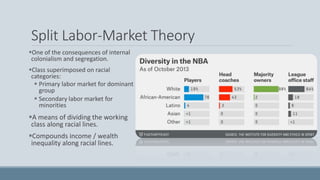
Patterns of racial and ethnic relations refer to the regular ways in which dominant groups treat subordinate groups. These patterns include internal colonialism, where non-white indigenous groups in colonized countries are controlled and exploited by white immigrant groups after independence, rather than whites from the colonizing country. Internal colonialism is created through population transfer or expulsion and results in slavery, segregation, discrimination, prejudice, violence, and intergenerational inequalities. It also leads to a split labor market with a primary market for the dominant group and a secondary market for minorities, dividing the working class along racial lines and compounding income and wealth inequality.