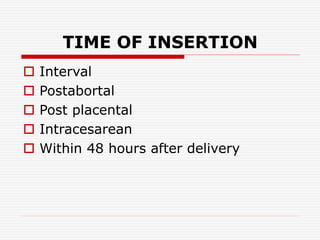
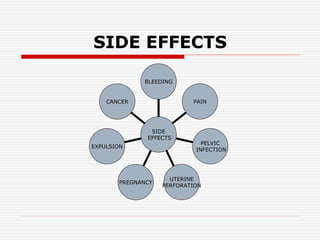
The document discusses intrauterine contraceptive devices (IUCDs), including their history, types, mechanisms of action, commercially available devices, advantages, disadvantages, and the role of nurses. It provides details on copper IUCDs and hormonal IUCDs. Some key points are:
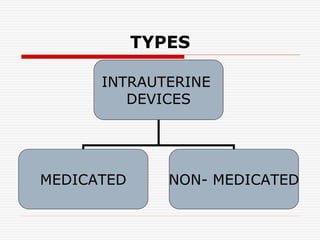
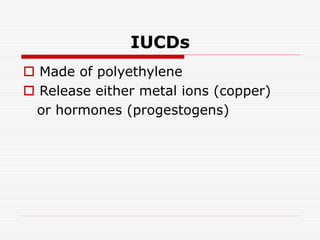
1. IUCDs are small devices inserted in the uterus to prevent pregnancy, either releasing copper ions or hormones.
2. The first IUCDs were developed in the early 1900s but were improved upon with the Lippes Loop in the 1960s and additions of copper in later generations.
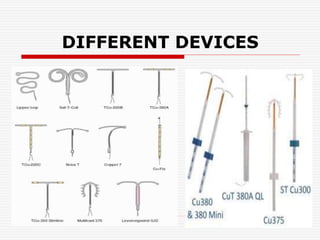
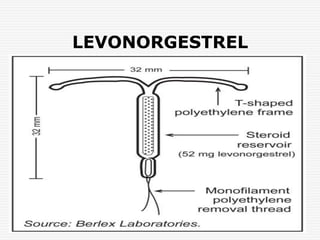
3. Common devices now include Copper T, Multiload Cu 250, and Mirena, which releases