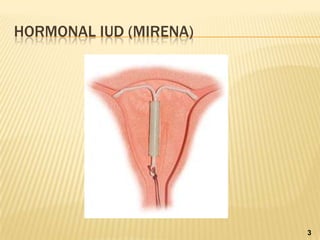
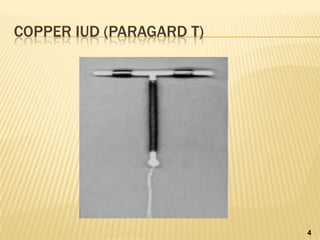
Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are small T-shaped plastic devices inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy for 12 years or more. There are two main types - copper IUDs last 10 years while hormonal IUDs release progestin and last 5 years. IUDs work by affecting sperm and egg movement and thickness of cervical mucus to prevent fertilization and implantation. They have few side effects and are over 99% effective while allowing for natural intercourse. Risks include heavier periods or cramps with copper IUDs and potential expulsion or perforation during insertion.