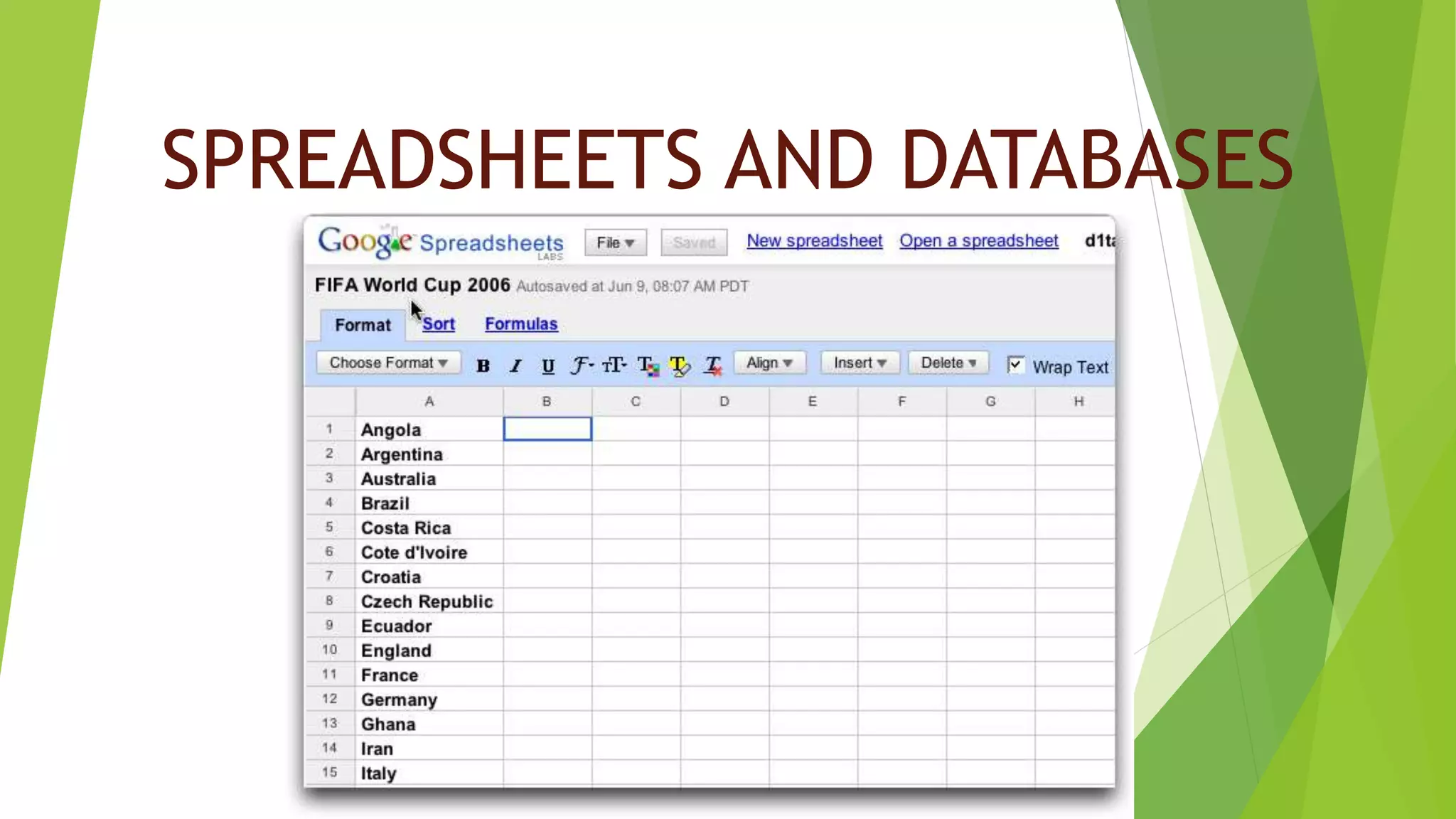
This document provides an overview of spreadsheets and databases, highlighting their components and functionality. It discusses how spreadsheets manage financial data through cells organized in rows and columns, and describes databases as systems for storing and retrieving information organized into records and fields. Additionally, it covers various types of graphics software, including image manipulation and computer-aided design, used for creating and editing visual content.