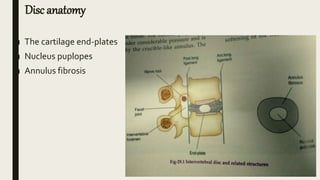
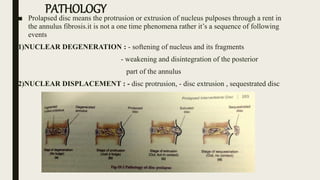
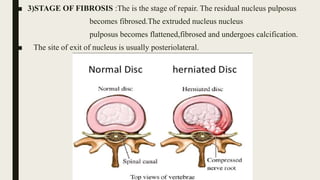
This document discusses intervertebral disc prolapse. It begins by describing disc anatomy, development, and location in the spine. It then explains the pathology of prolapse, which involves nuclear degeneration, displacement, and fibrosis. Risk factors for prolapse include heavy lifting, smoking, obesity, and improper posture. Clinical features include low back pain radiating to the buttocks, aggravated by certain movements. Investigations include CT, MRI, and myelography. Treatment options range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to operative procedures like fenestration, hemi-laminectomy, and endoscopic discectomy.