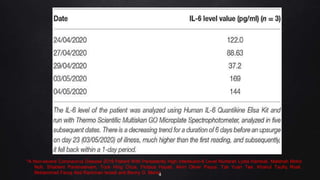
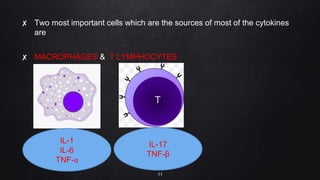
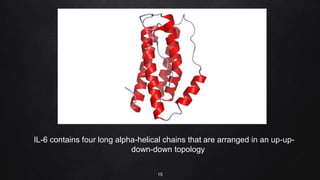
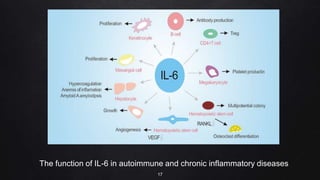
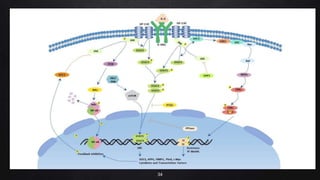
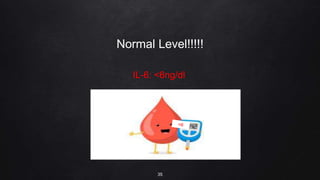
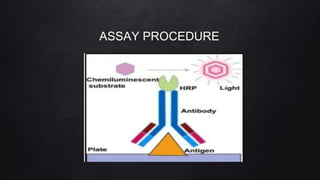
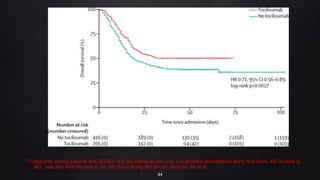
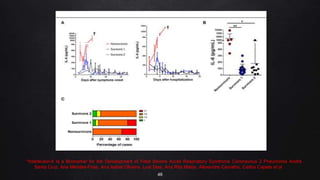
The document presents a case study on interleukin-6 (IL-6), detailing its role as a cytokine involved in inflammatory responses, particularly in COVID-19 where elevated levels are associated with severe disease outcomes. It describes IL-6's signaling pathways, production by various cells, and its implications in several autoimmune and chronic diseases. The study emphasizes that IL-6 acts as a biomarker for disease severity and discusses potential therapeutic approaches targeting IL-6 receptors in inflammatory conditions.