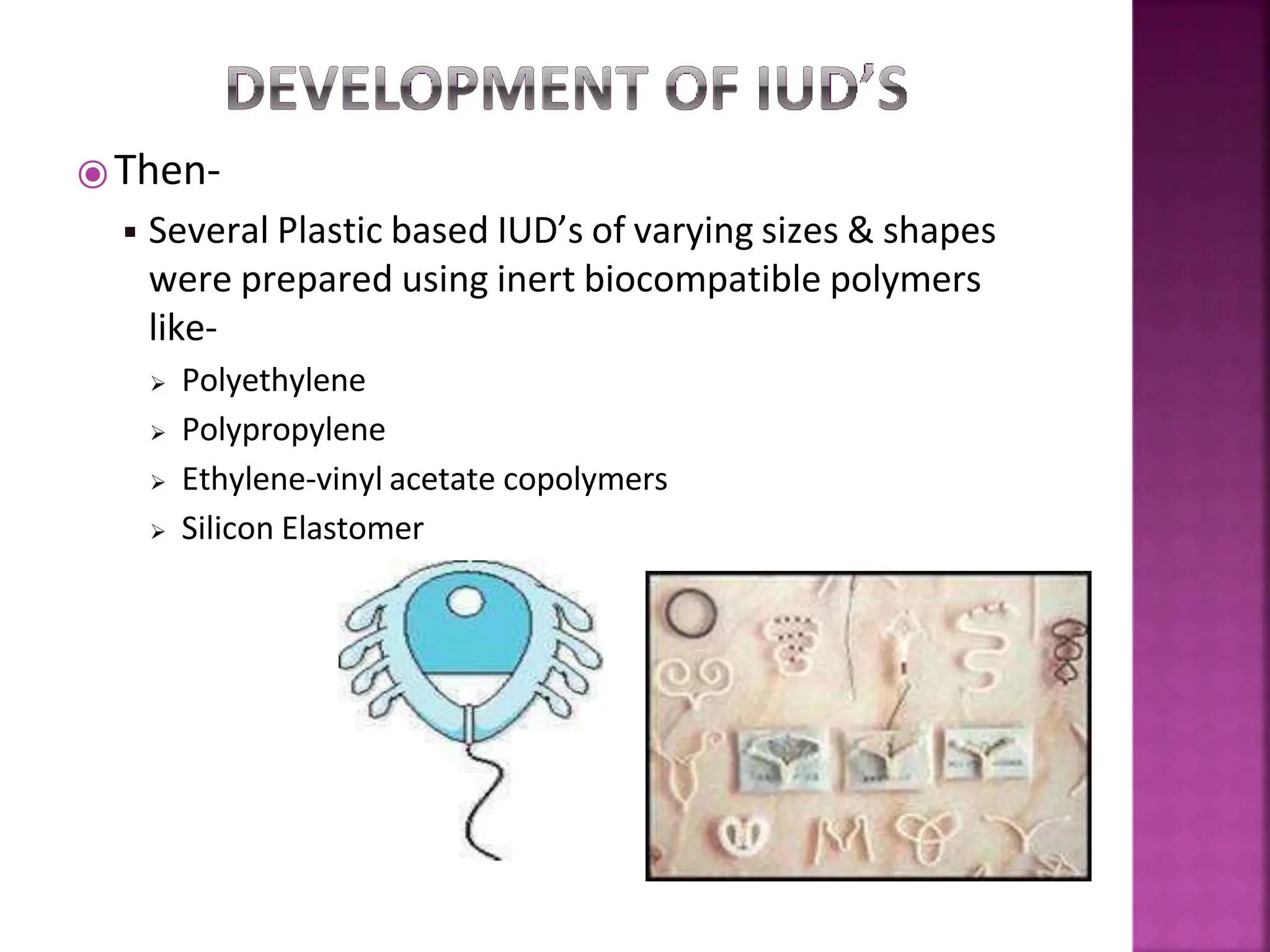
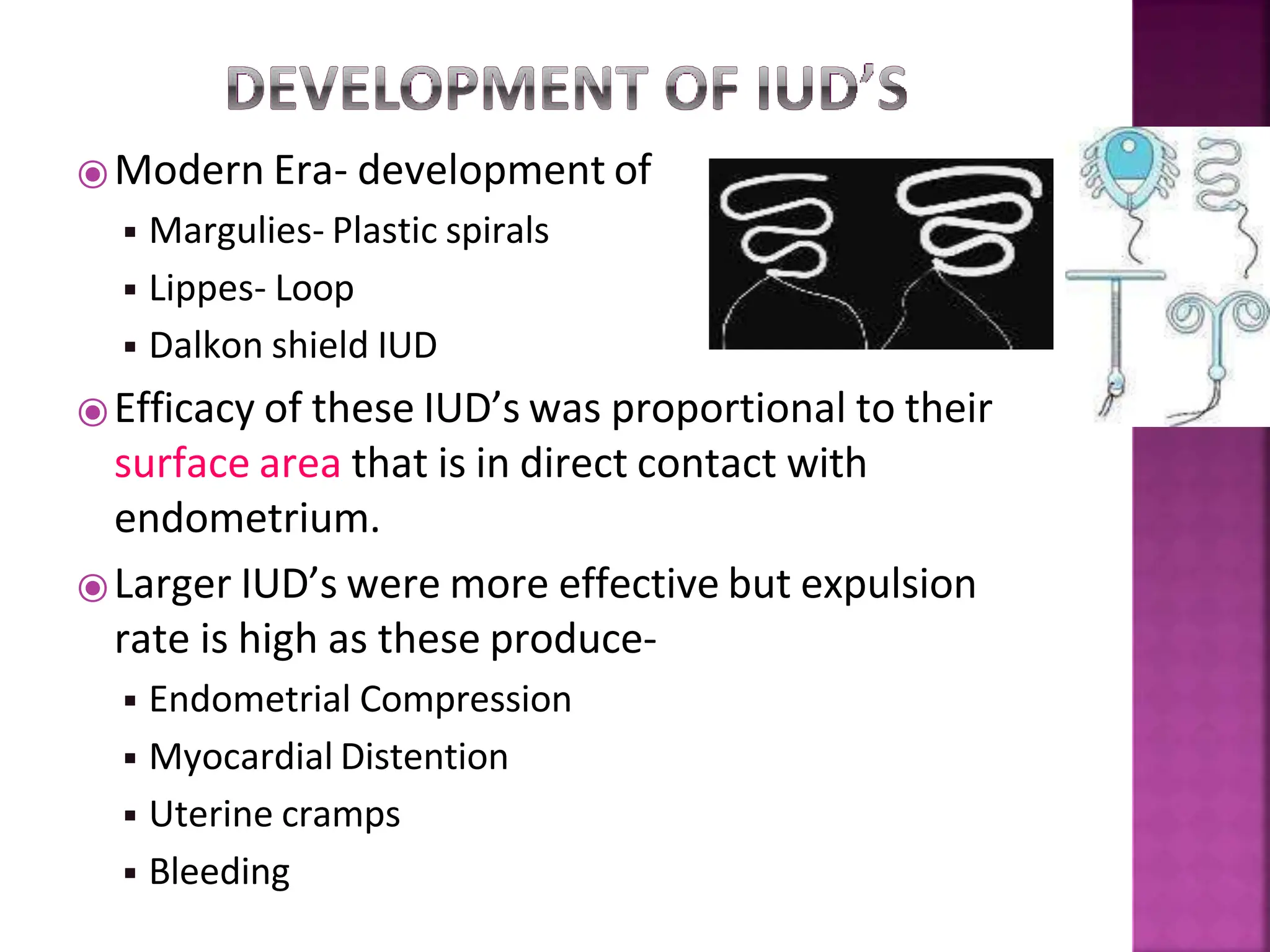
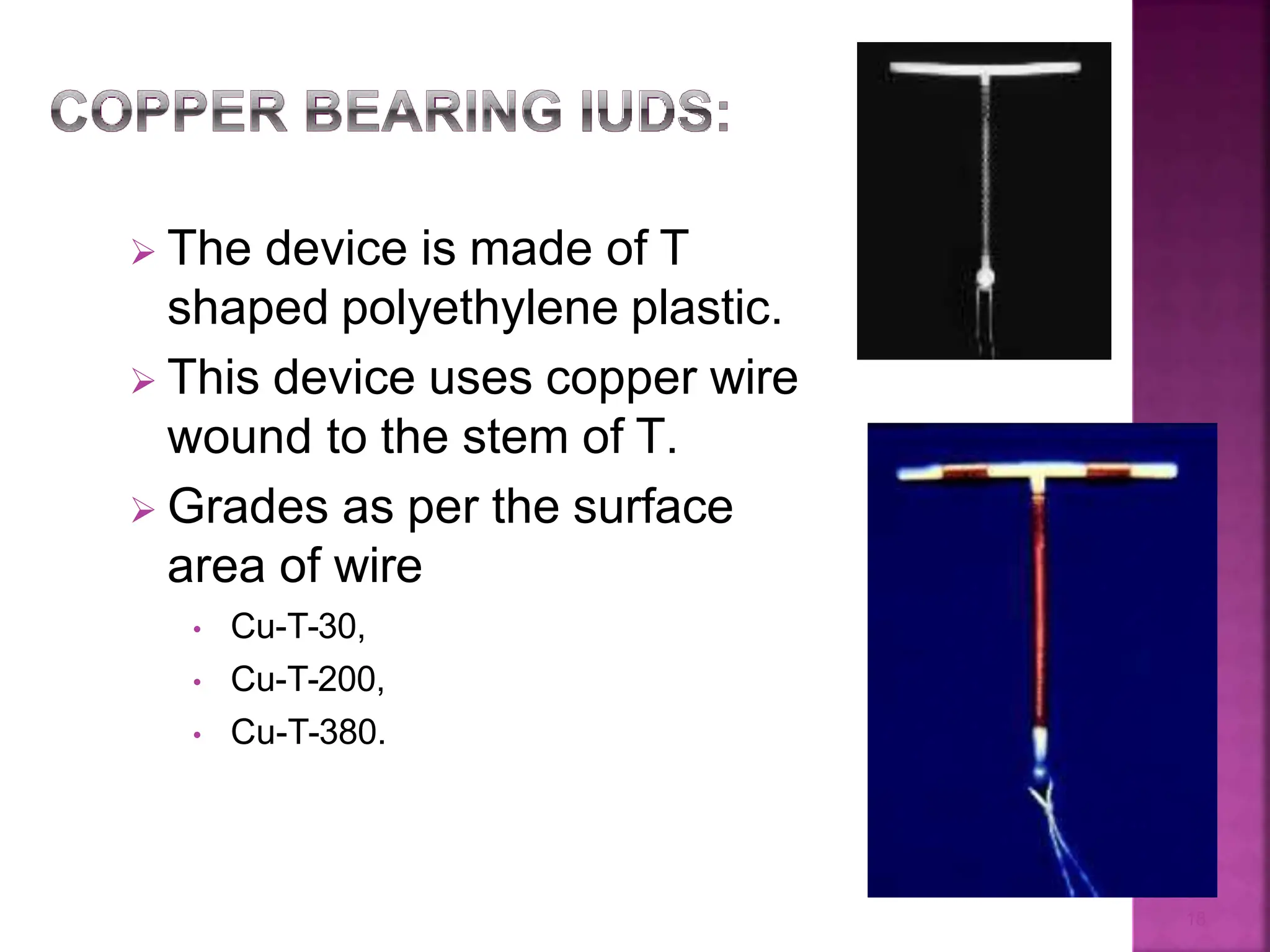
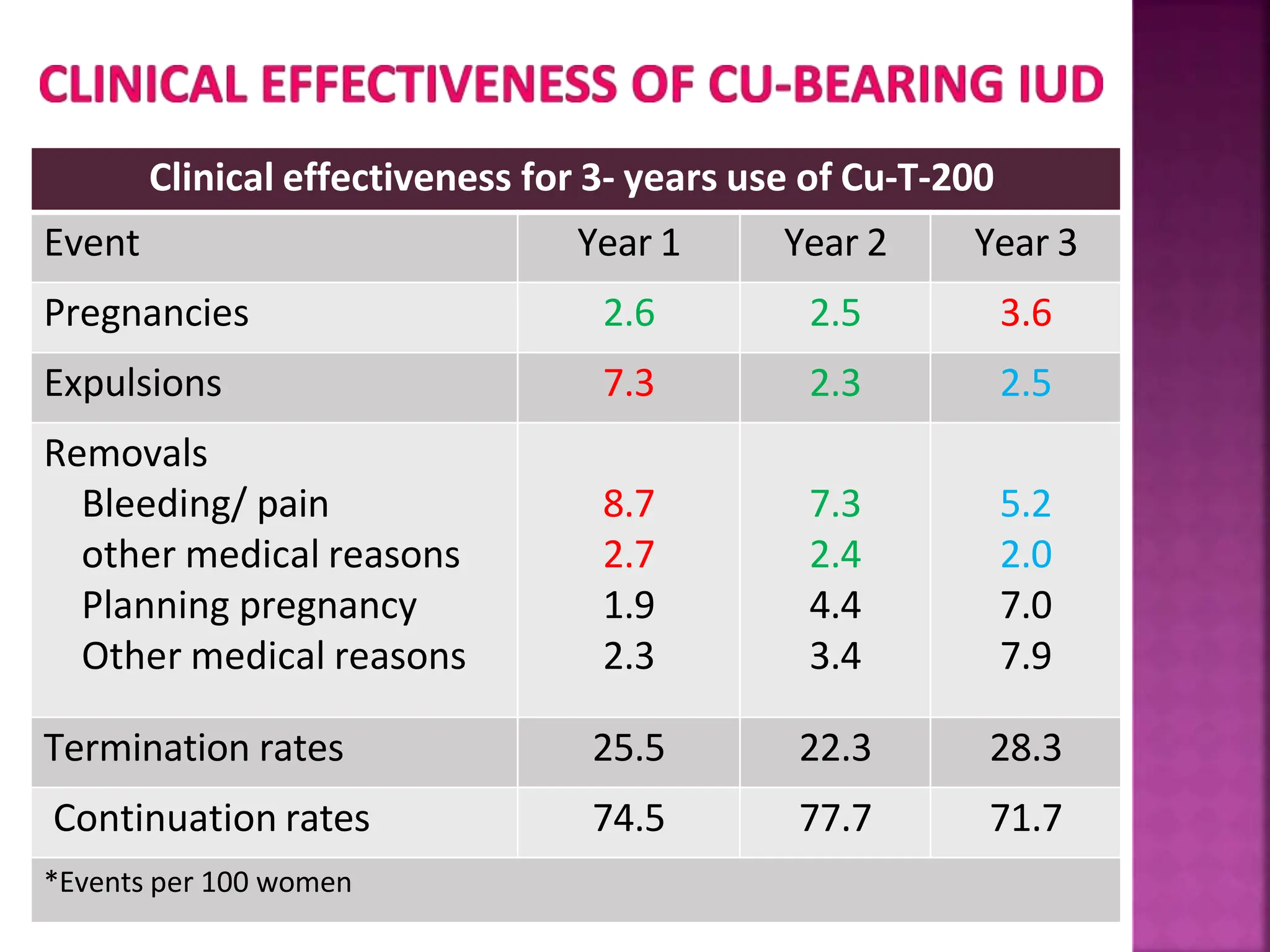
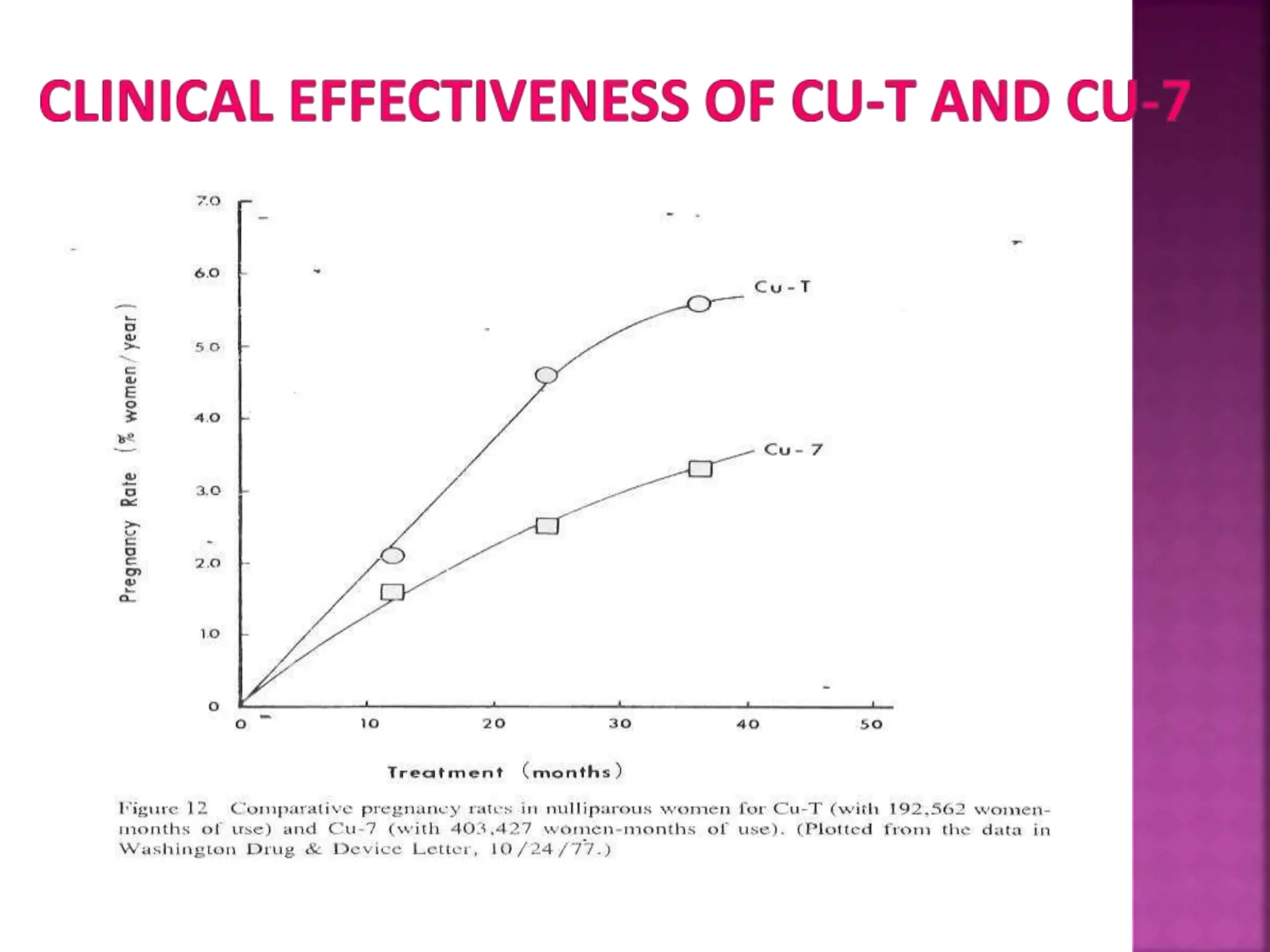
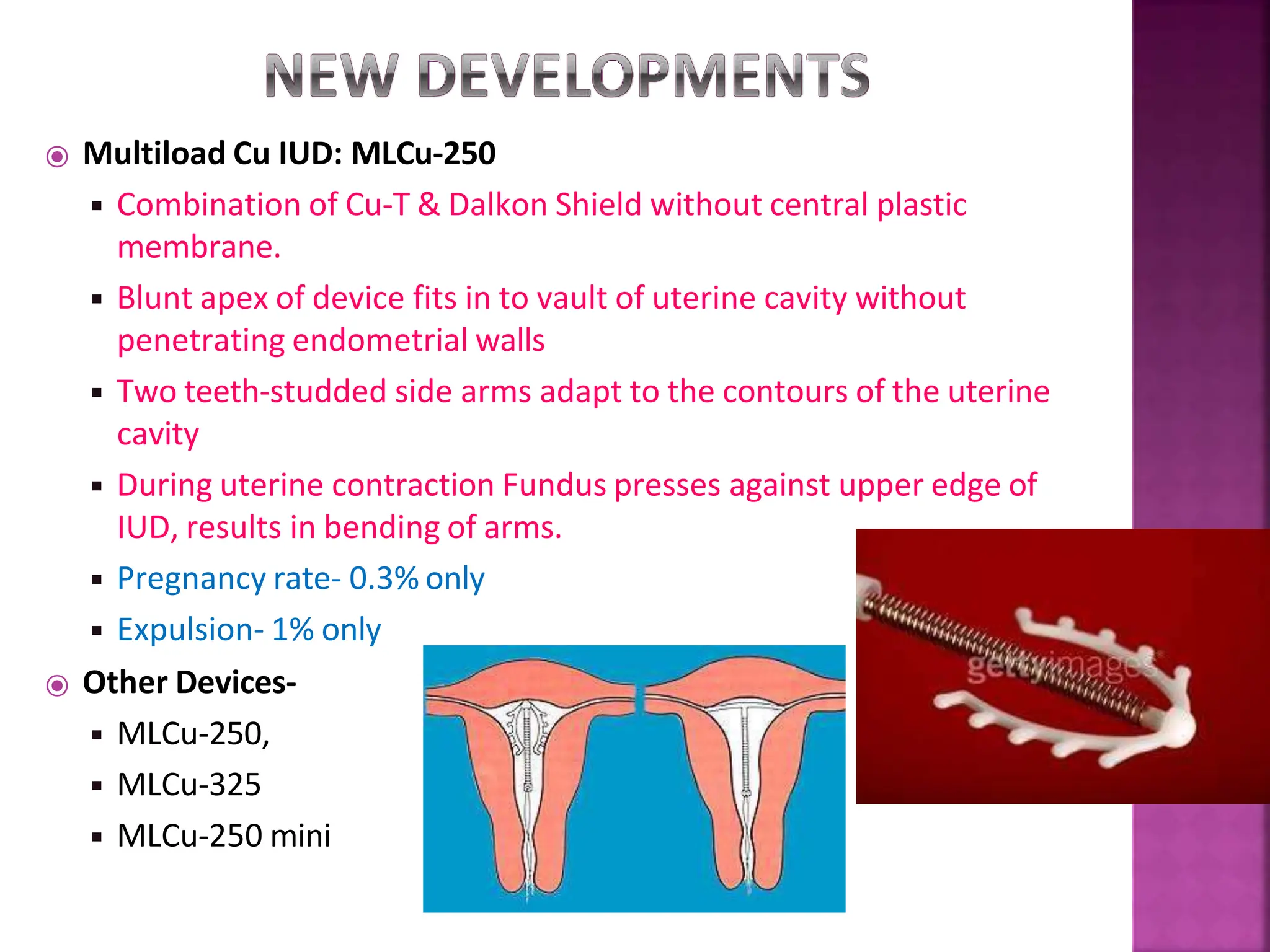
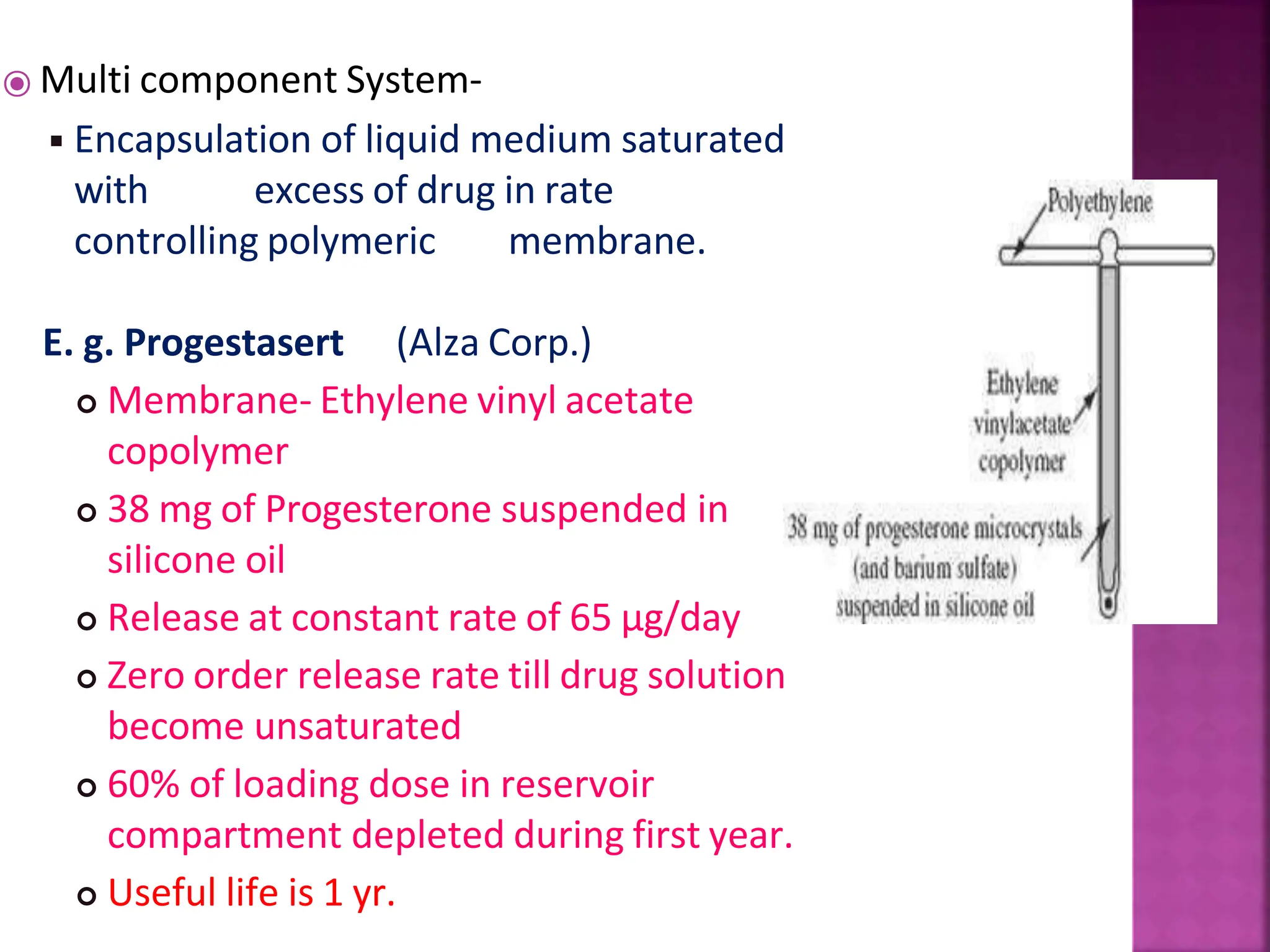
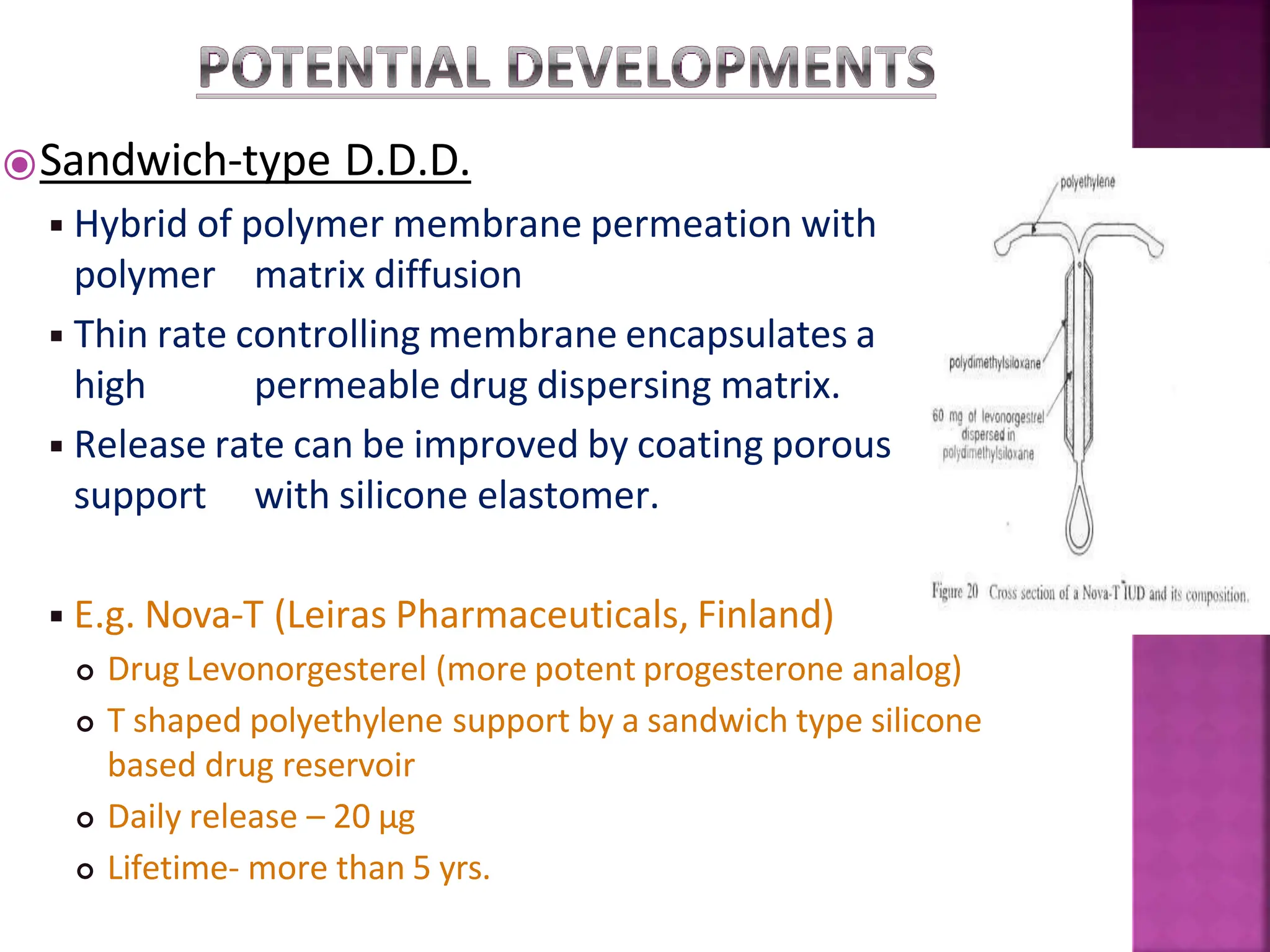
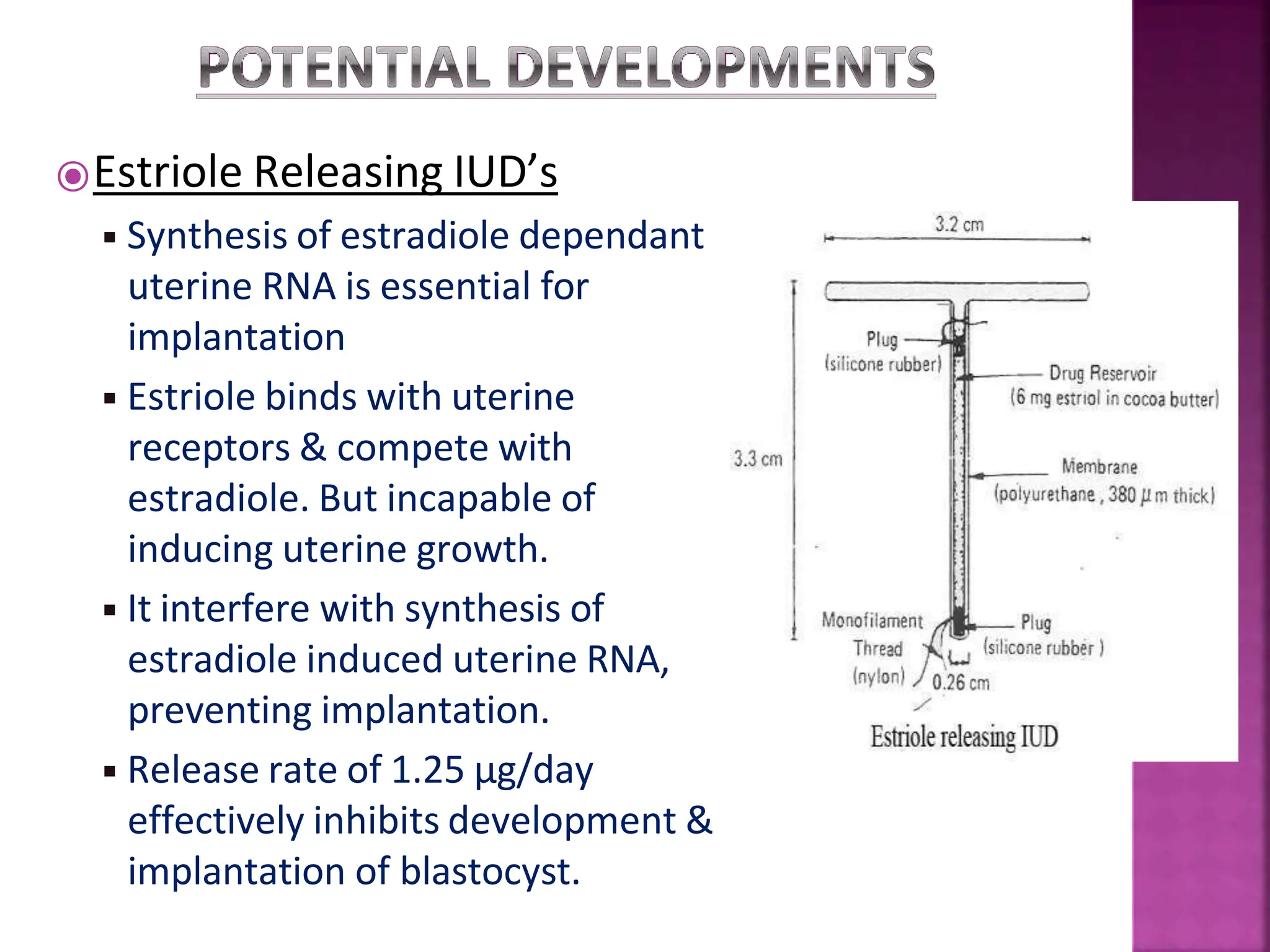
This document discusses intrauterine devices (IUDs) including their history, types, advantages, and disadvantages. It describes the development of medicated IUDs including copper-bearing and hormone-releasing IUDs. Comparative efficacy data is presented showing progesterone-releasing IUDs are associated with less bleeding and cramping than copper IUDs. Newer IUD designs aim to provide long-acting contraception through controlled drug release over extended periods.