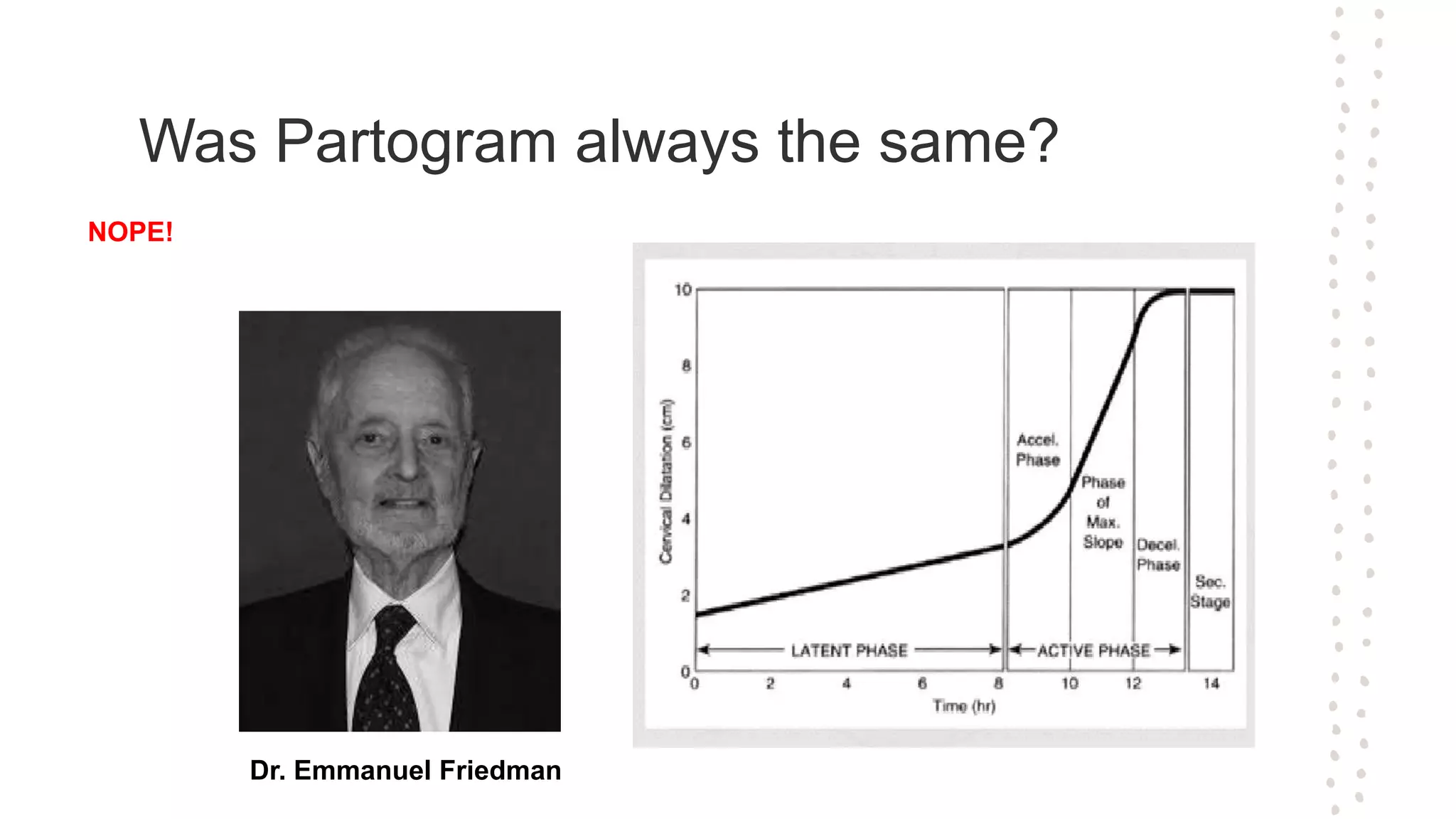
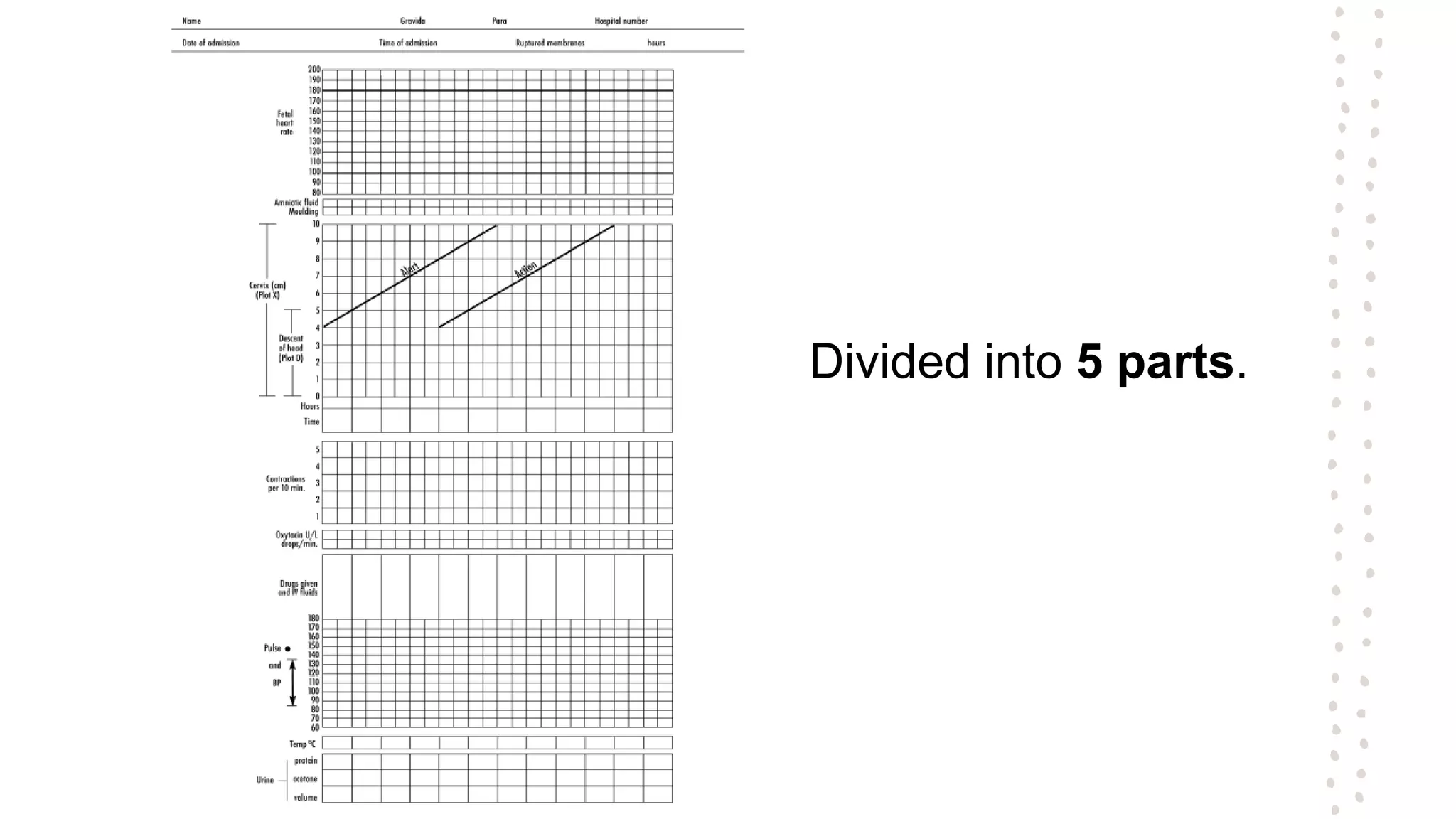
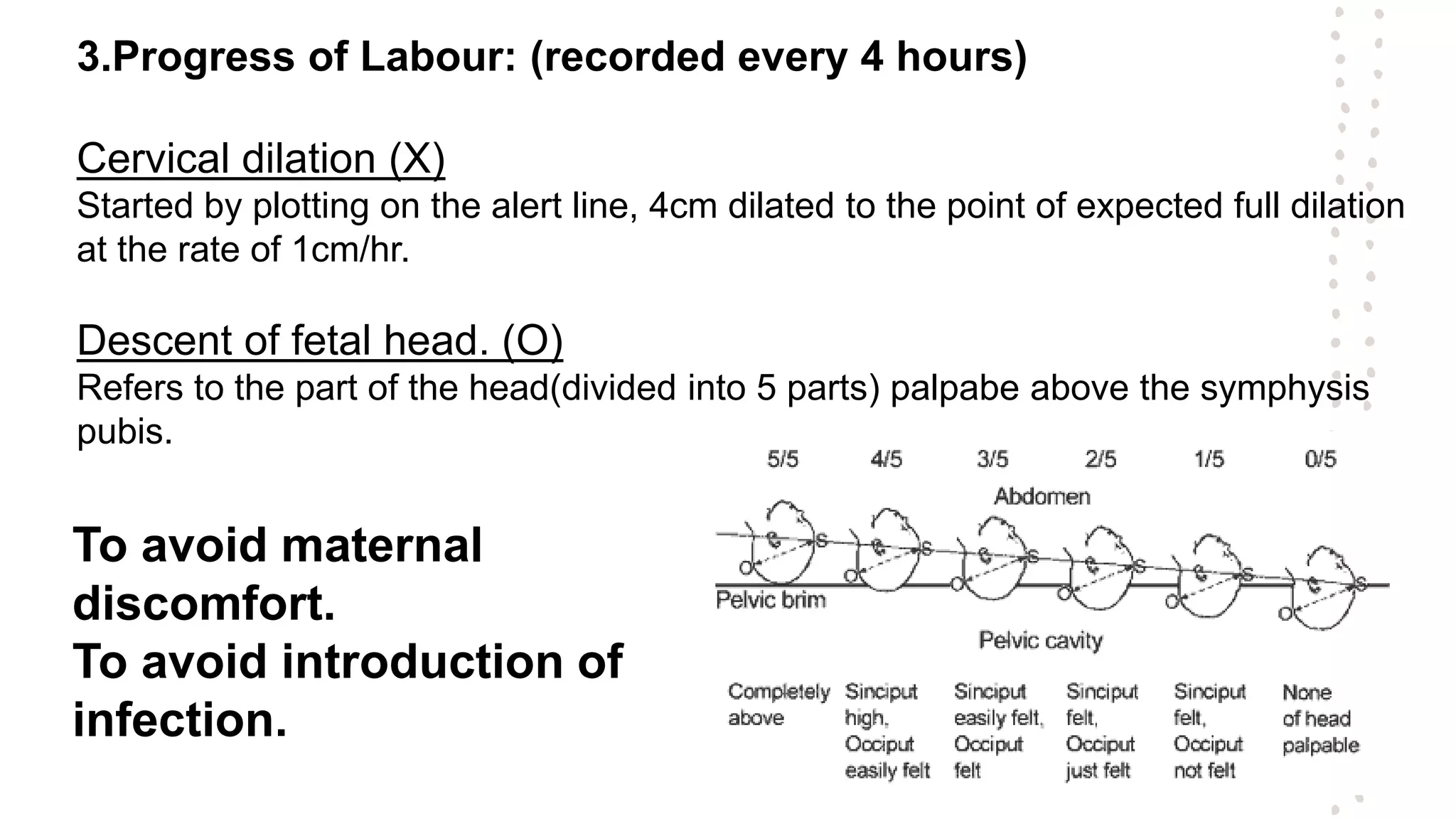
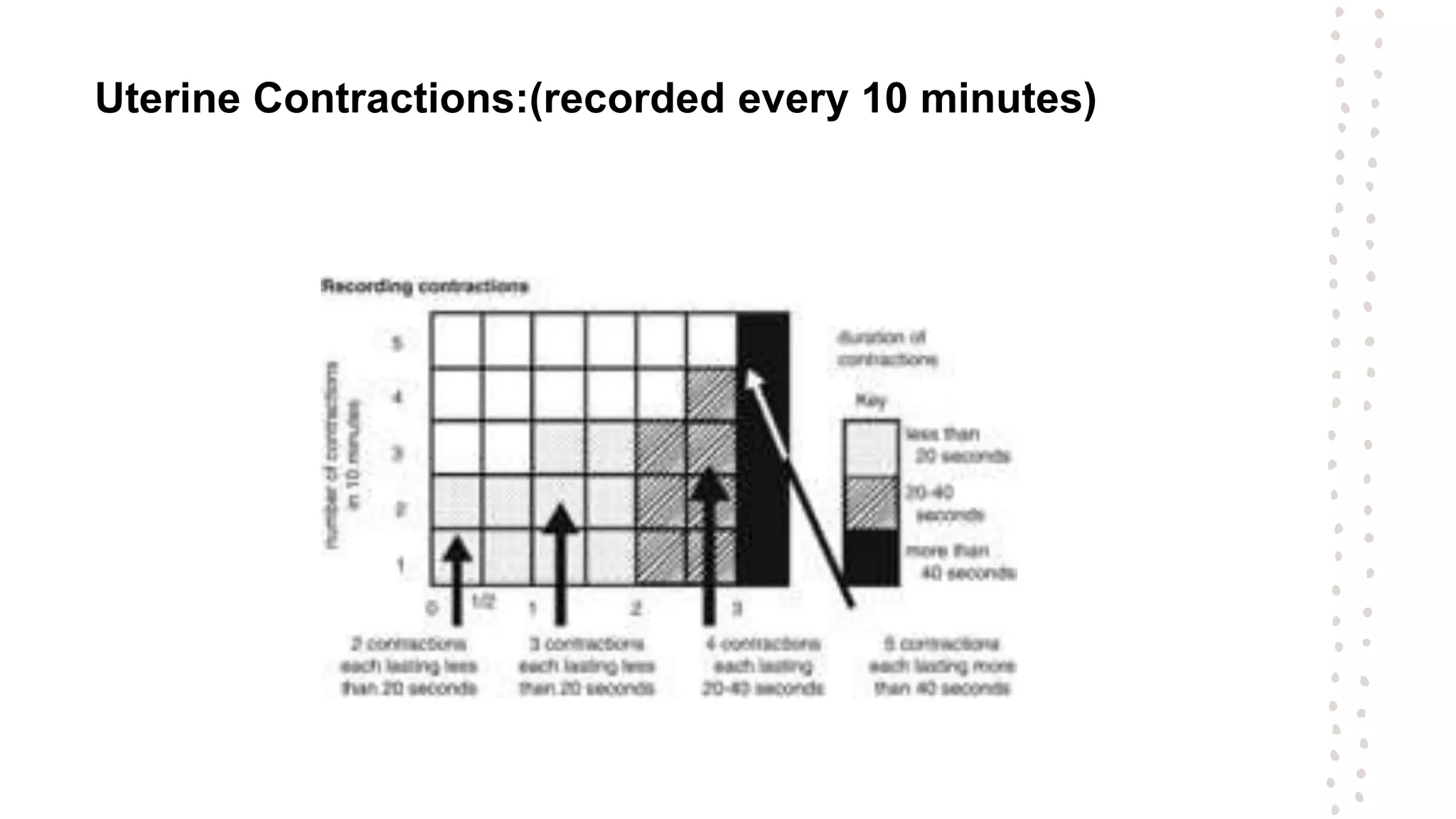
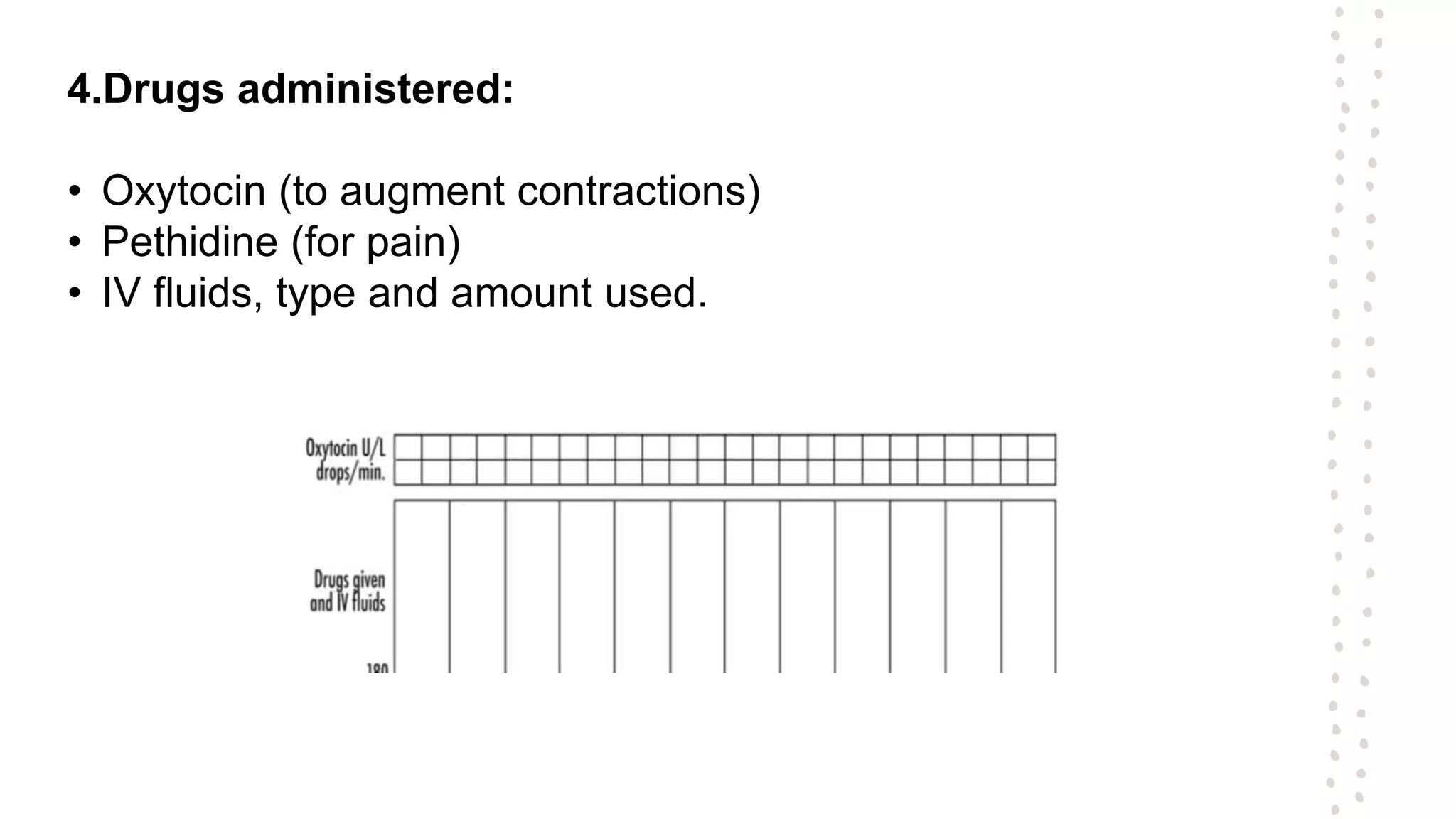
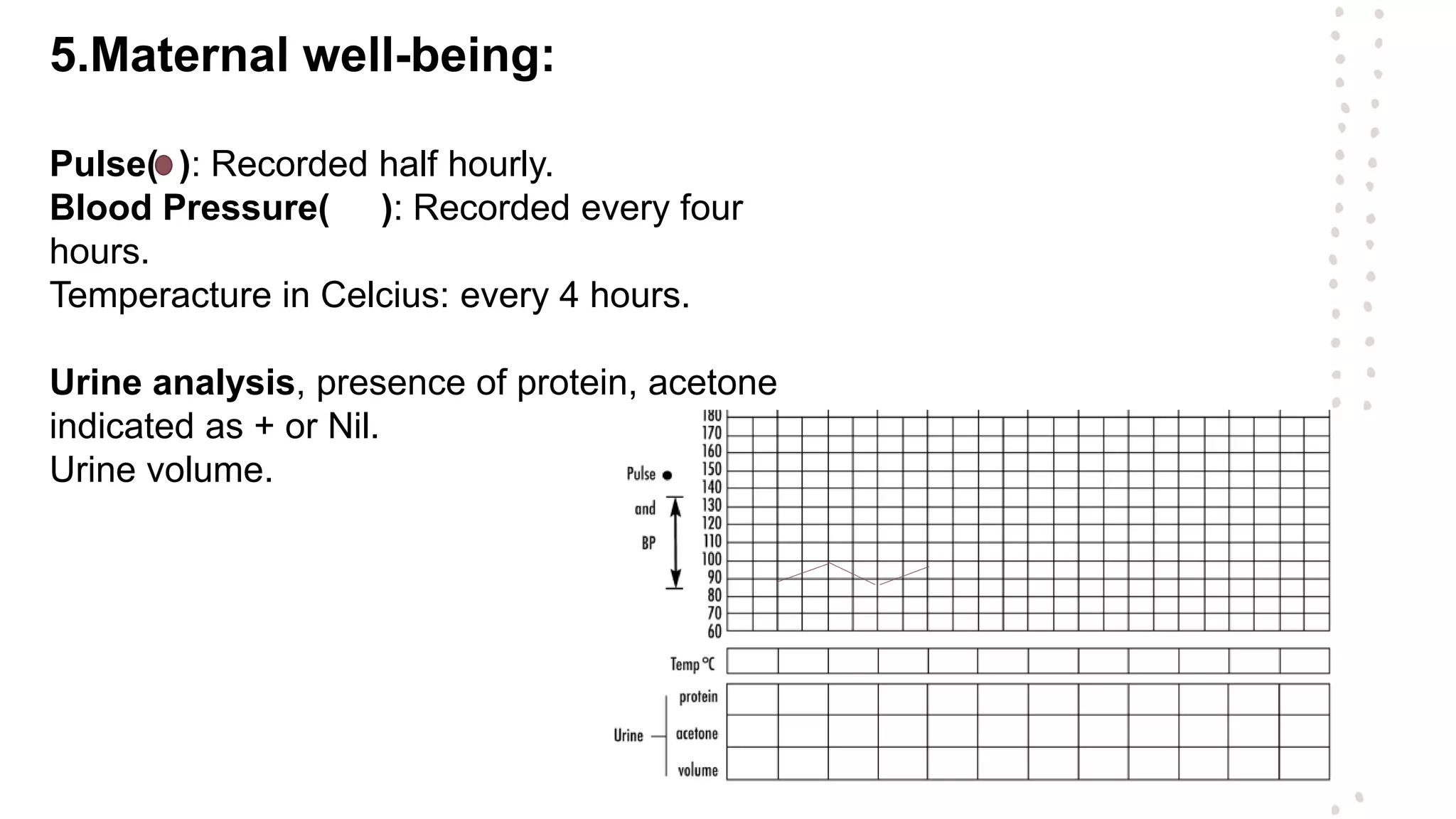
A partogram is a graphical record that monitors fetal and maternal well-being during labor, providing a quick overview of progress and facilitating early detection of abnormalities. The document outlines the evolution of the partogram, highlighting improvements such as the introduction of alert and action lines to assist in management decisions. Key components of a modern partogram include maternal details, fetal condition, labor progress, drugs administered, and maternal well-being indicators.