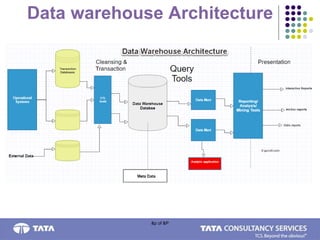
A data warehouse is a consolidated view of enterprise data structured for dynamic queries and analytics. It has the following key characteristics: integrated, subject-oriented, time-variant, and non-volatile. A data warehouse uses a three-tier architecture including a database bottom tier, middle OLAP server tier, and top reporting tools tier. It enables improved decision making by storing large volumes of historical data separately from operational systems and facilitating analysis through dimensional modeling.