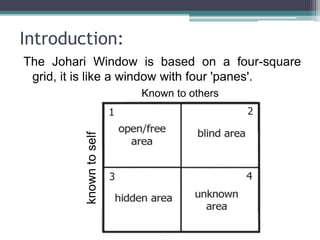
The Johari Window model illustrates the relationship between what a person knows about themselves and what others know about them. It divides information into four quadrants: Open Self (known to self and others), Blind Spot (known to others but not self), Hidden Self (known to self but not others), and Unknown (unknown to both self and others). The goal is to increase the Open Self by soliciting feedback, disclosing information, and engaging in self-discovery to reduce the Blind Spot, Hidden Self, and Unknown areas. The model aims to improve self-awareness and mutual understanding within groups.