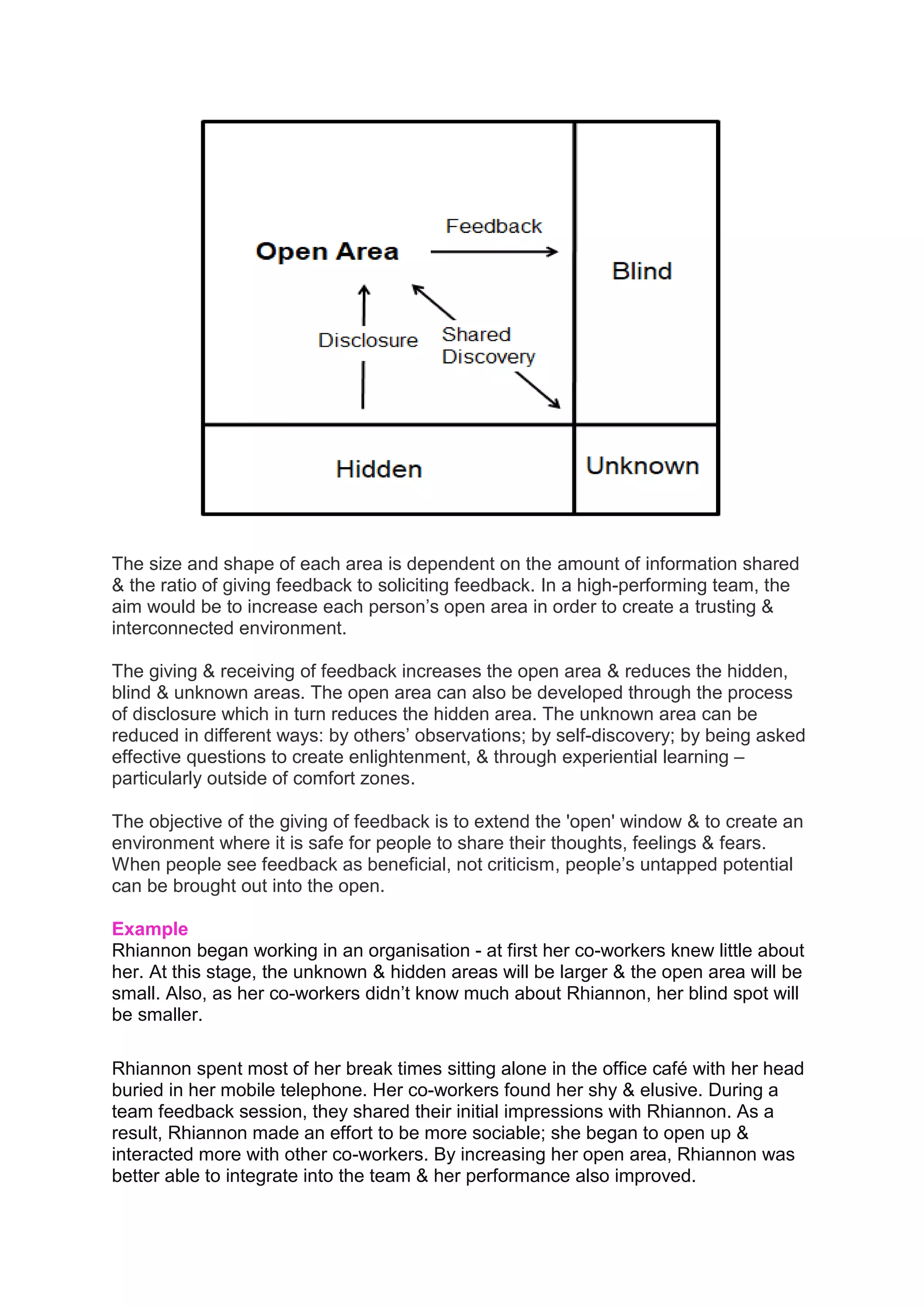
The Johari Window model, developed by Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham in 1955, is a tool for enhancing self-awareness and communication among individuals and groups through self-disclosure and feedback. The model consists of four quadrants (open, blind, hidden, and unknown) which represent varying degrees of self-awareness and information sharing, and its effectiveness can be increased by fostering an environment of trust and openness. As individuals engage in feedback and self-discovery practices, the sizes of the quadrants can change, ultimately improving personal relationships and team dynamics.