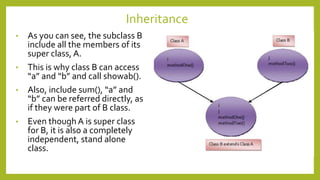
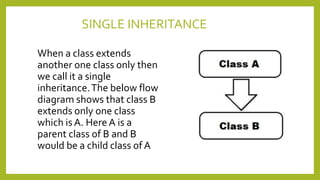
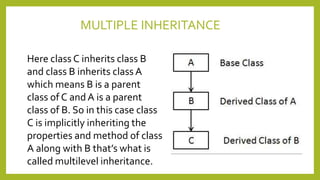
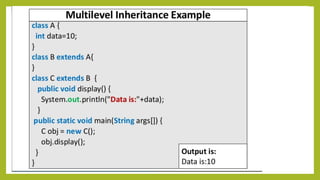
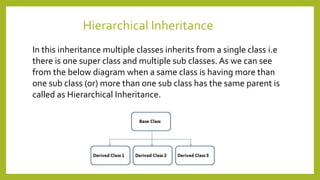
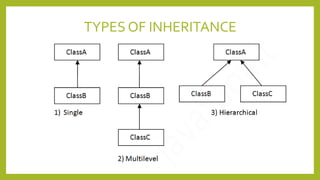
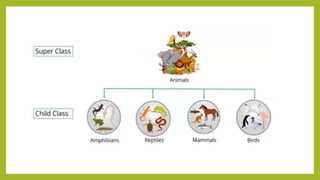
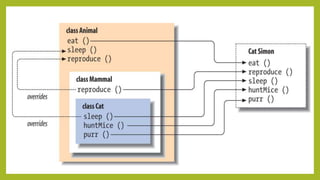
This document discusses inheritance in Java. It defines inheritance as a mechanism where a subclass inherits the properties and behaviors of its parent class. It provides an example of single inheritance in Java where class B extends class A, inheriting its attributes and methods. The document also describes different types of inheritance like multilevel inheritance where a class inherits from another subclass, and hierarchical inheritance where a parent class has multiple subclasses. It provides an example of inheritance between different animal classes to demonstrate these concepts.



![//Creating a SubClass
class A{
int a=10, b=20;
void showab(){
System.out.println(“a: “+a+ “b: ”+b);
}
}
//Creating a SubClass by extanding A class
class B extends A{
void sum(){
System.out.println(“Sum of a and b is: ”+(a+b));
}
}
//Creating Main Class
class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
A obj1= new A();
obj1.showab();
B obj2= new B();
obj2.sum();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-180426194348/85/Inheritance-In-Java-6-320.jpg)








![SAMPLE PROGRAM
public class Animal{
}
public class Amphibians extends Animal{
}
public class Reptiles extends Animal{
}
public class Mammals extends Animal{
}
public class Birds extends Animal{
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]){
// write your code
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-180426194348/85/Inheritance-In-Java-22-320.jpg)

![public class Animal{
eat();
reproduce();
sleep();
}
public class Amphibians extends Animal {
swim();
}
public class Reptiles extends Animal{
crawl();
}
public class Mammals extends Animal{
giveMilk();
}
public class Birds extends Animal {
fly();
}
public class Main{
public static void main (String args[] ){
Amphibians obj1=new Amphibians();
Reptiles obj2=new Reptiles();
Mammals obj3=new Mammals();
Birds obj4=new Birds();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inheritance-180426194348/85/Inheritance-In-Java-25-320.jpg)
