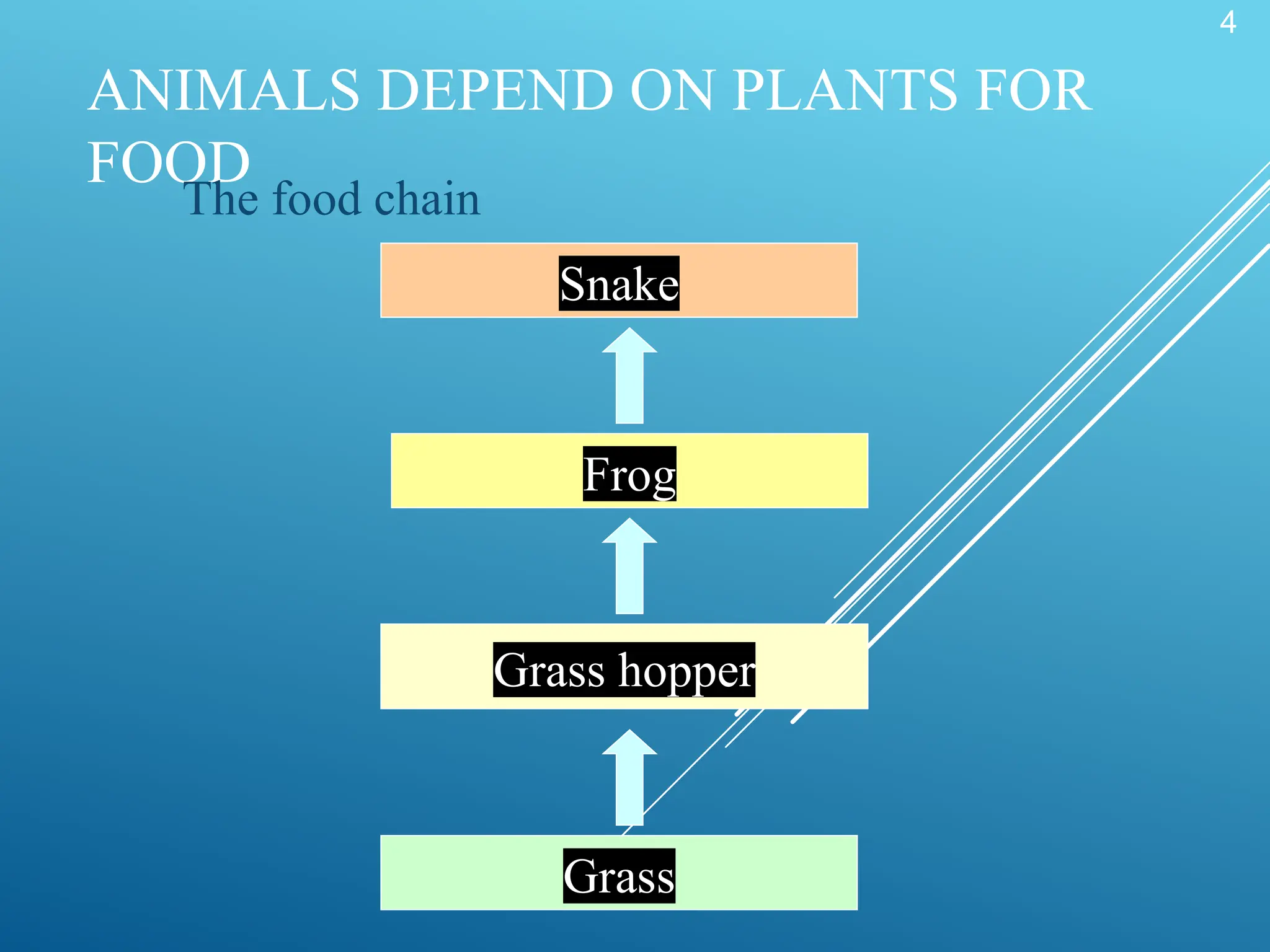
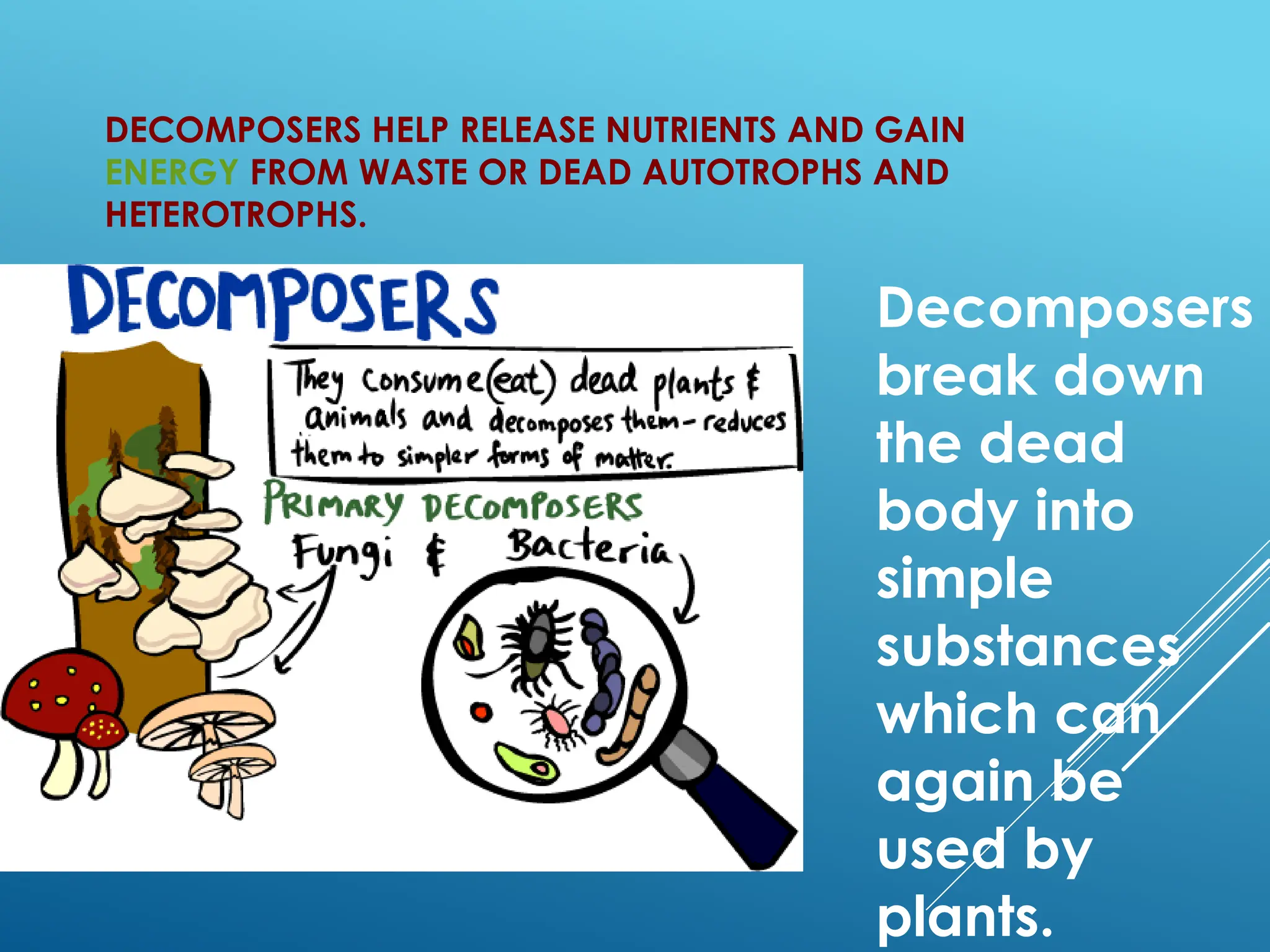
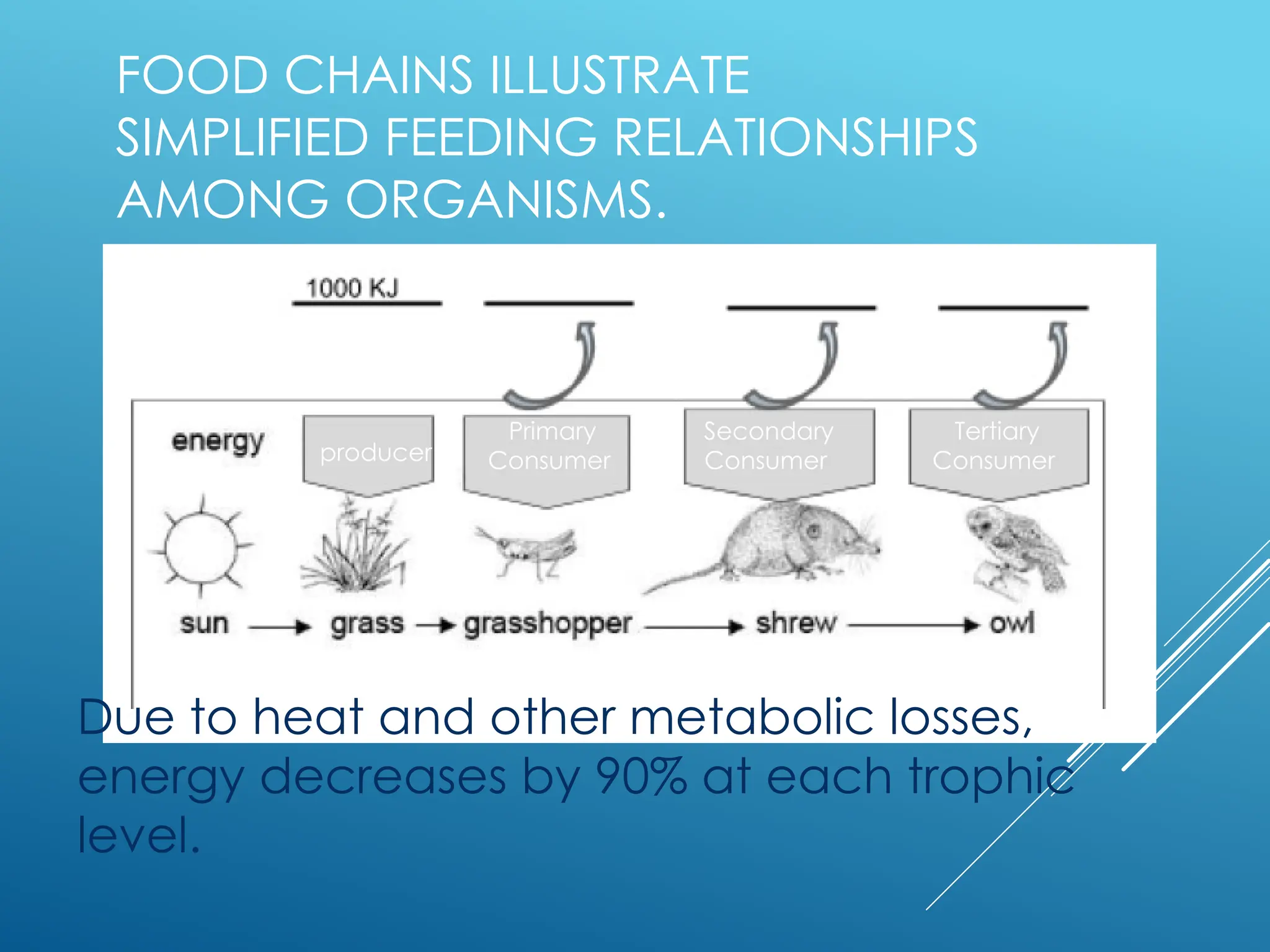
The document discusses the interdependence of plants and animals in ecosystems, highlighting that plants provide food, oxygen, and shelter to animals while animals aid in plant reproduction. It outlines the food chain and its categories, such as producers, consumers, and decomposers, emphasizing the role of photosynthesis in energy transfer. Additionally, it explains the significance of water and soil in maintaining life processes for both plants and animals.