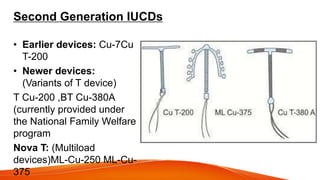
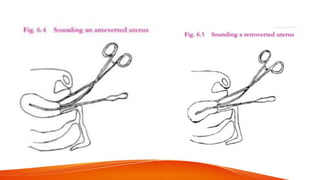
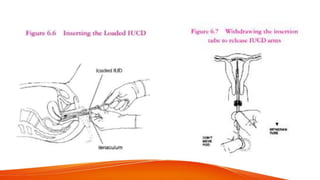
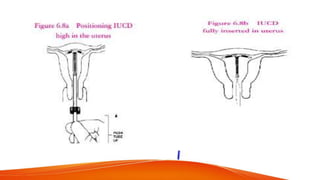
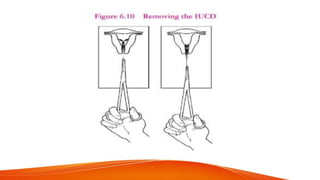
1. IUCDs can be non-medicated like the Lippes Loop or medicated with copper or hormones. Common copper IUCDs include T-380 and T-200 while the LNG-IUS releases levonorgestrel.
2. Copper IUCDs prevent pregnancy primarily by interfering with sperm motility and survival while also preventing implantation. The LNG-IUS thickens cervical mucus and thins the uterine lining.
3. Medical eligibility criteria from WHO categorizes conditions as having no restrictions, generally able to use with additional care, or not recommended due to risks outweighing benefits for IUCD use. Proper training is required for insertion and removal to avoid risks.