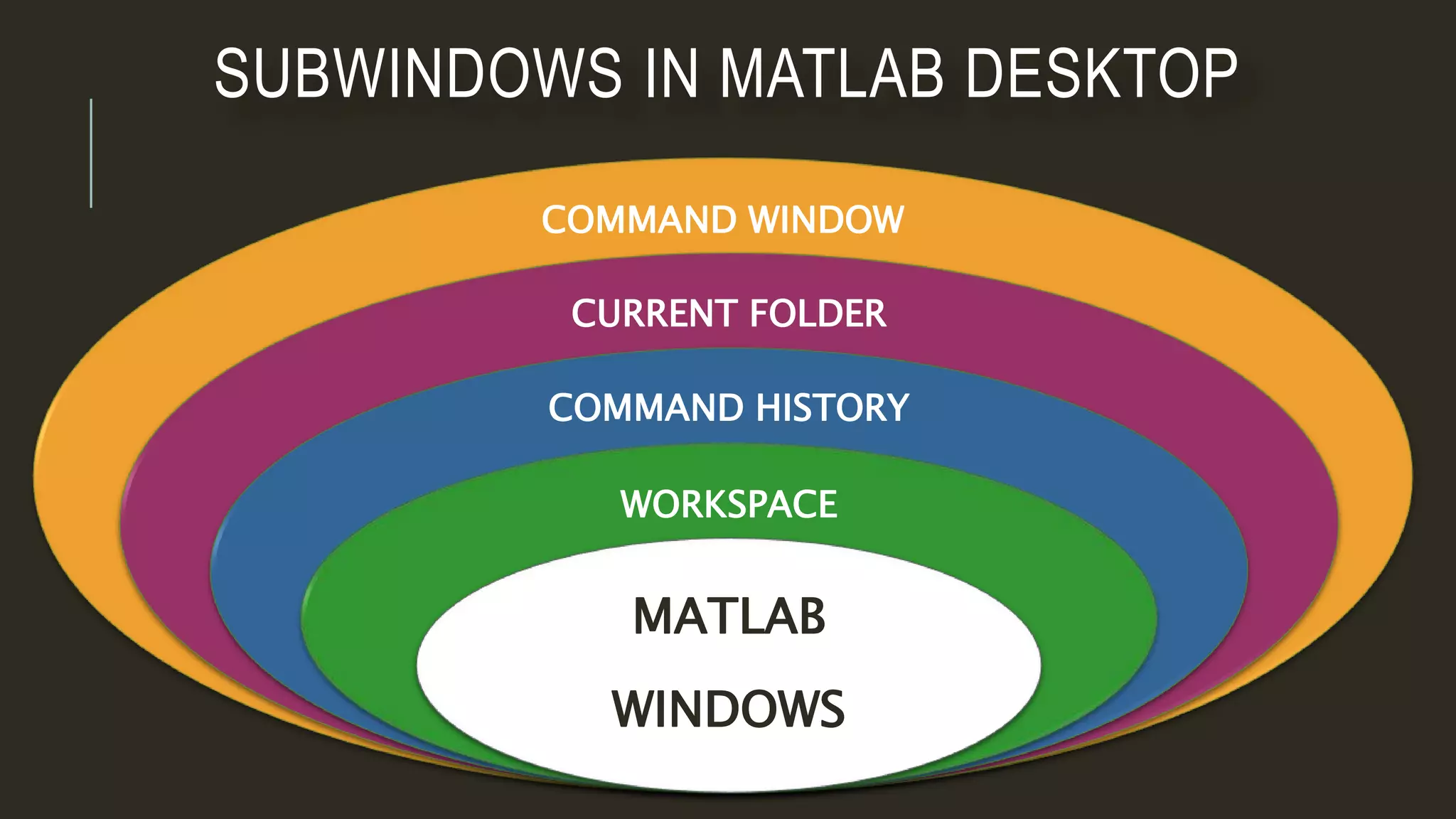
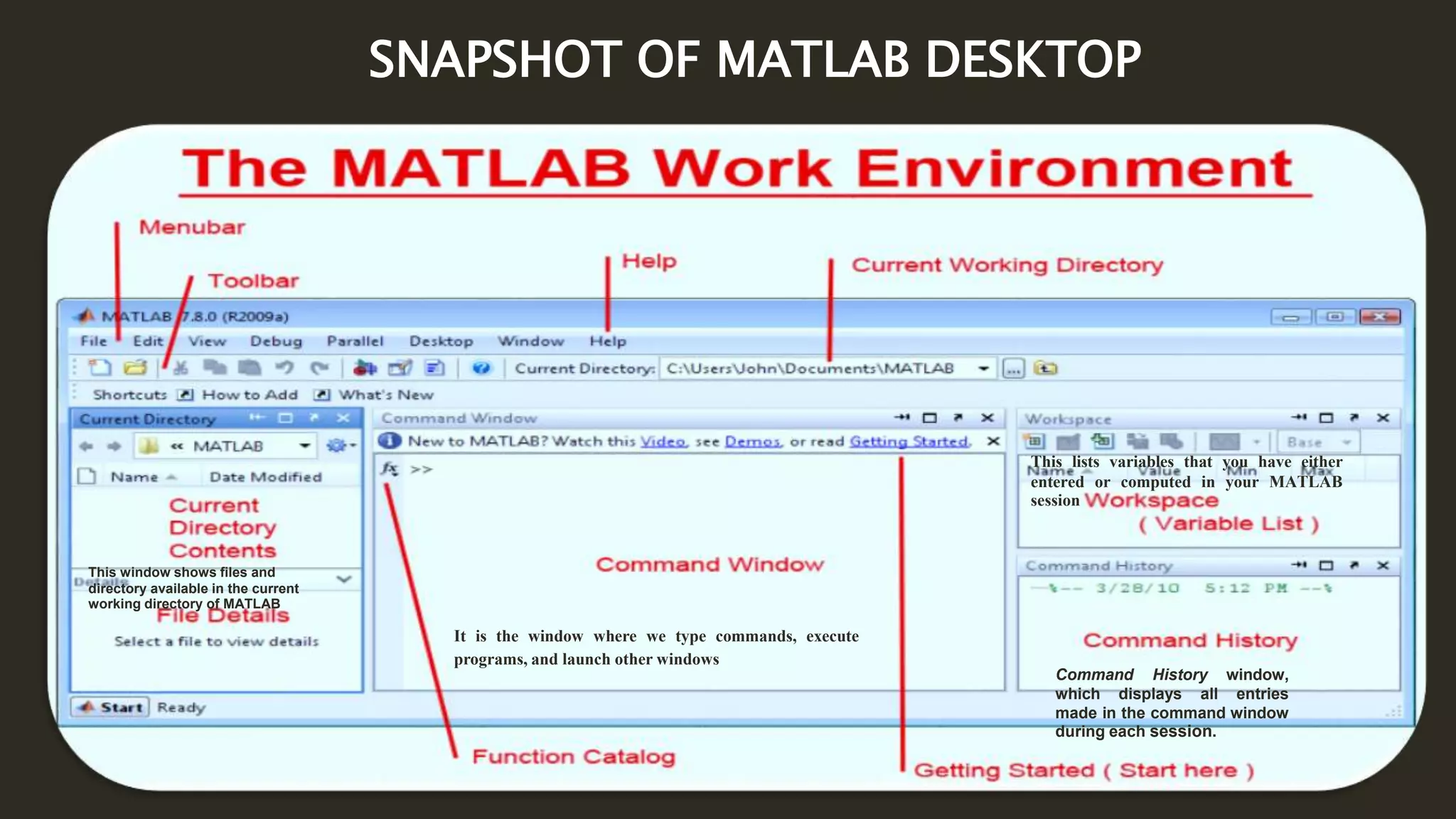
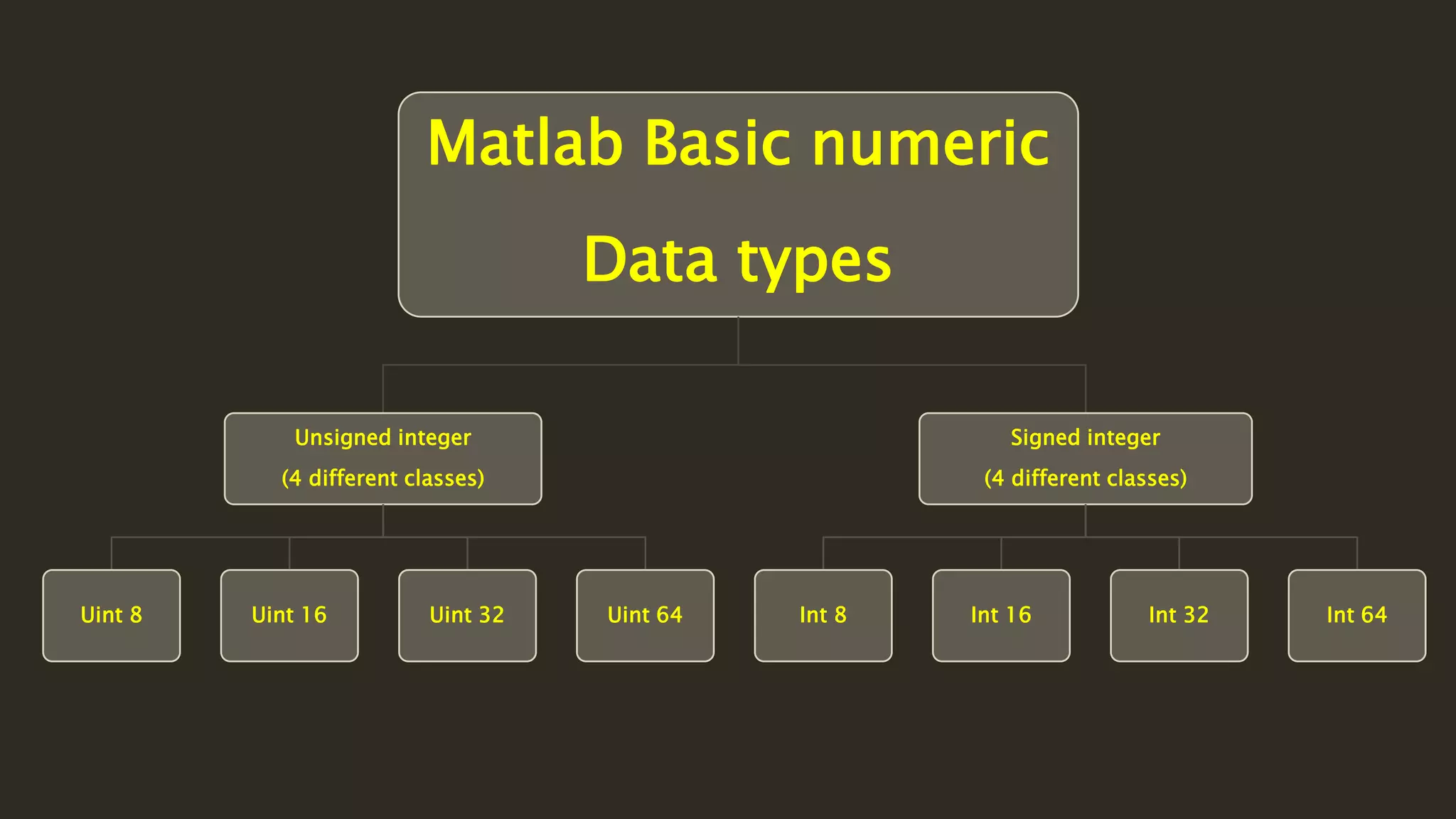
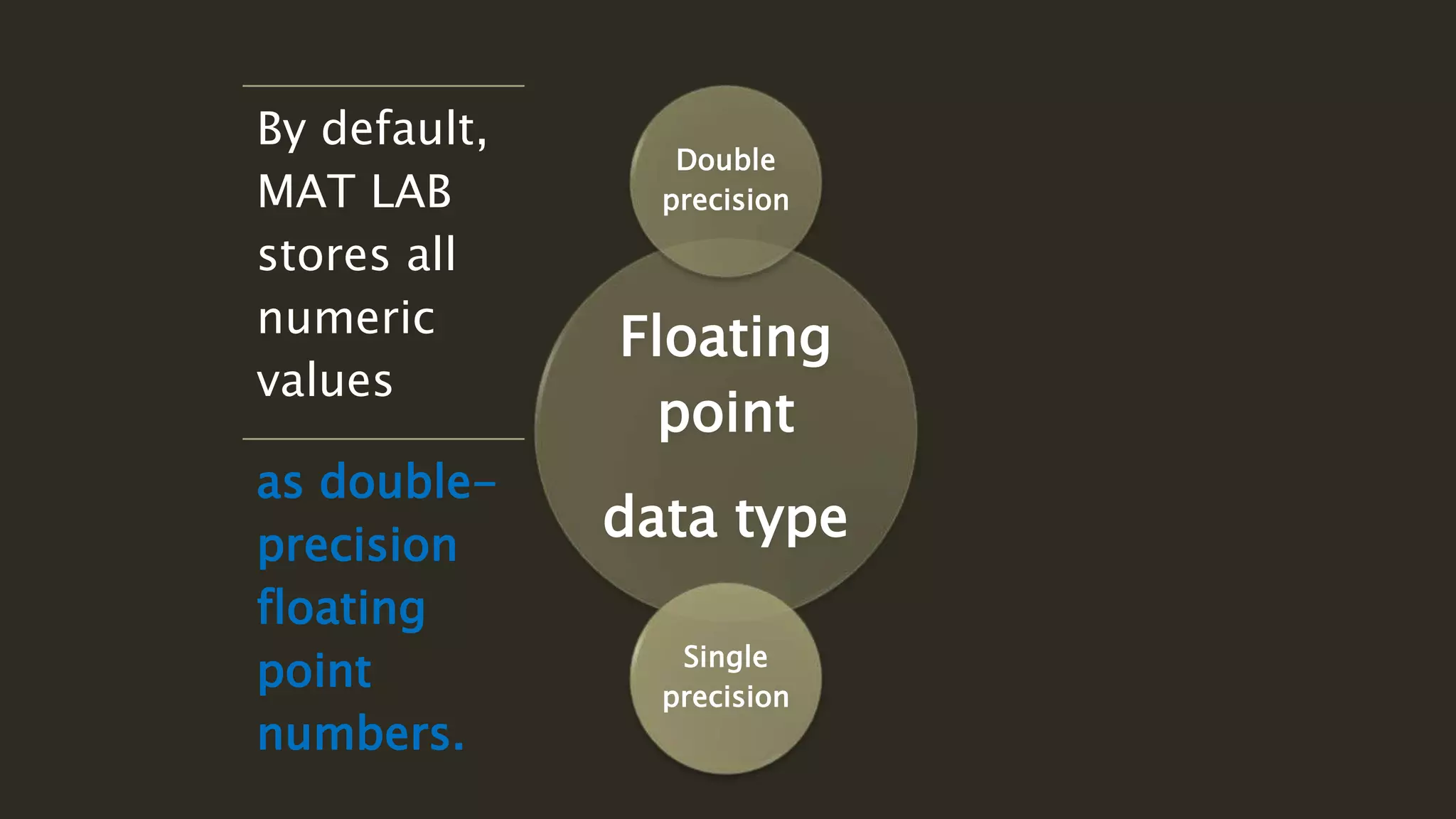
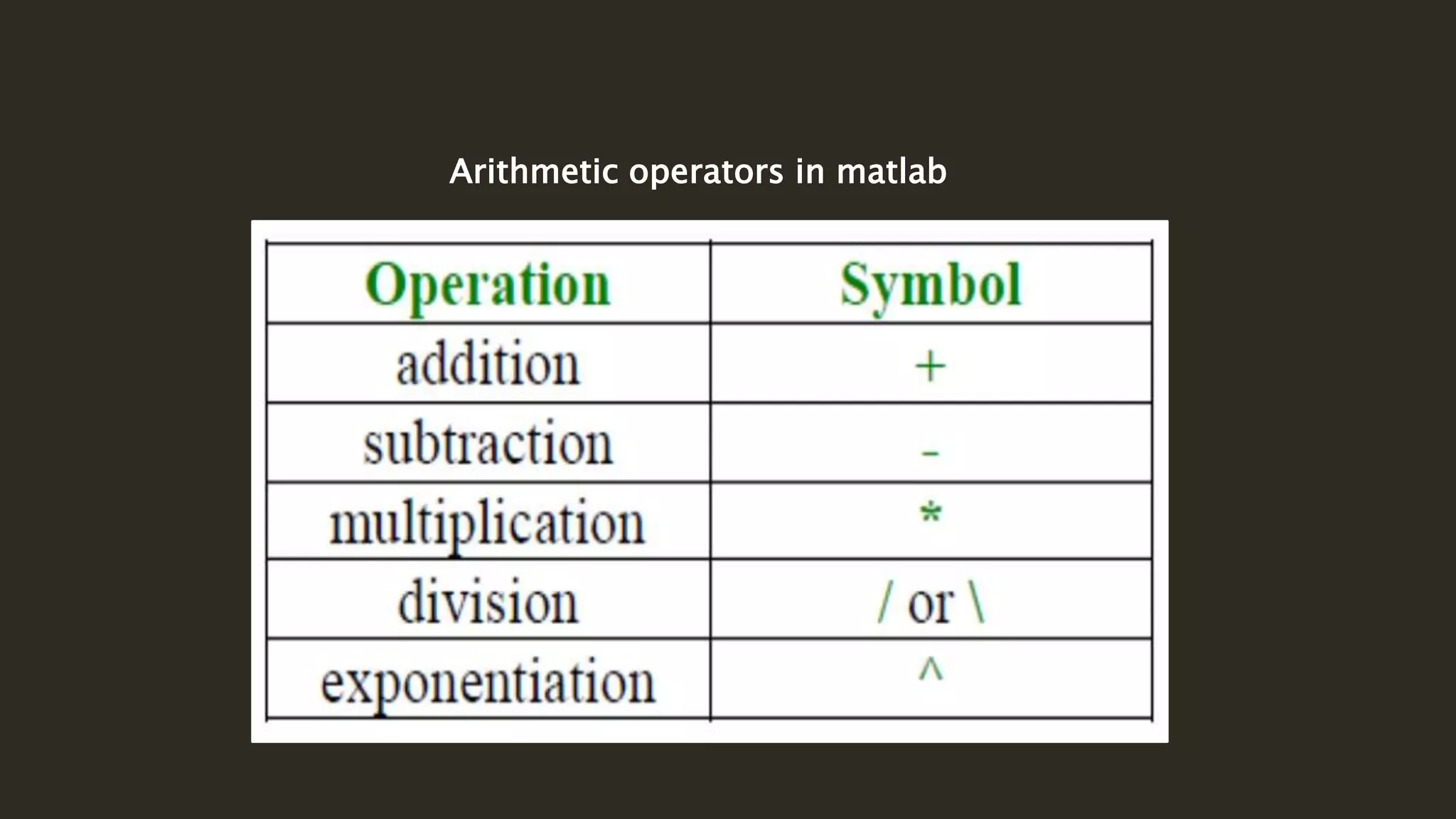
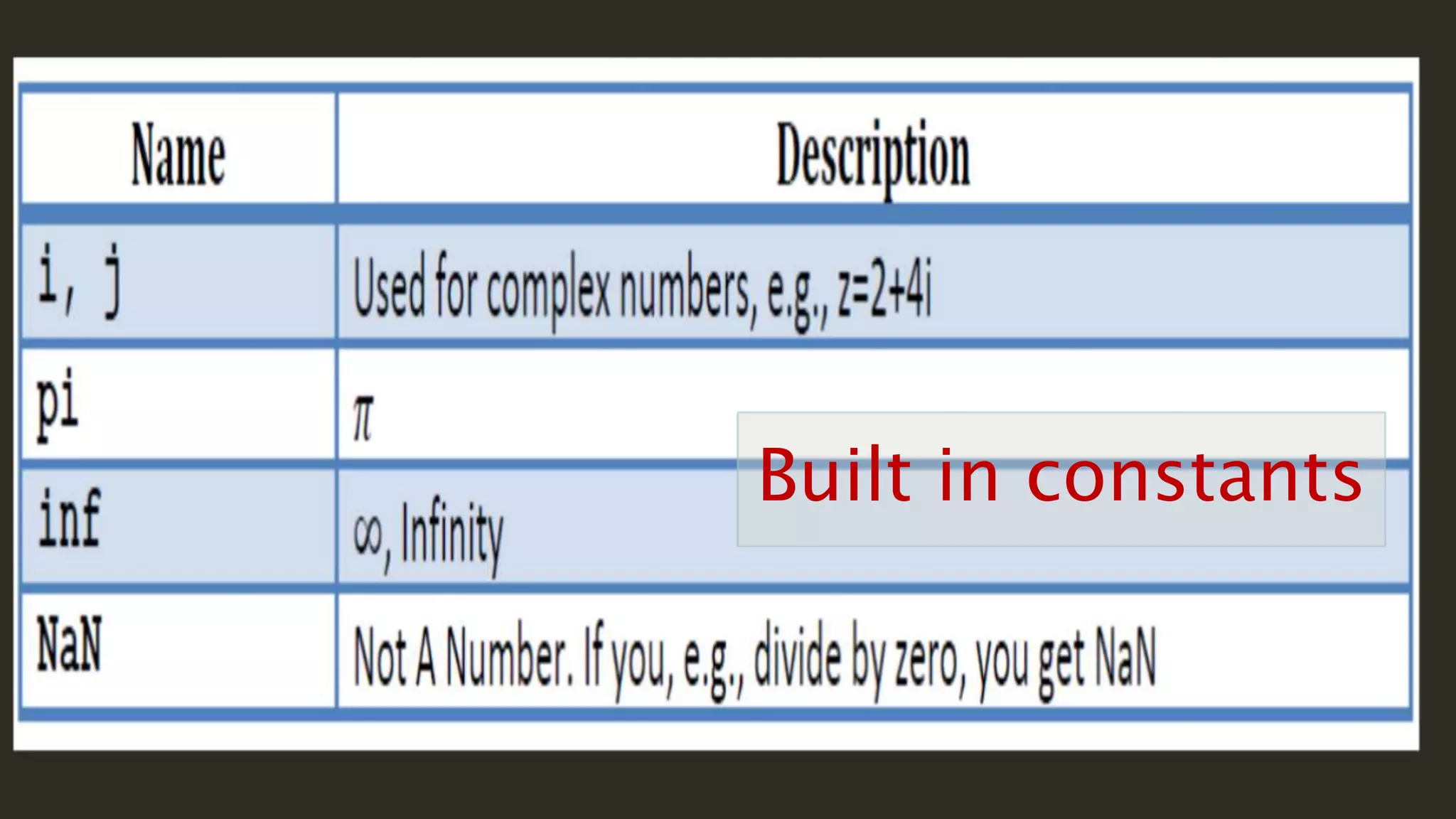
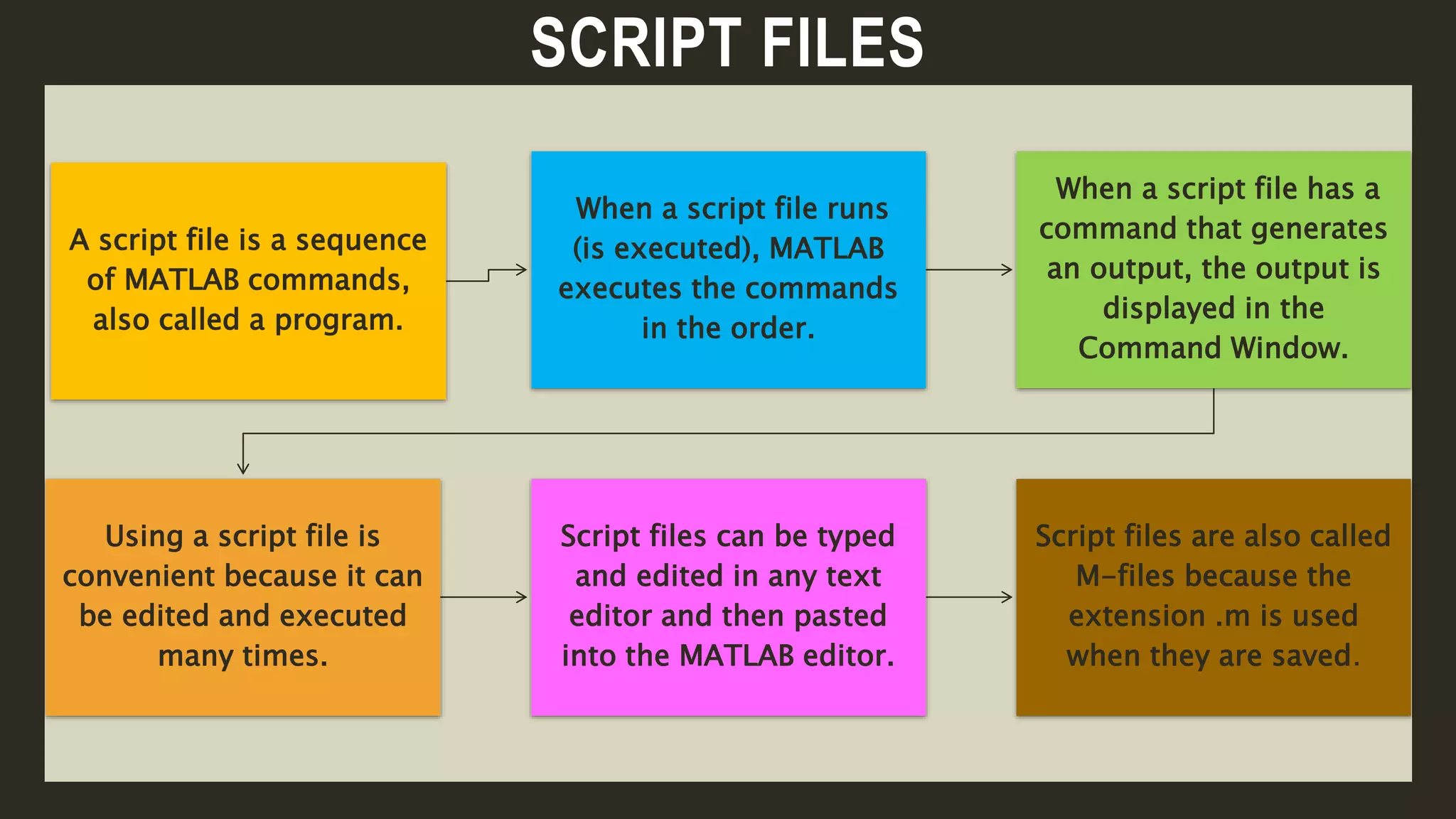
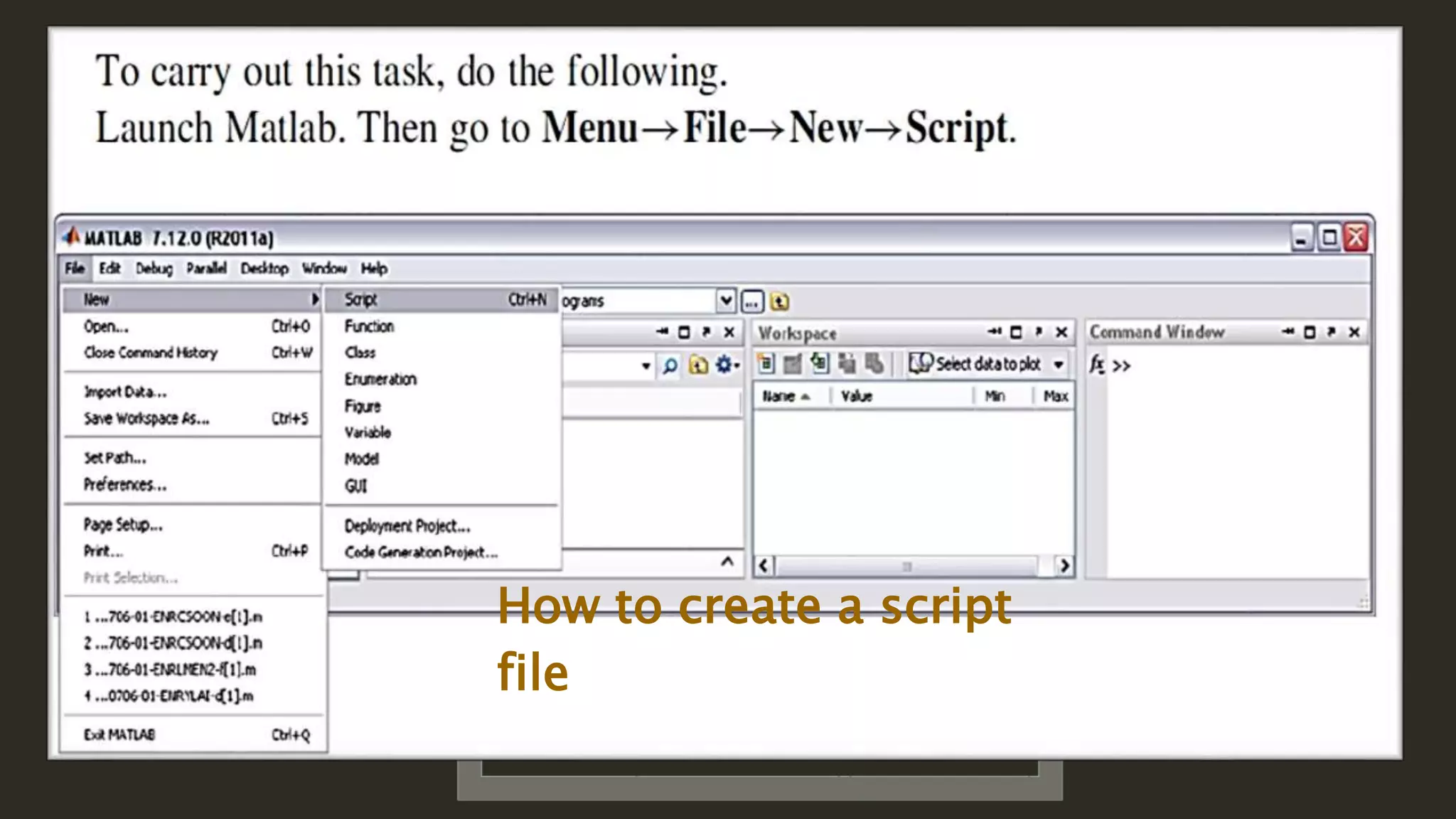
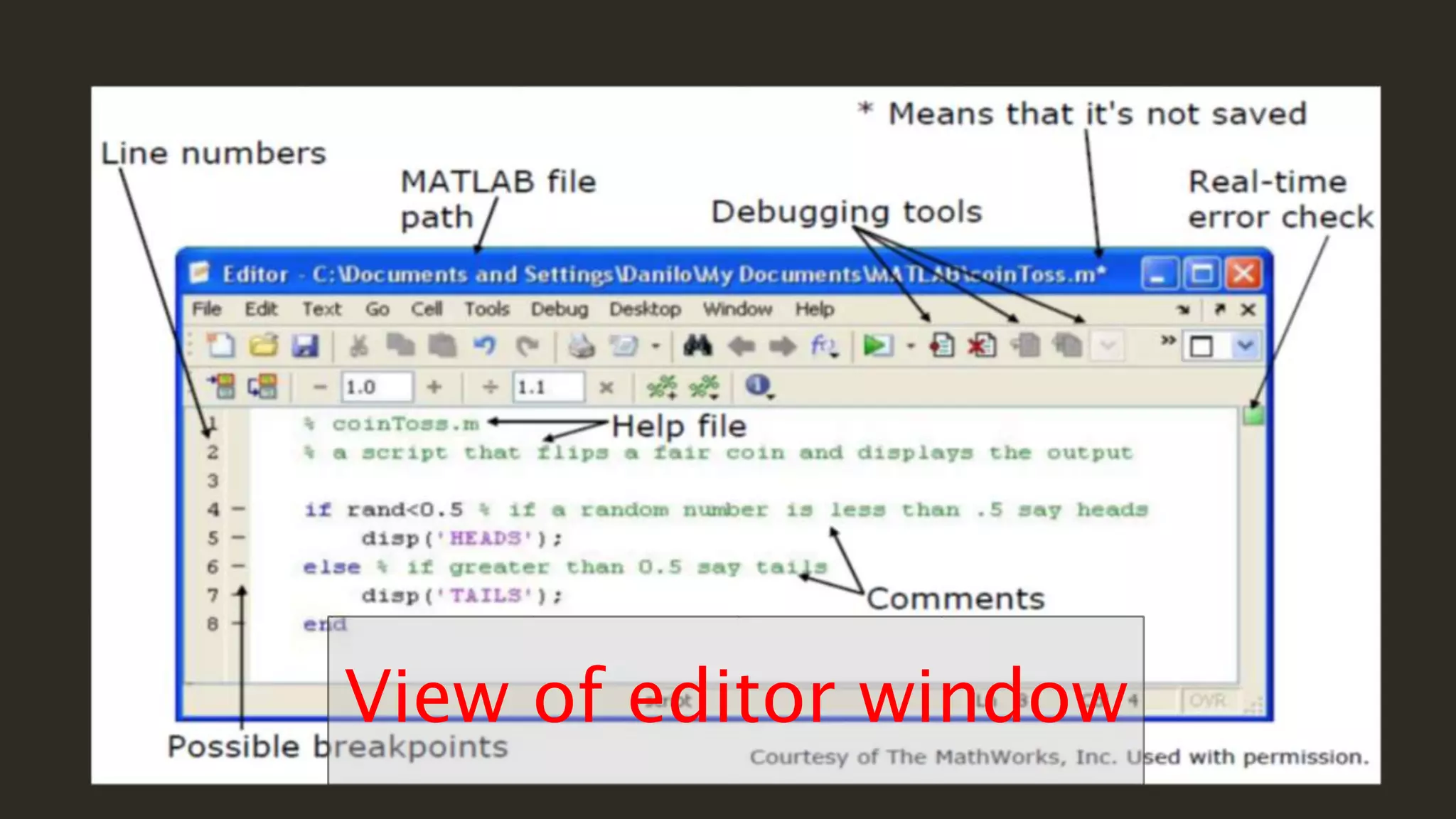
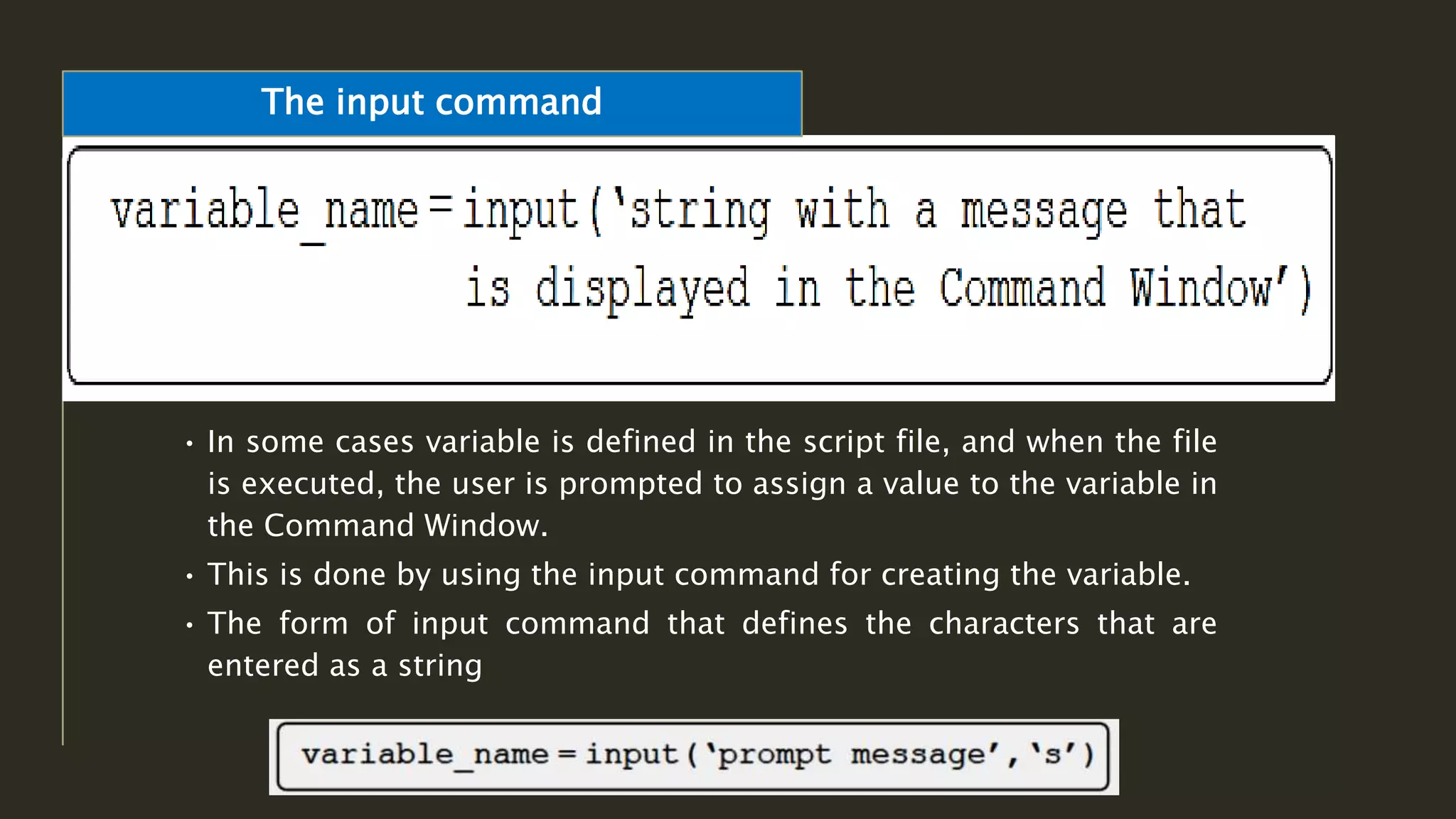
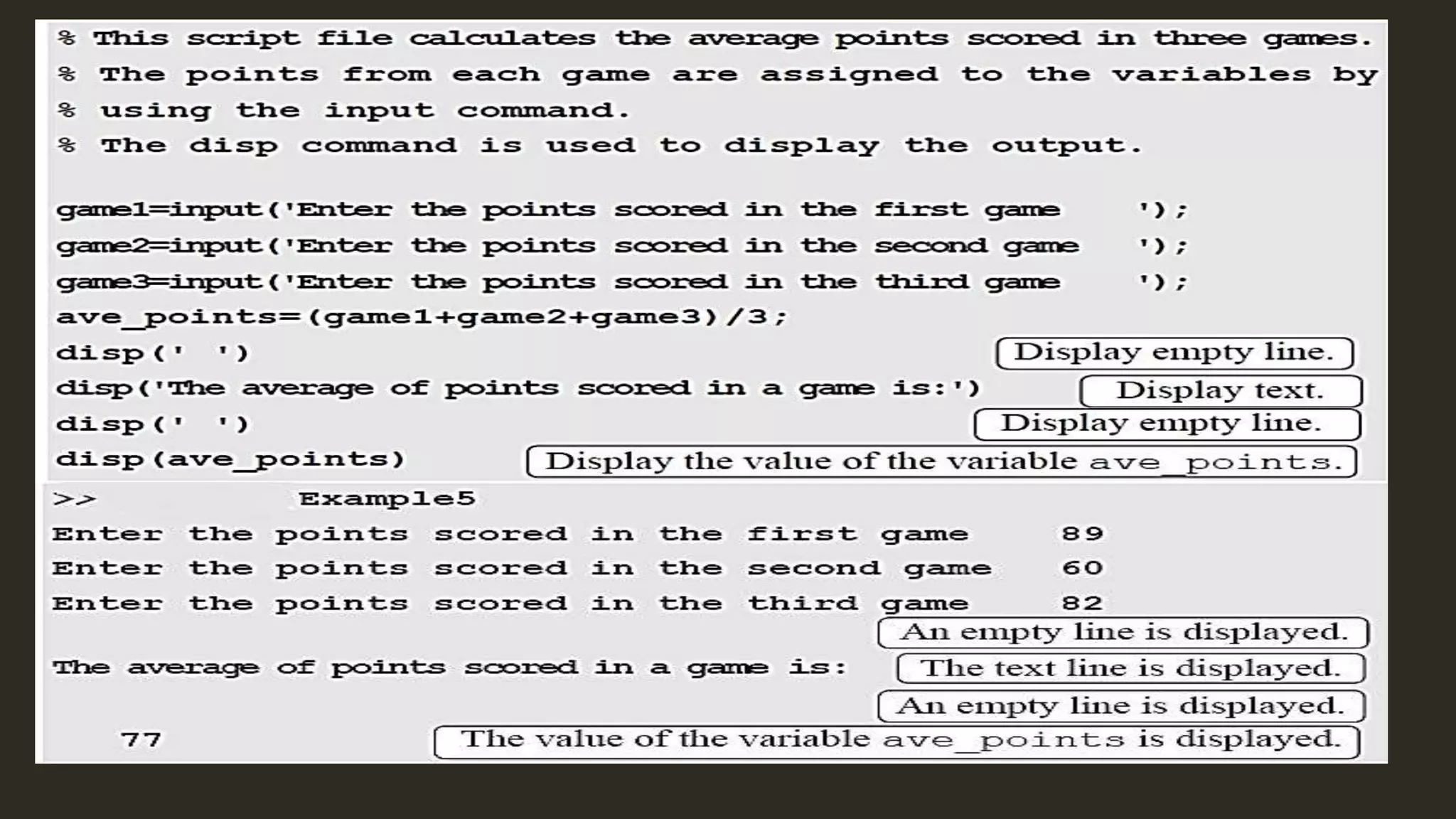
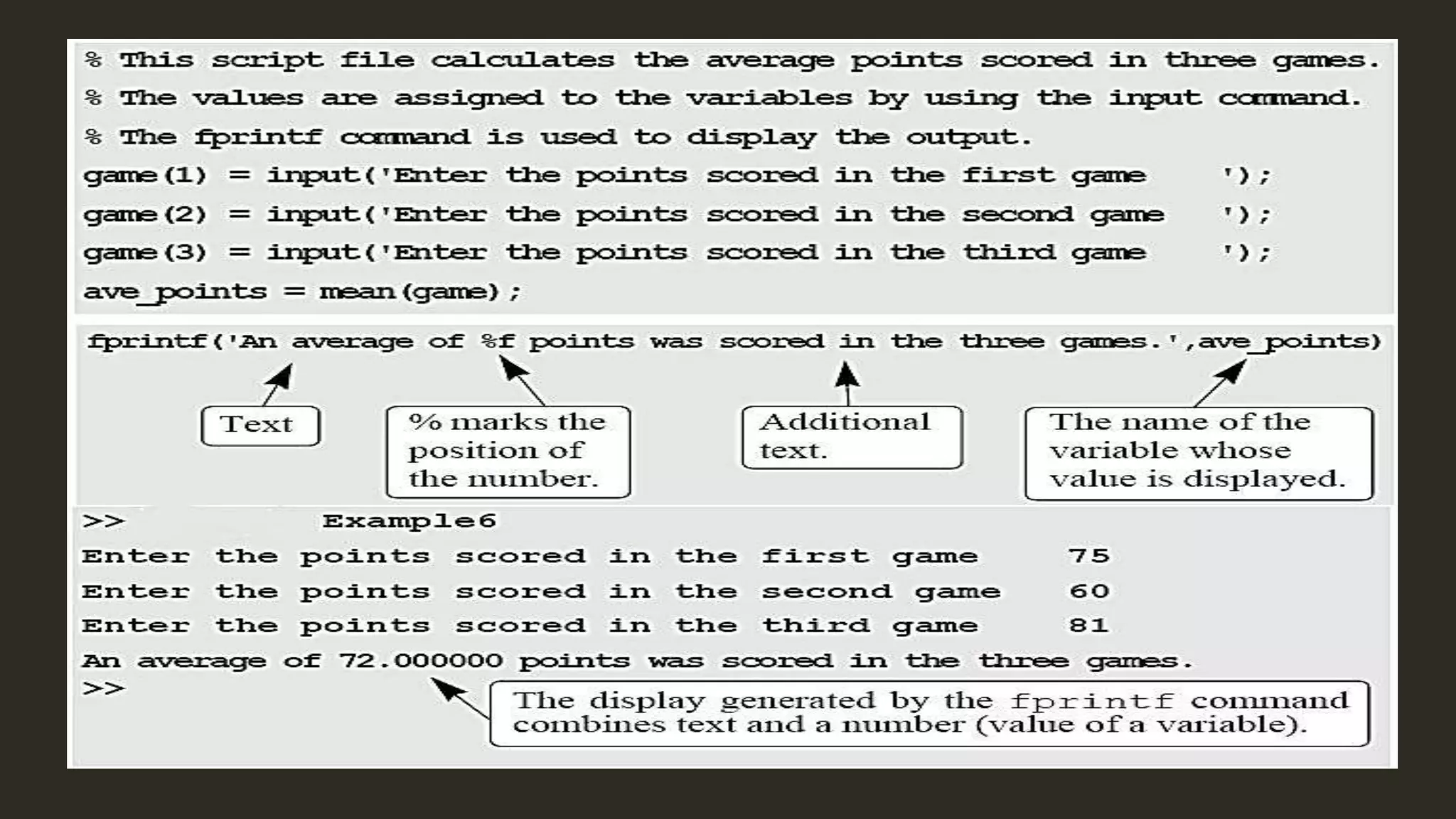
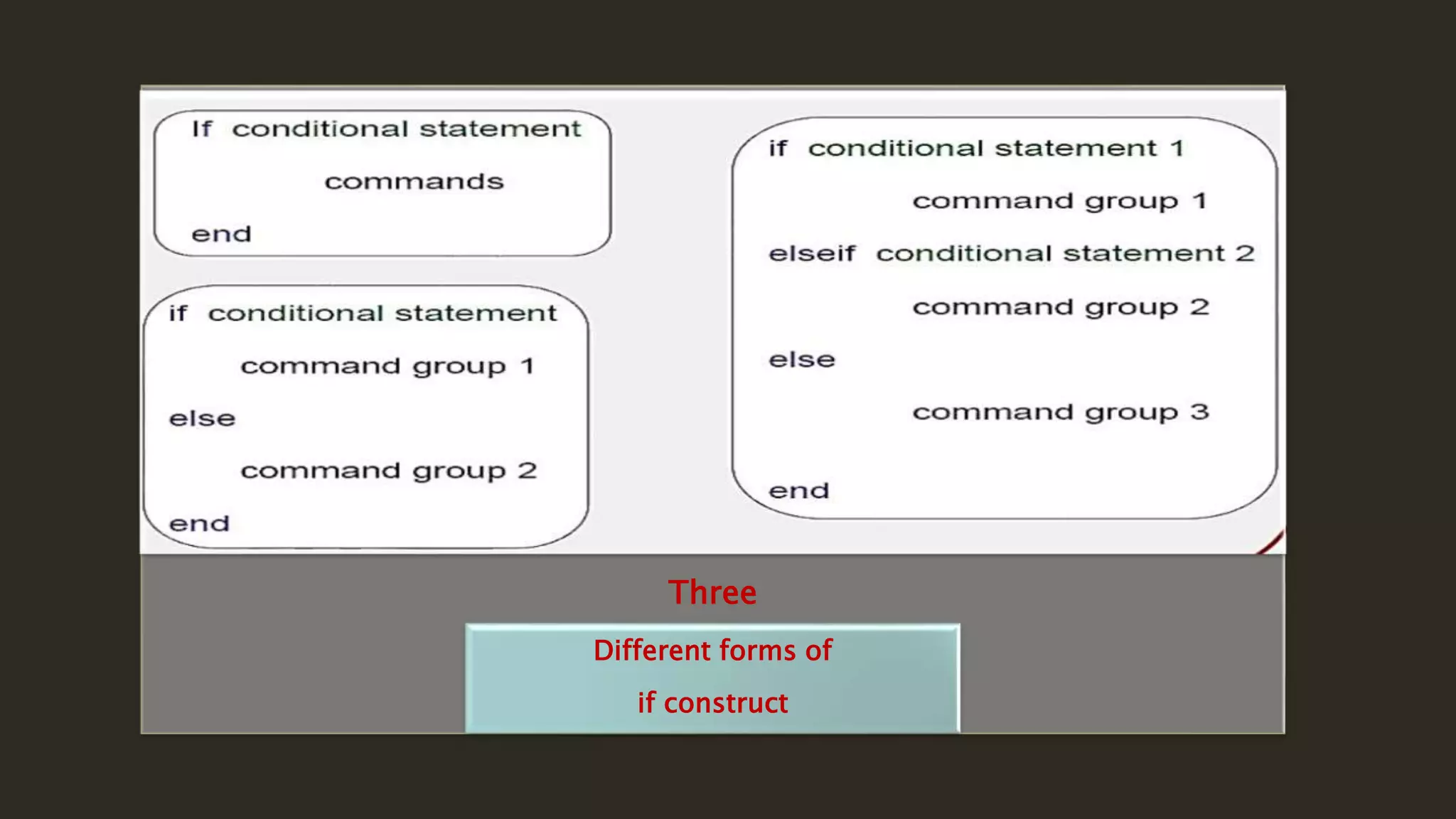
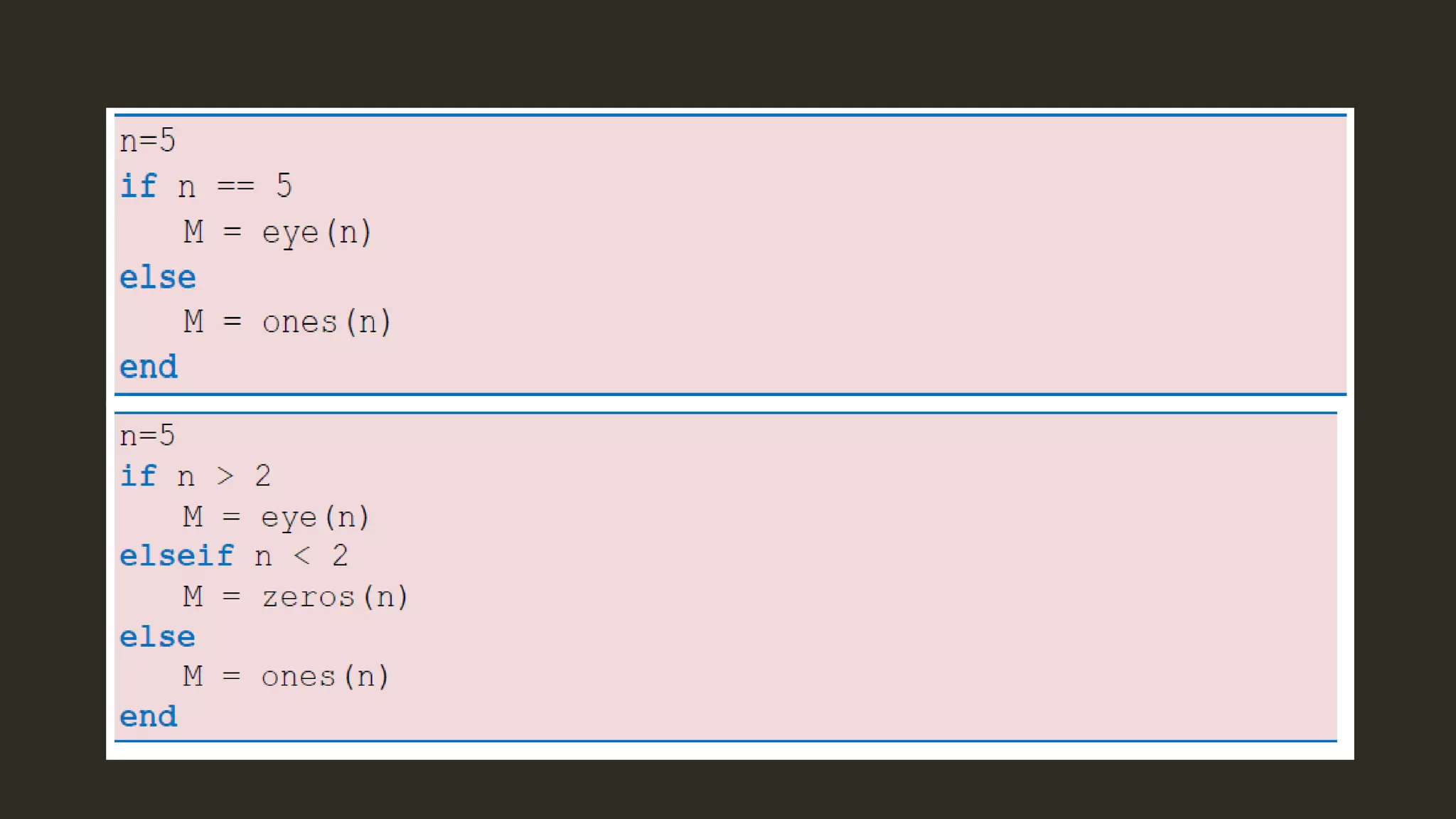
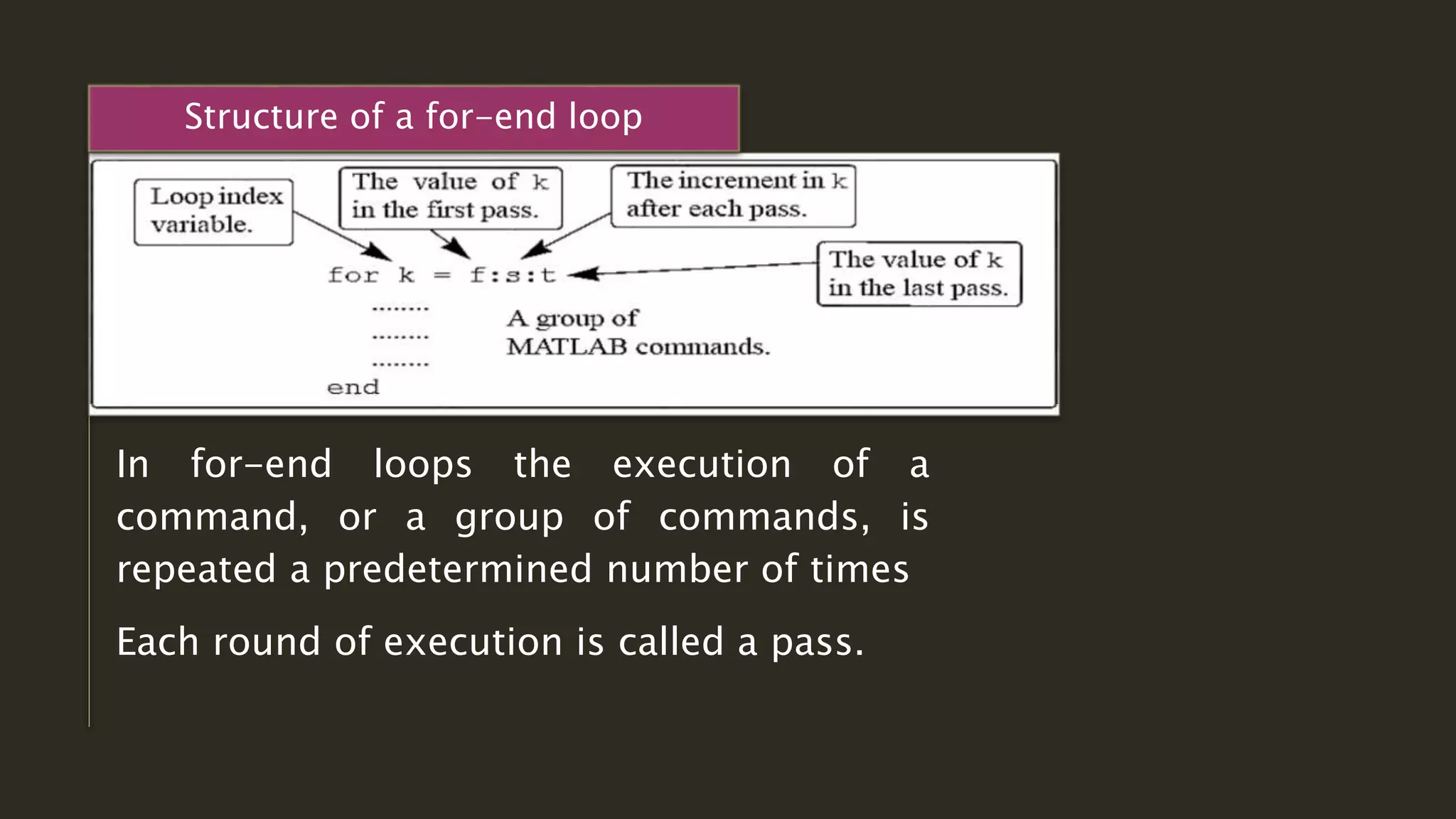
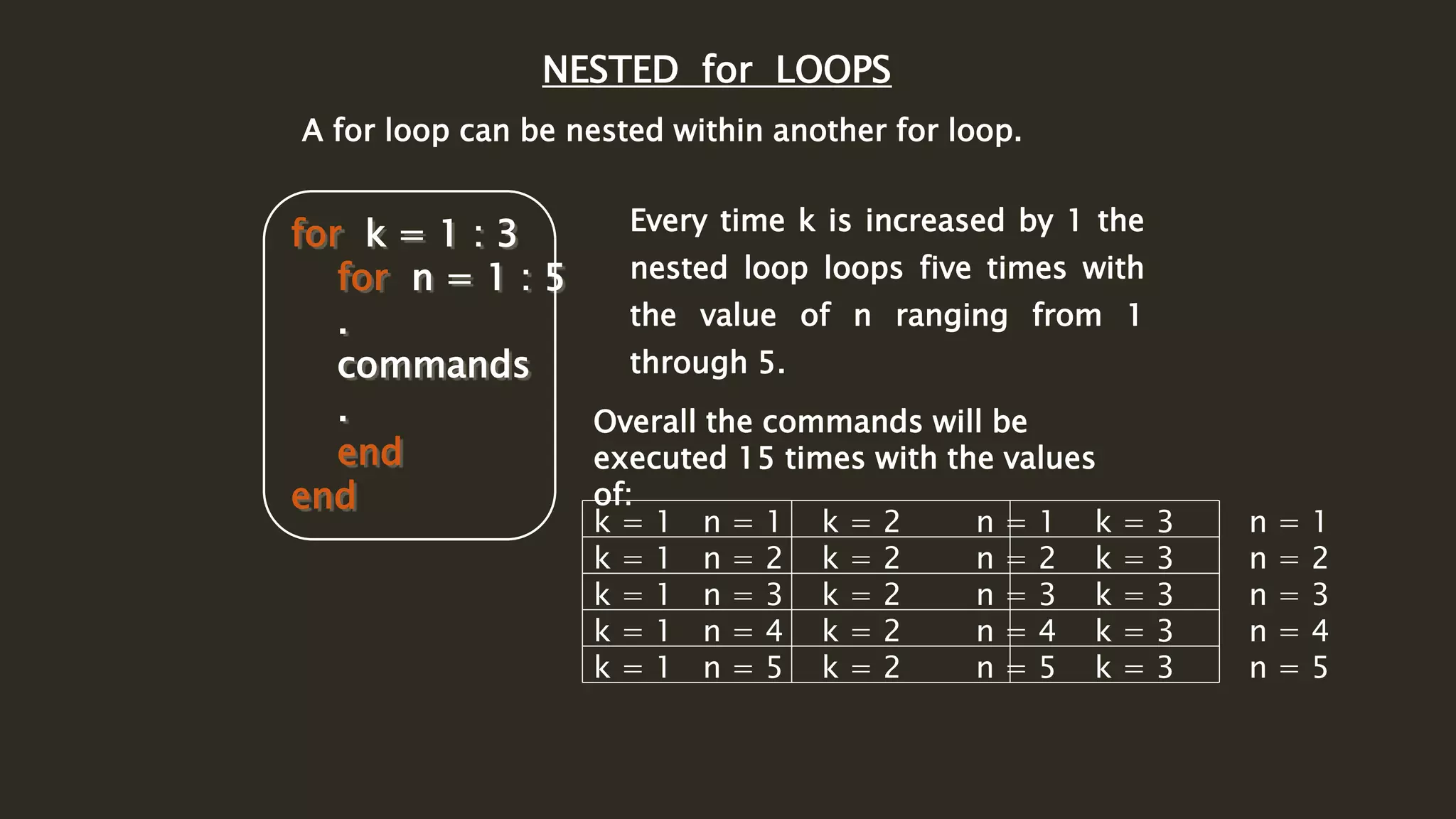
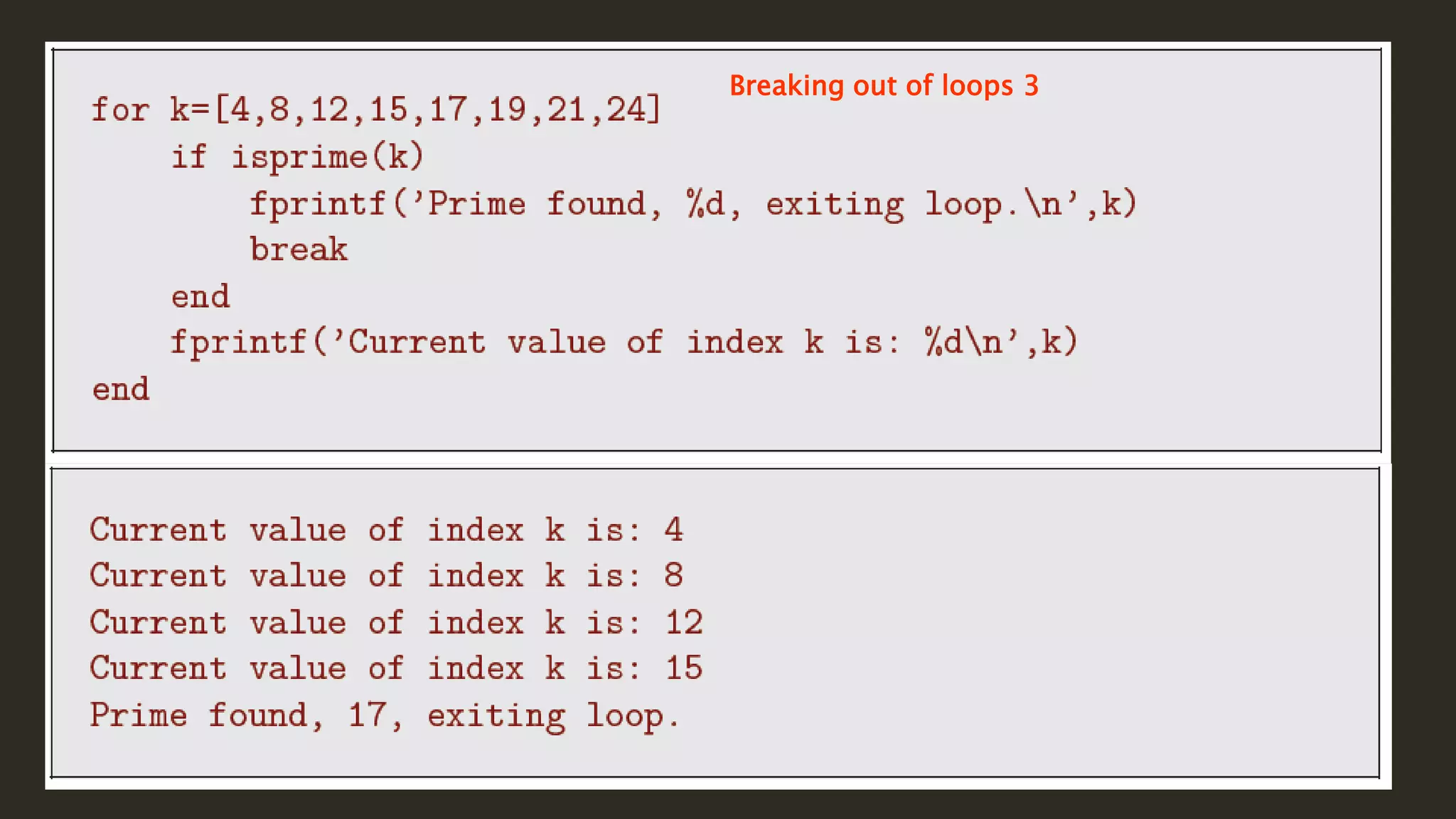
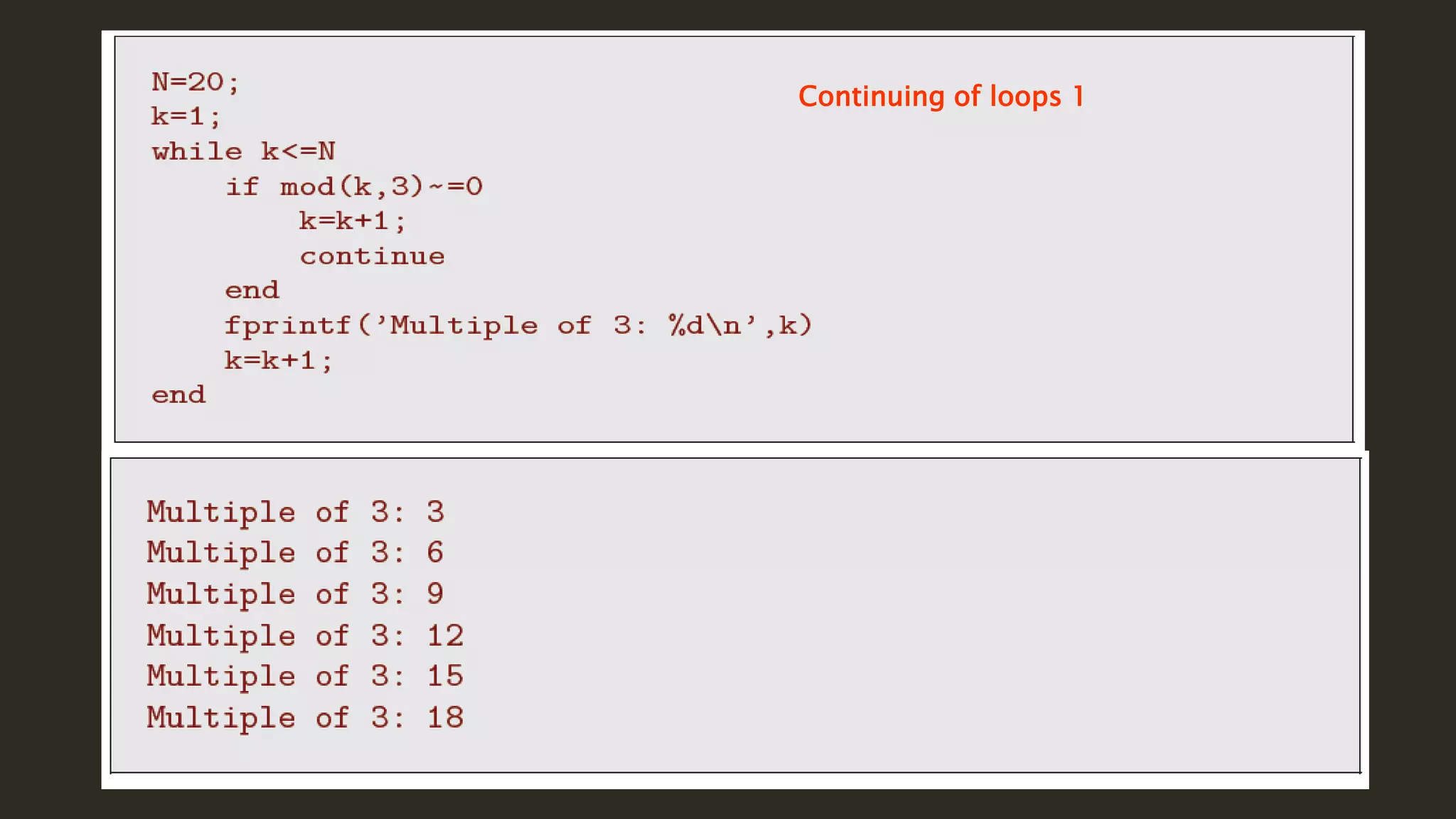
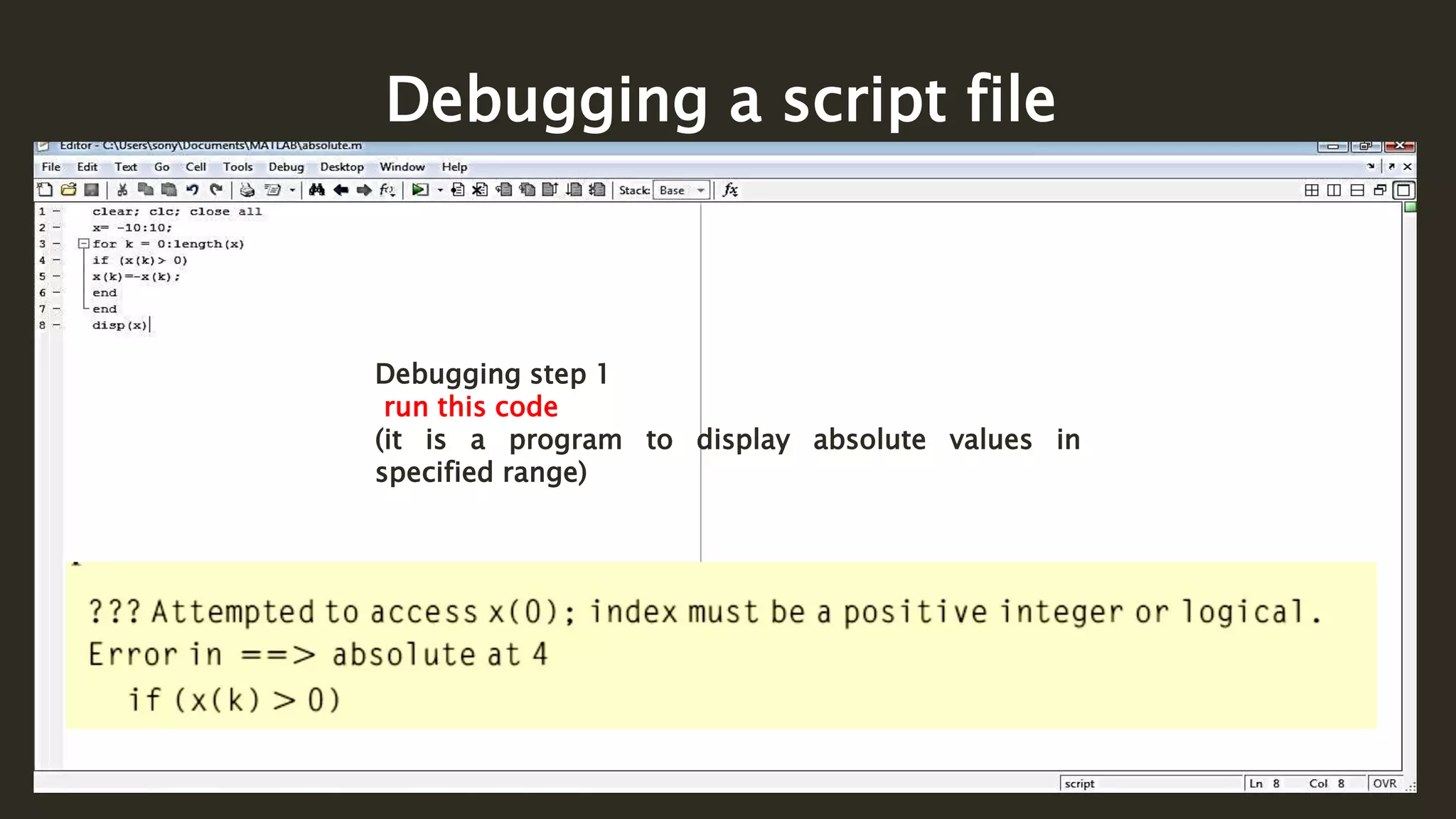
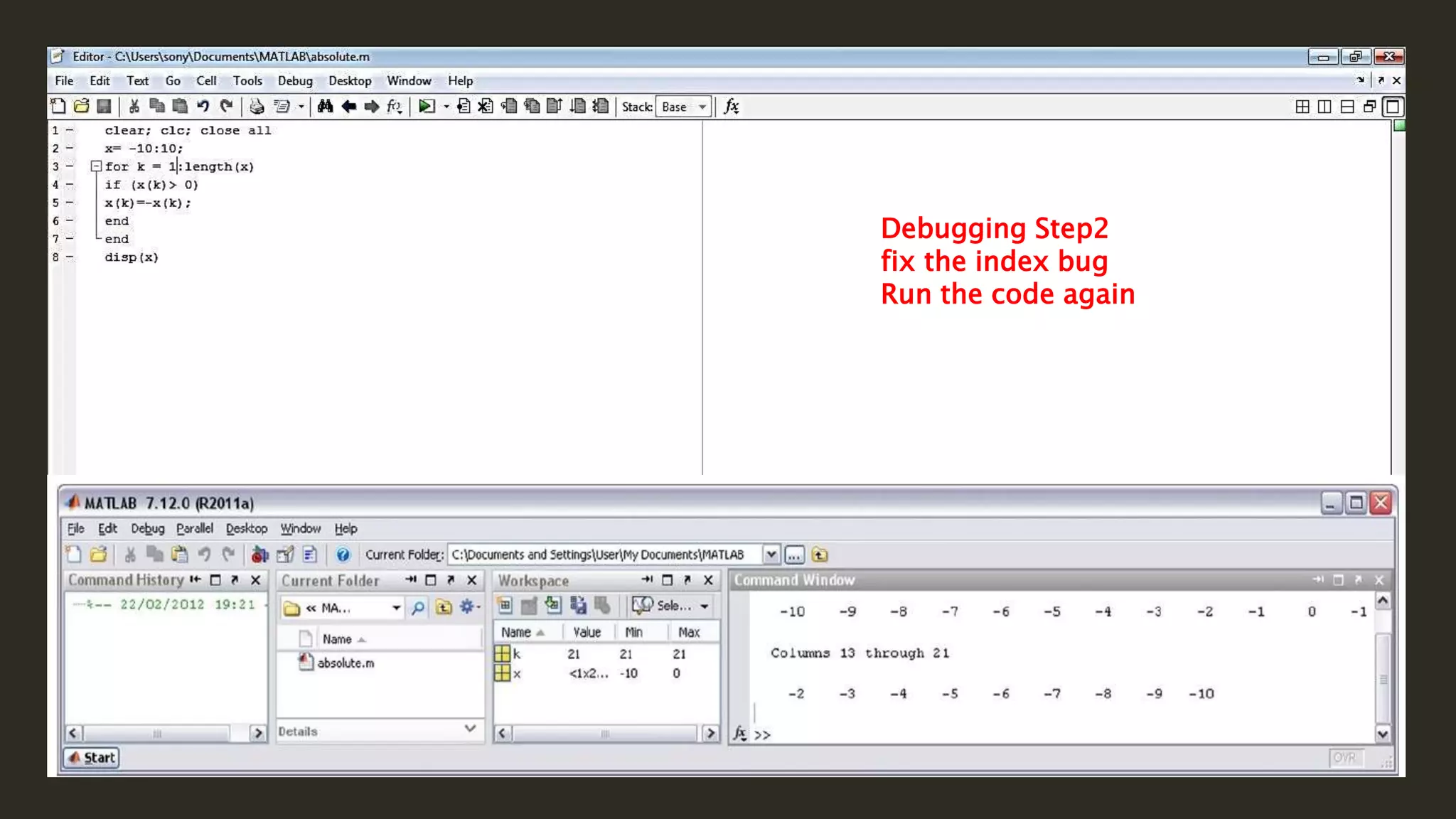
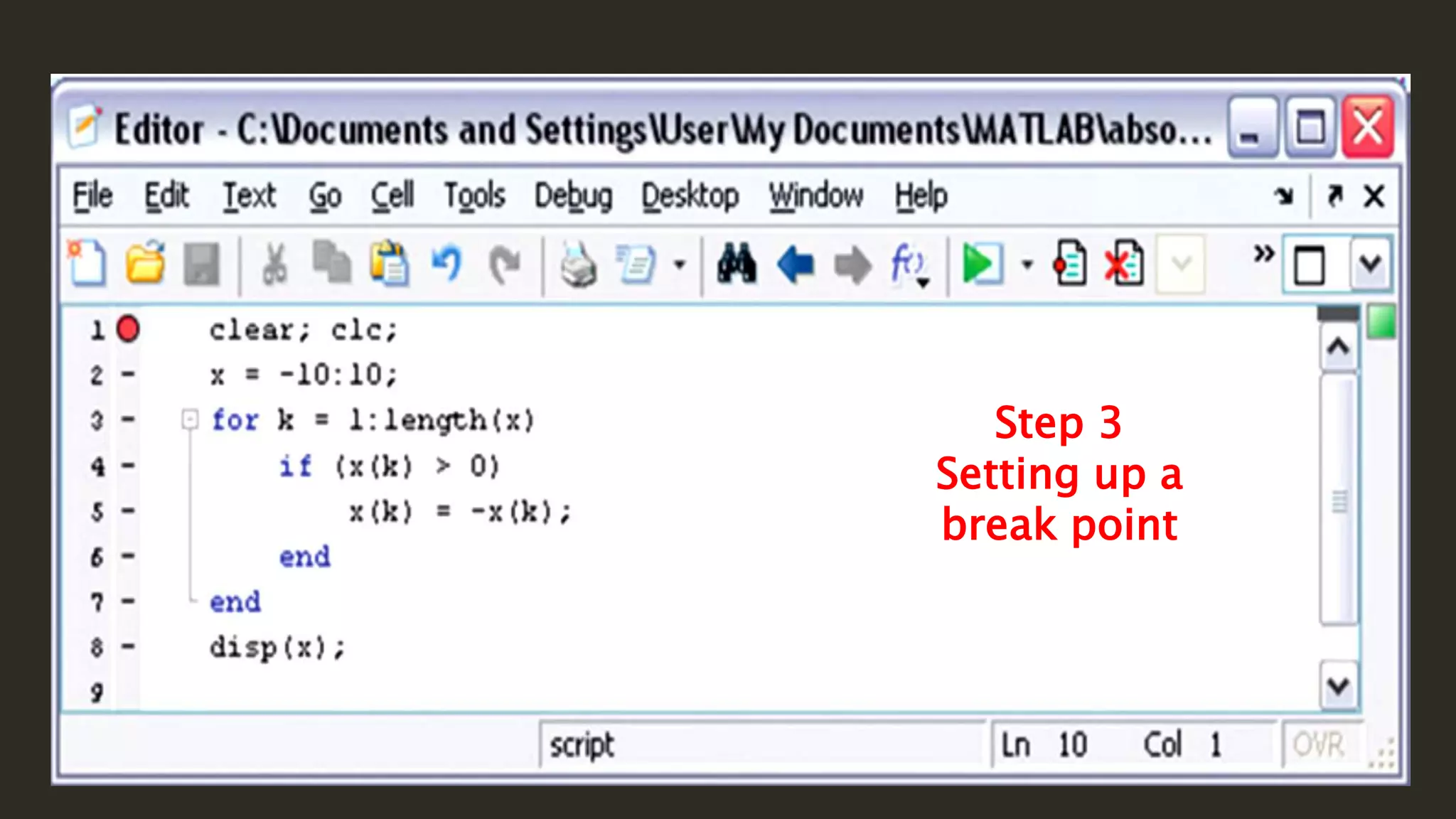
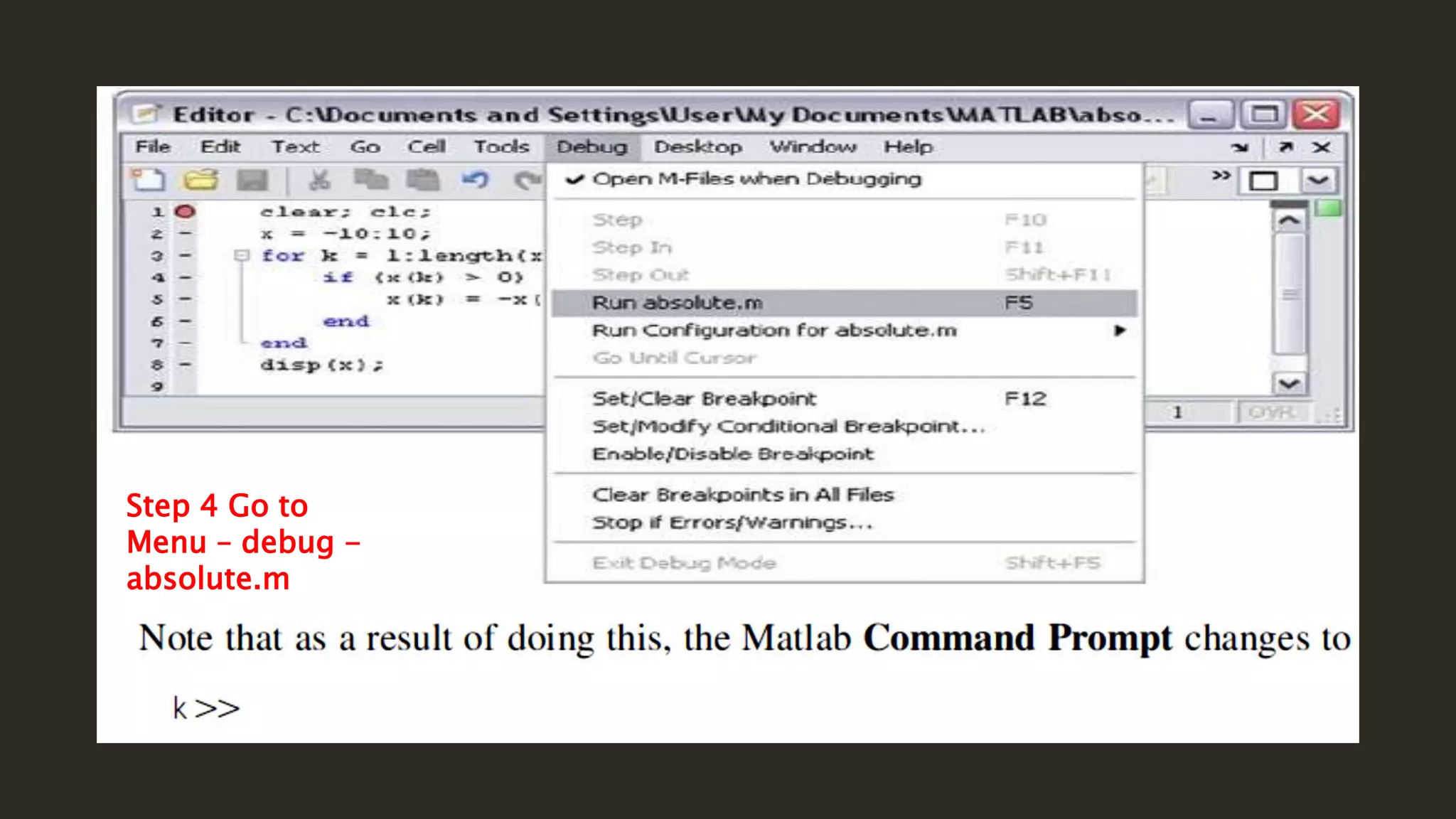
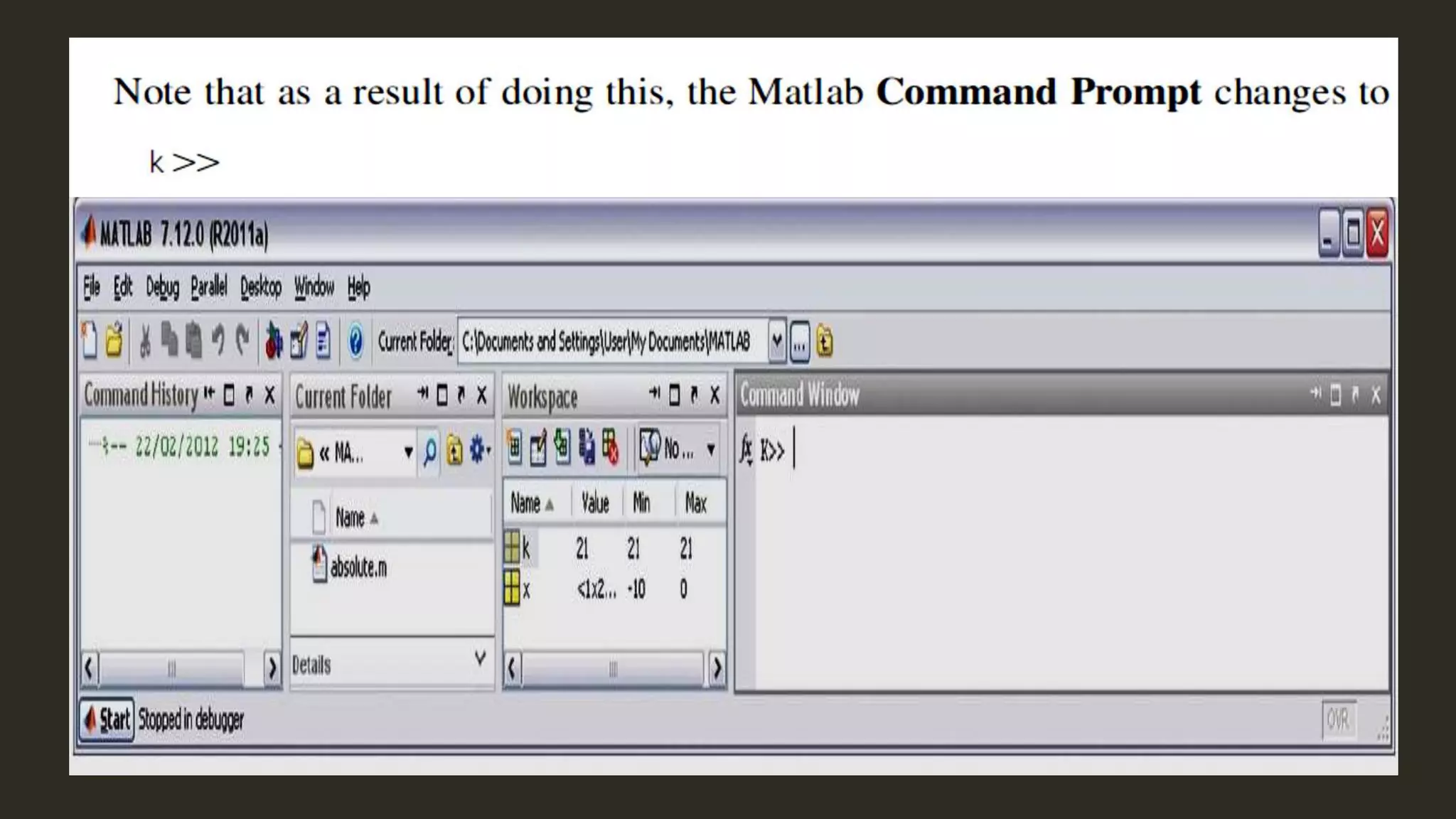
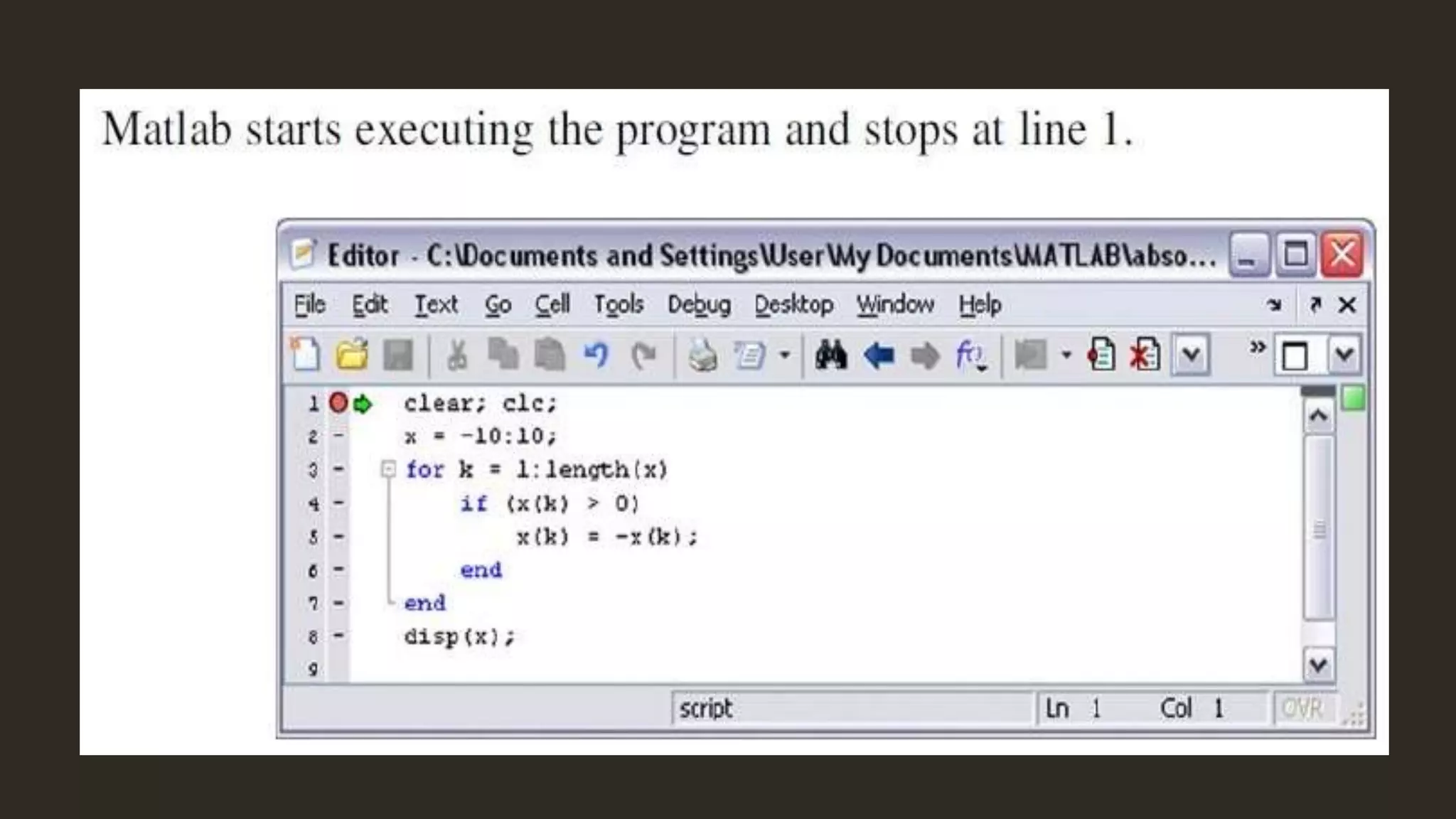
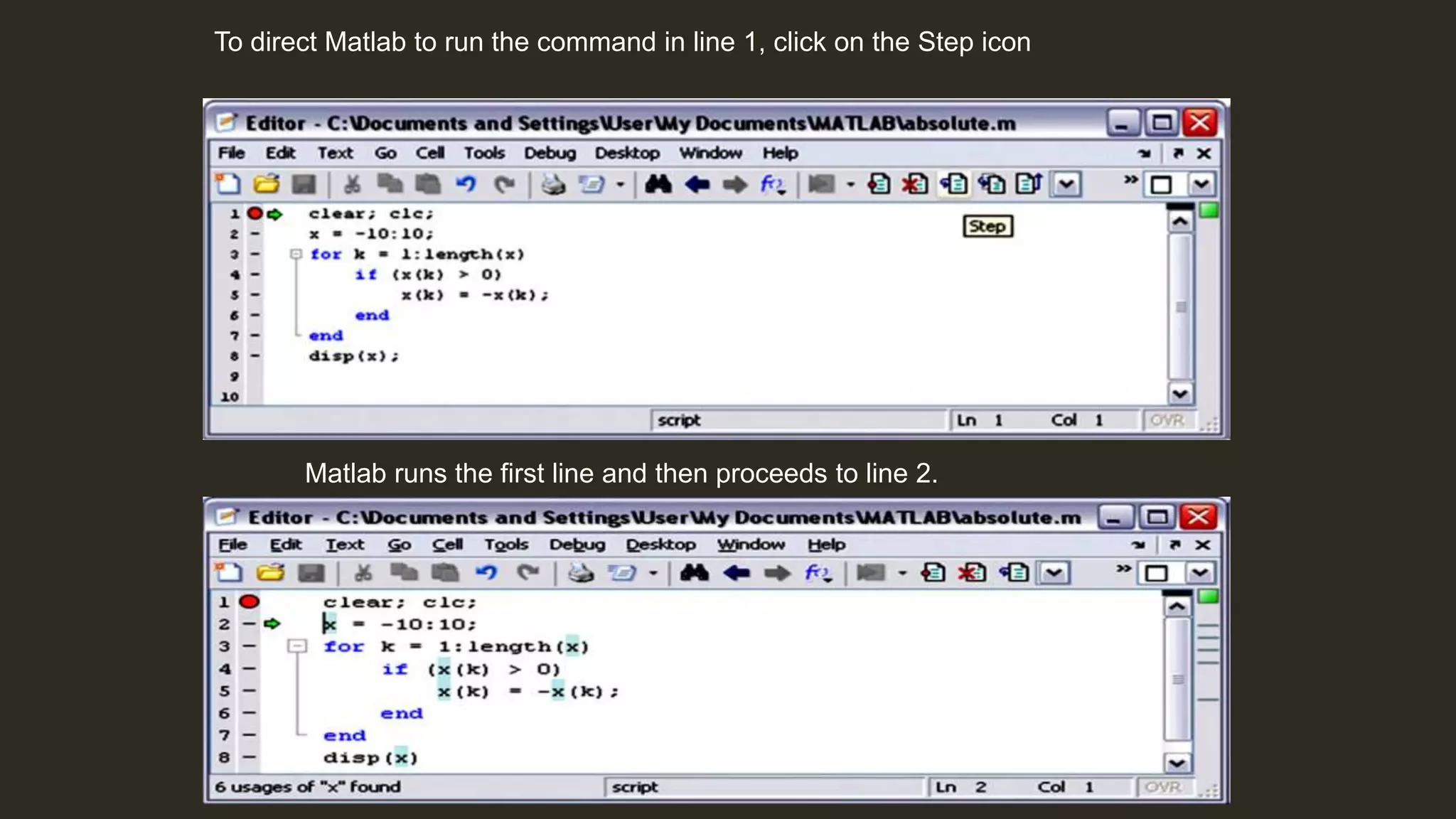
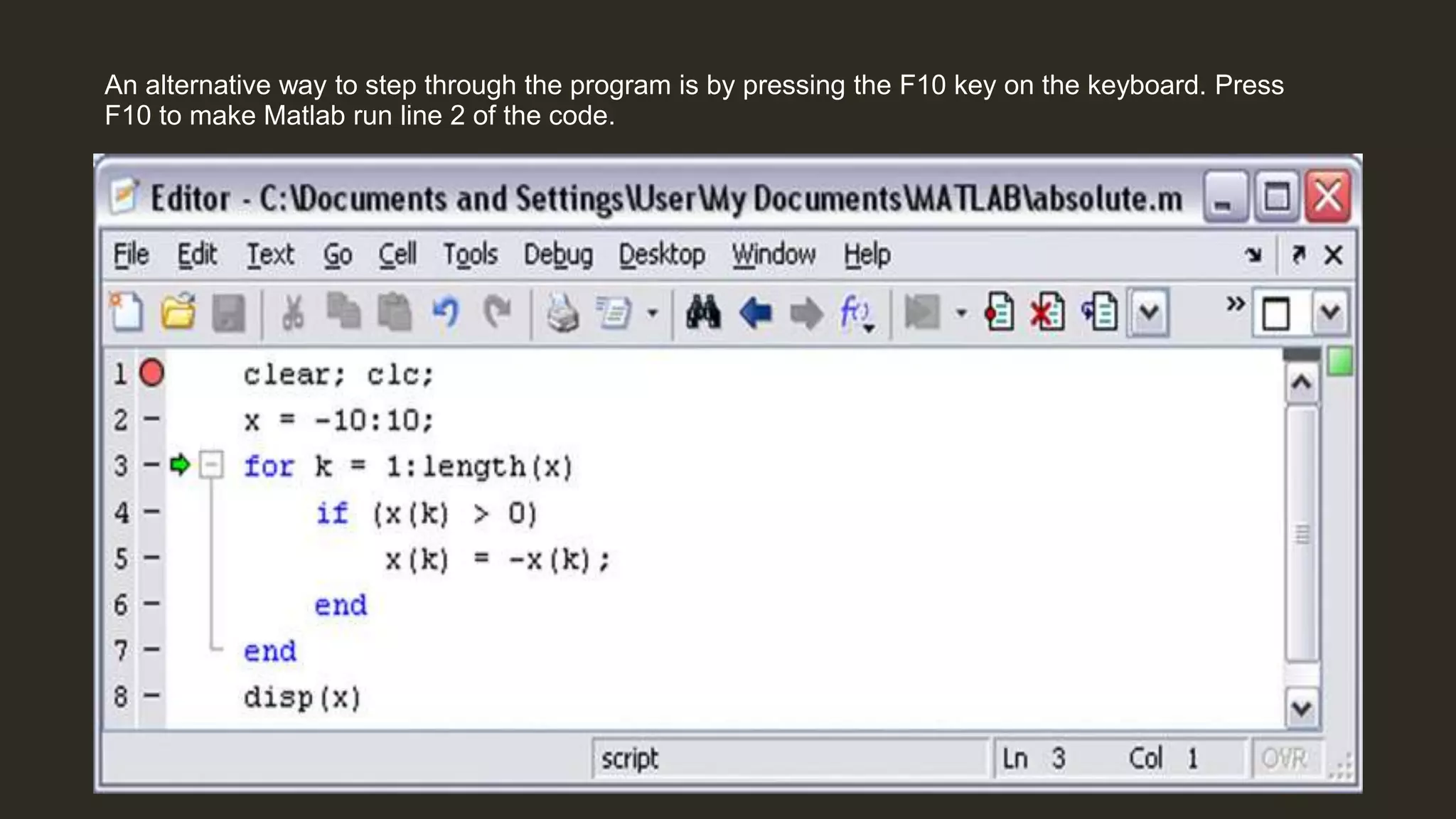
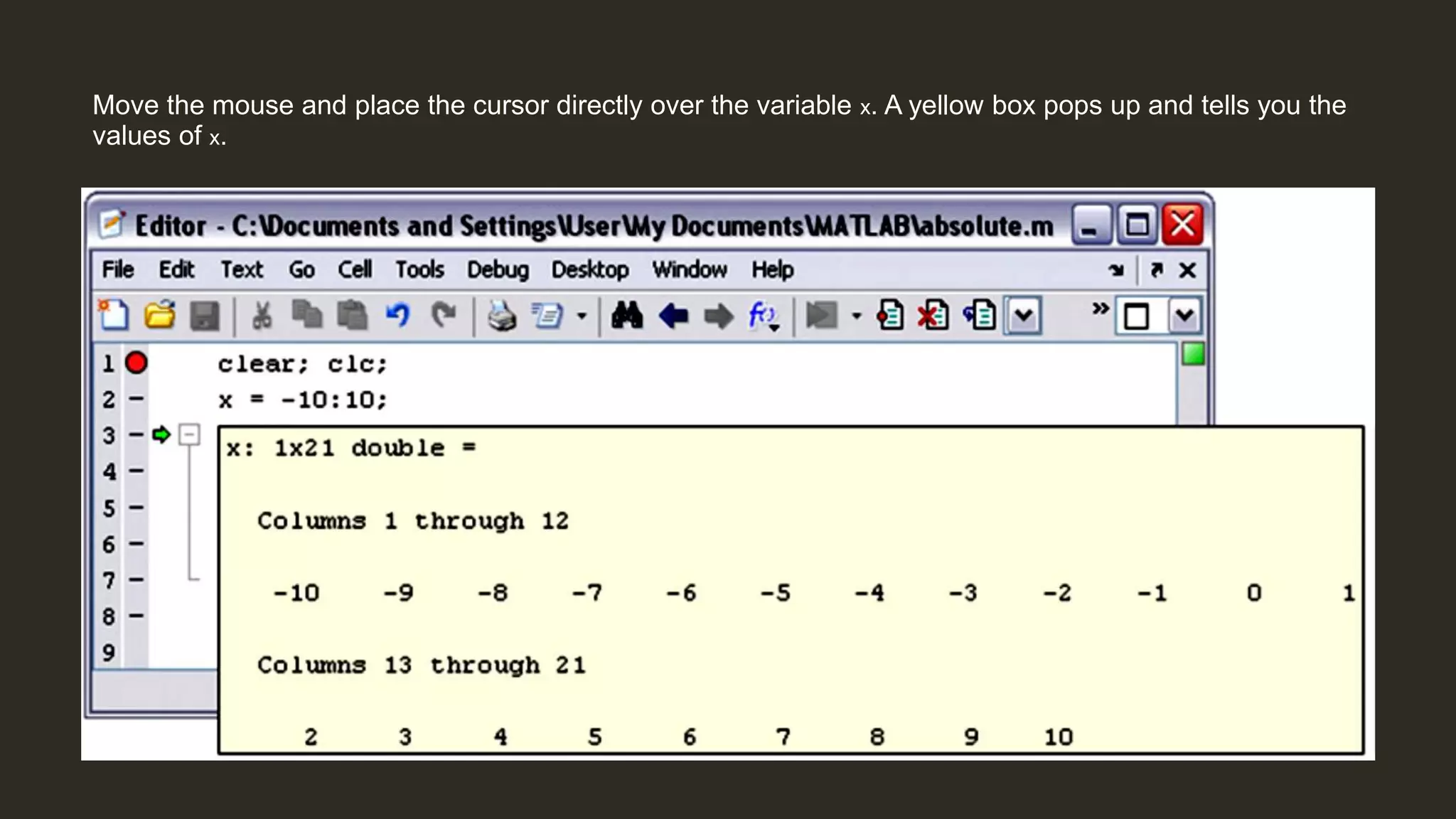
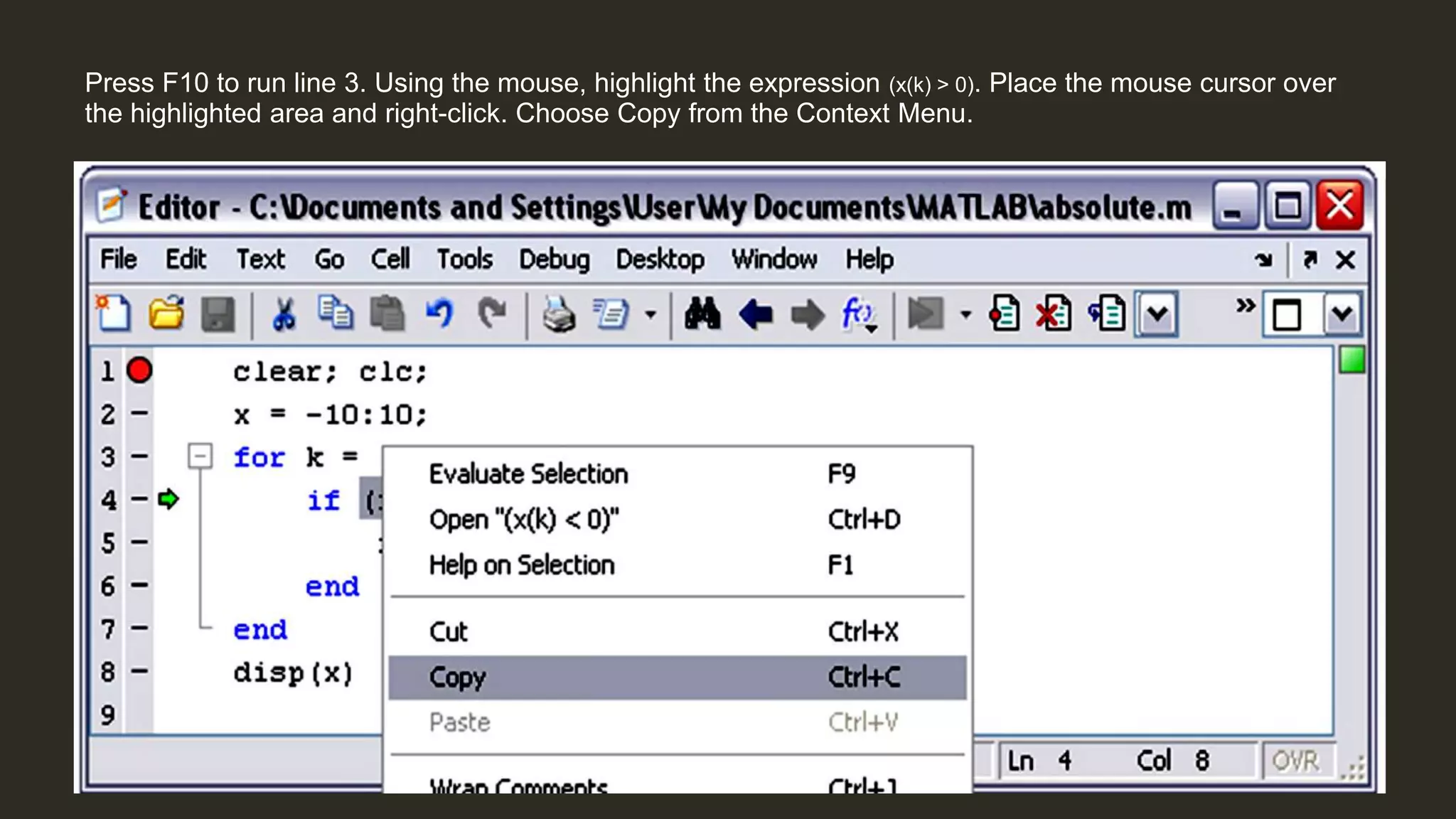
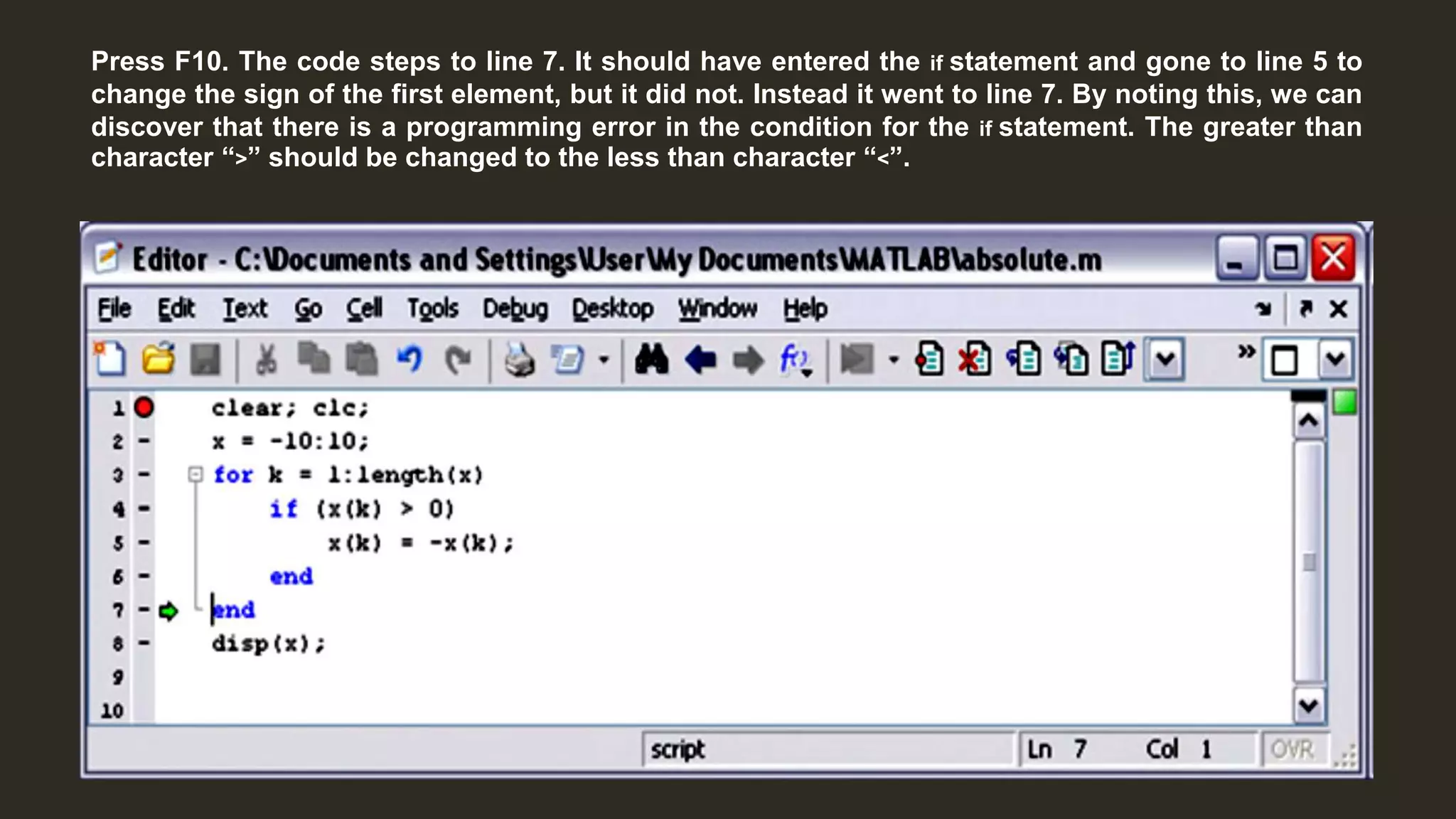
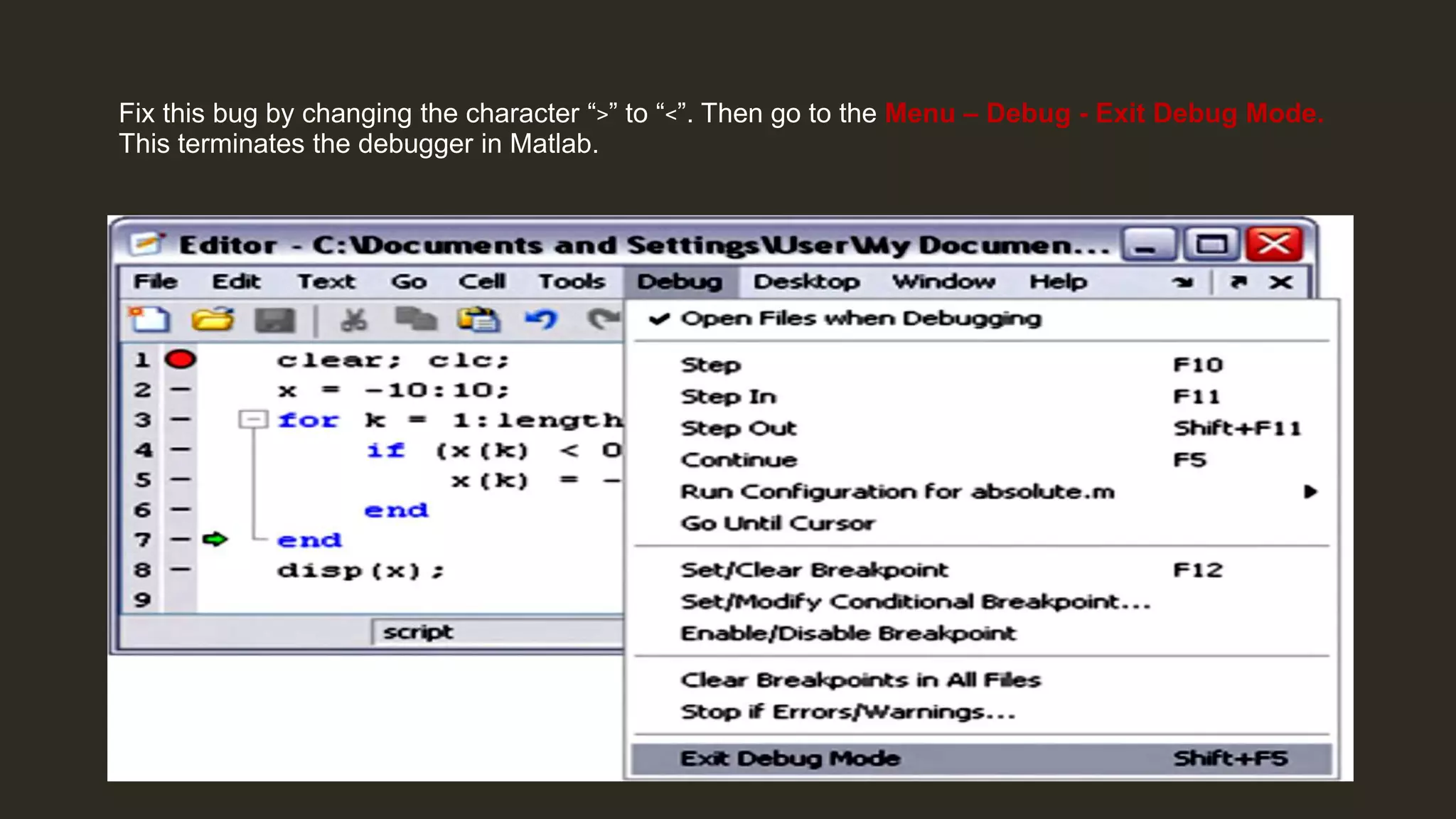
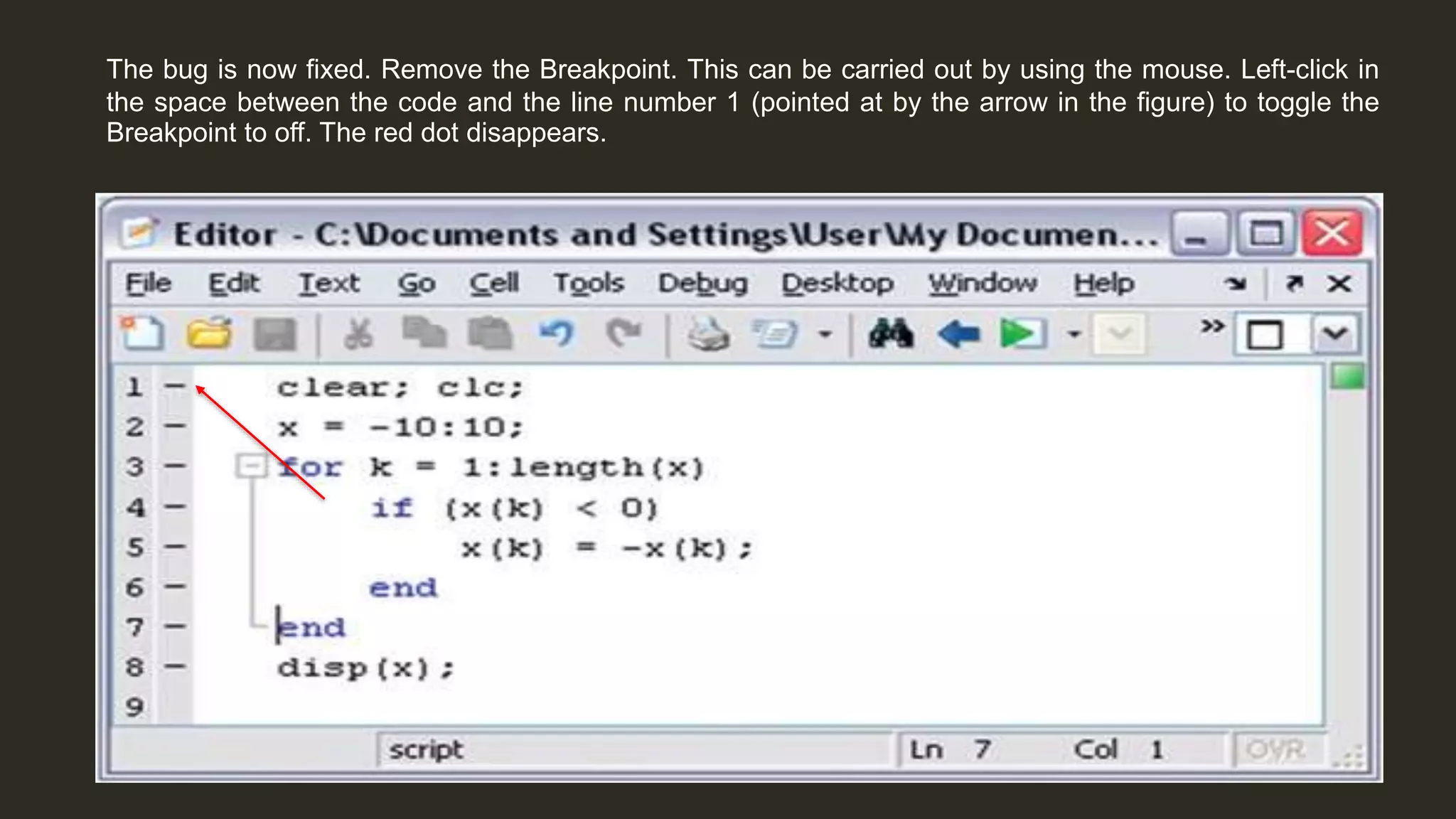
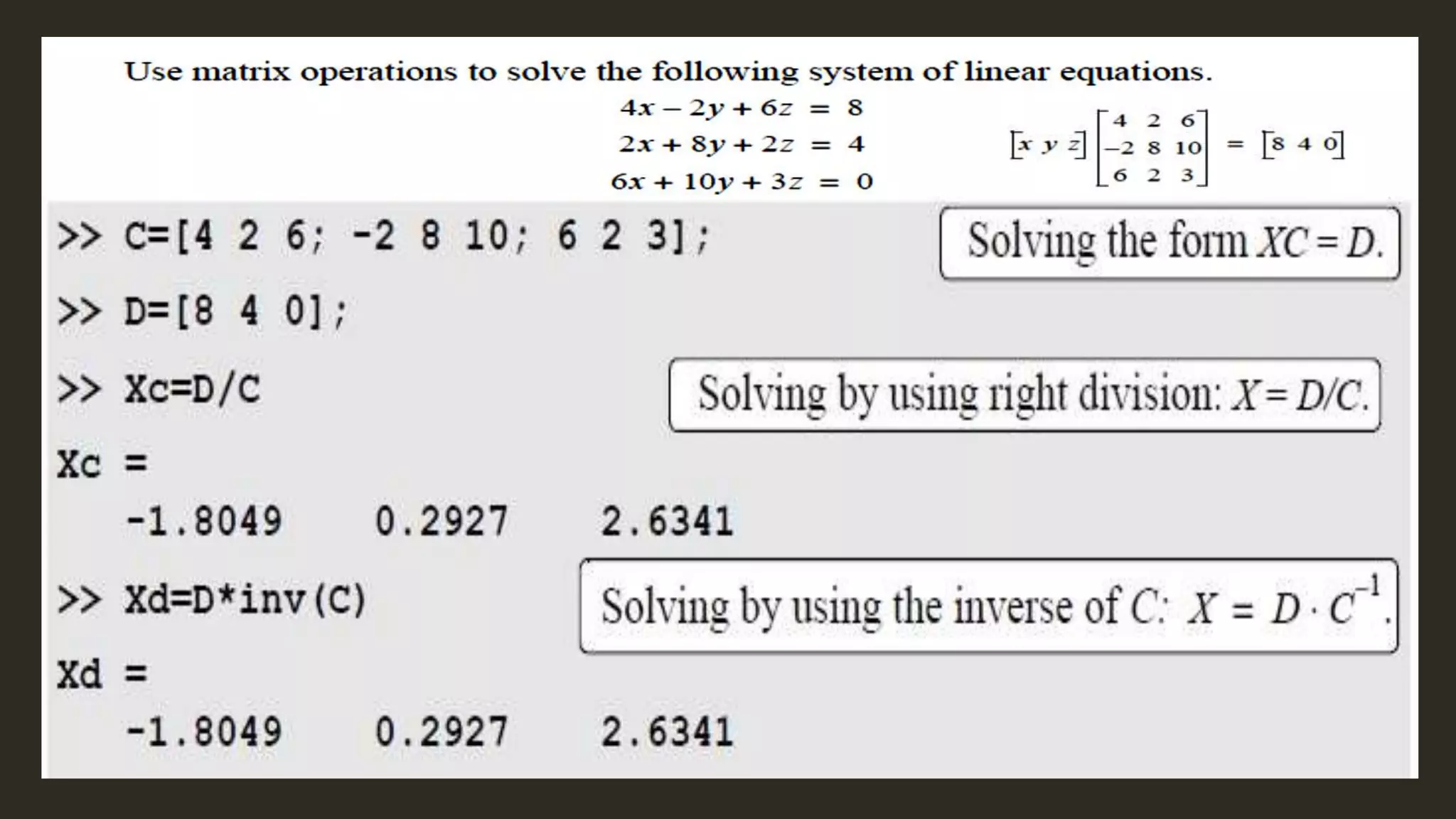
MATLAB is a powerful programming language for technical computing. It allows matrix manipulation, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs in other languages. Some key features of MATLAB include its matrix-based data structure, built-in math and engineering functions, programming tools for algorithm development and testing, and integrated development environment. MATLAB also provides tools for debugging and optimizing code performance such as breakpoints, stepping through code, and the profiler.