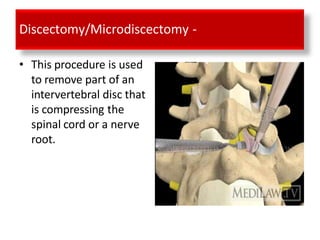
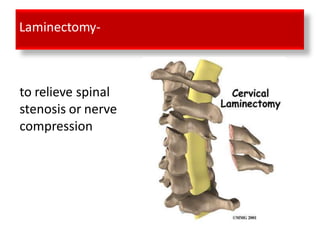
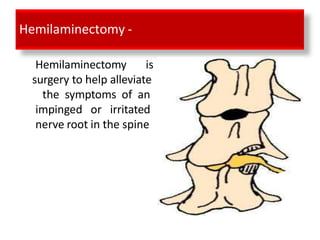
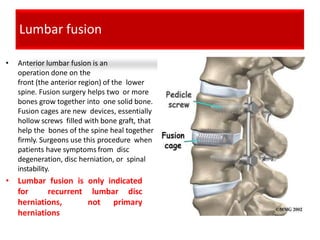
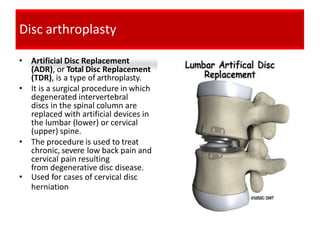
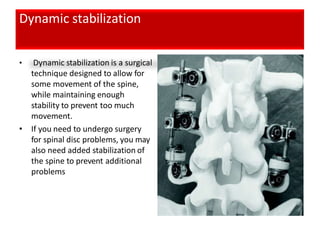
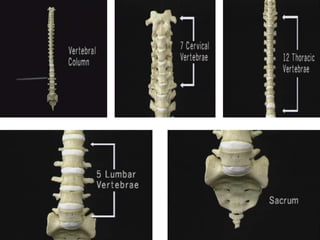
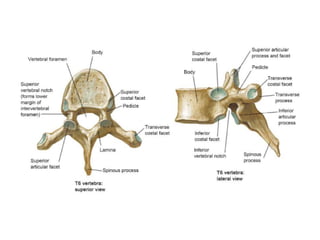
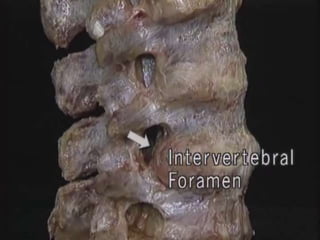
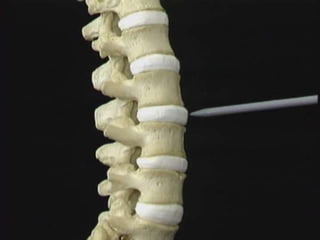
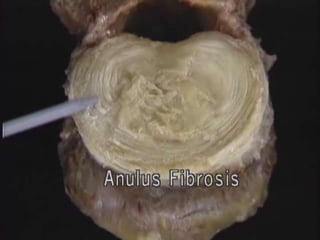
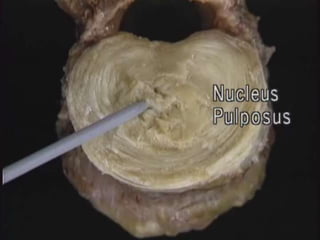
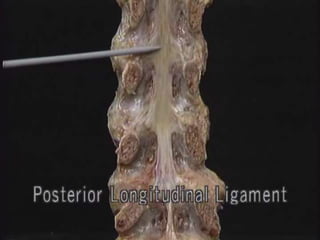
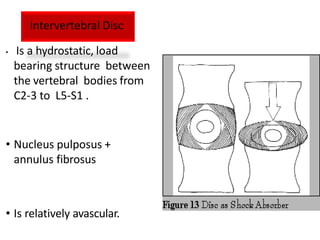
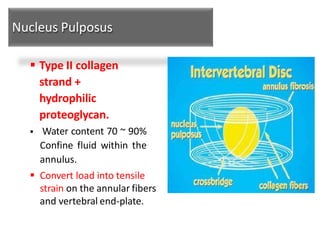
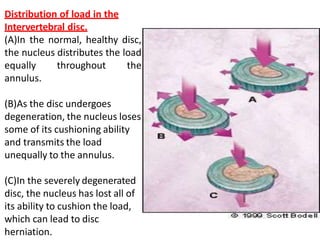
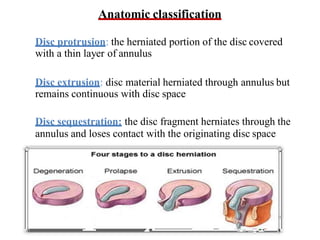
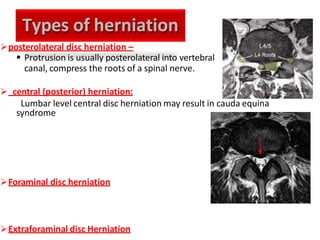
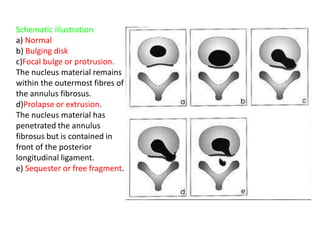
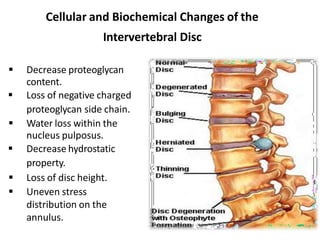
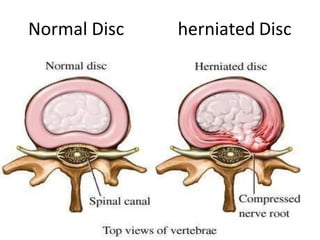
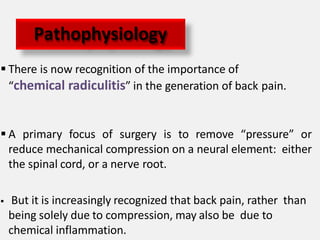
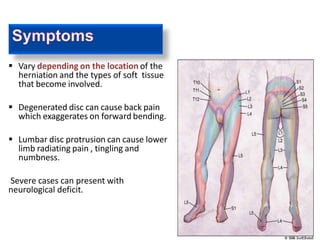
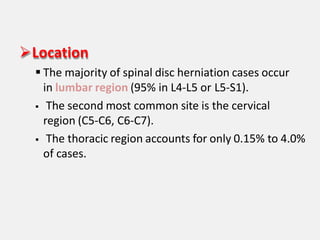
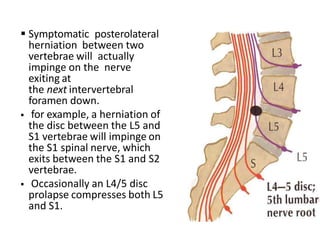
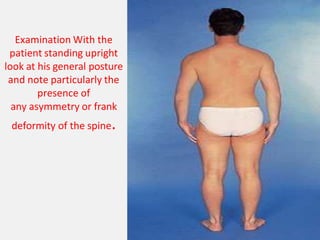
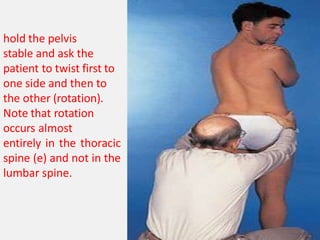
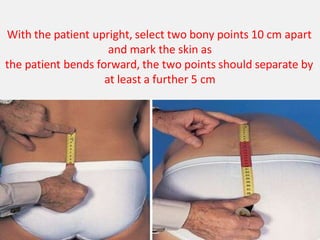
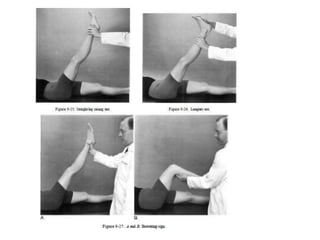
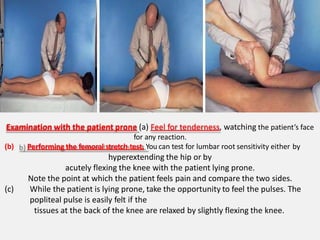
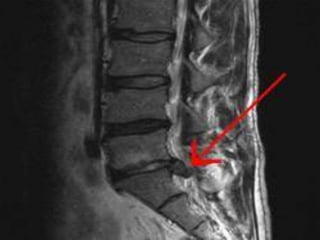
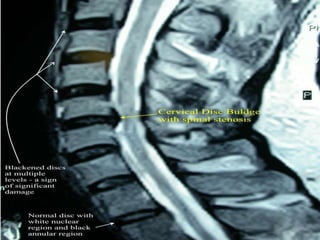
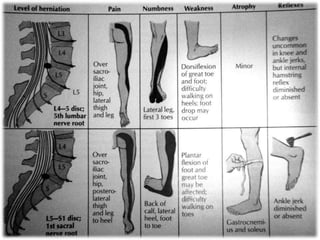
An intervertebral disc prolapse occurs when a tear in the annulus fibrosus allows the nucleus pulposus to bulge out. This most commonly affects the lumbar region, specifically the L4-L5 and L5-S1 discs. Symptoms include back pain radiating into the buttocks and legs. A physical exam reveals limited back movement, muscle spasms, and tenderness over the affected disc. Straight leg raises can reproduce the pain. Diagnosis is confirmed with imaging studies.



























![Chemonucleolysis-
• Chemonucleolysis is the term
used to denote chemical
destruction of nucleus pulposus
[Cehmo+nucleo+lysis].
• This involves intradiscal injection
ofchymopapain which causes
hydrolysis of he cementing
protein of the nucleus pulposus.
• This causes decrease in water
binding capacity leading to
reduction in size and drying the
disc.
• Chemonucleolysis is one of the
methods to treat disc herniation
not responding to conservative
therapy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pivdlecture-240219084842-8fe71871/85/Prolapse-Intervertebral-Disc-LECTURE-pdf-60-320.jpg)