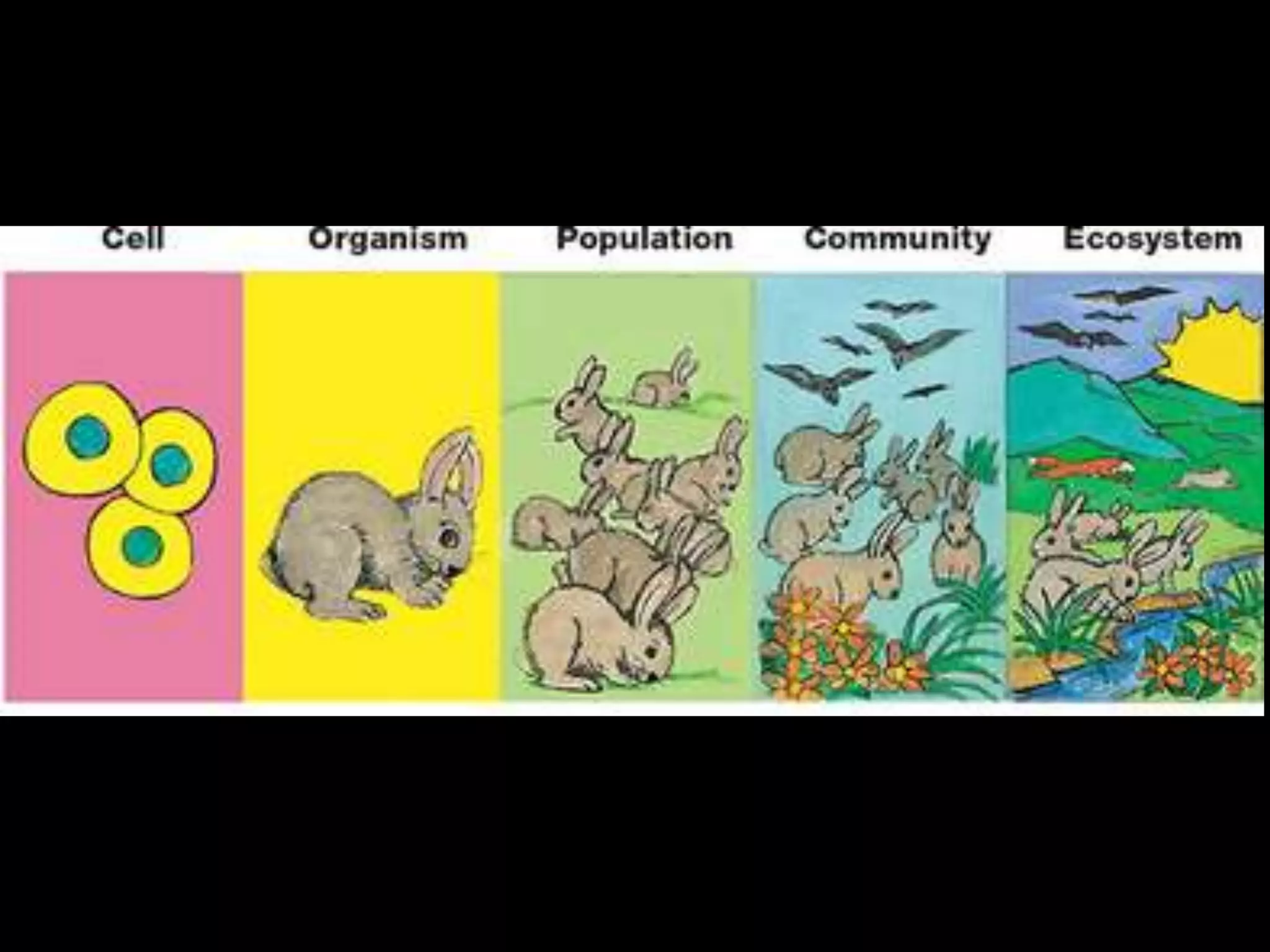
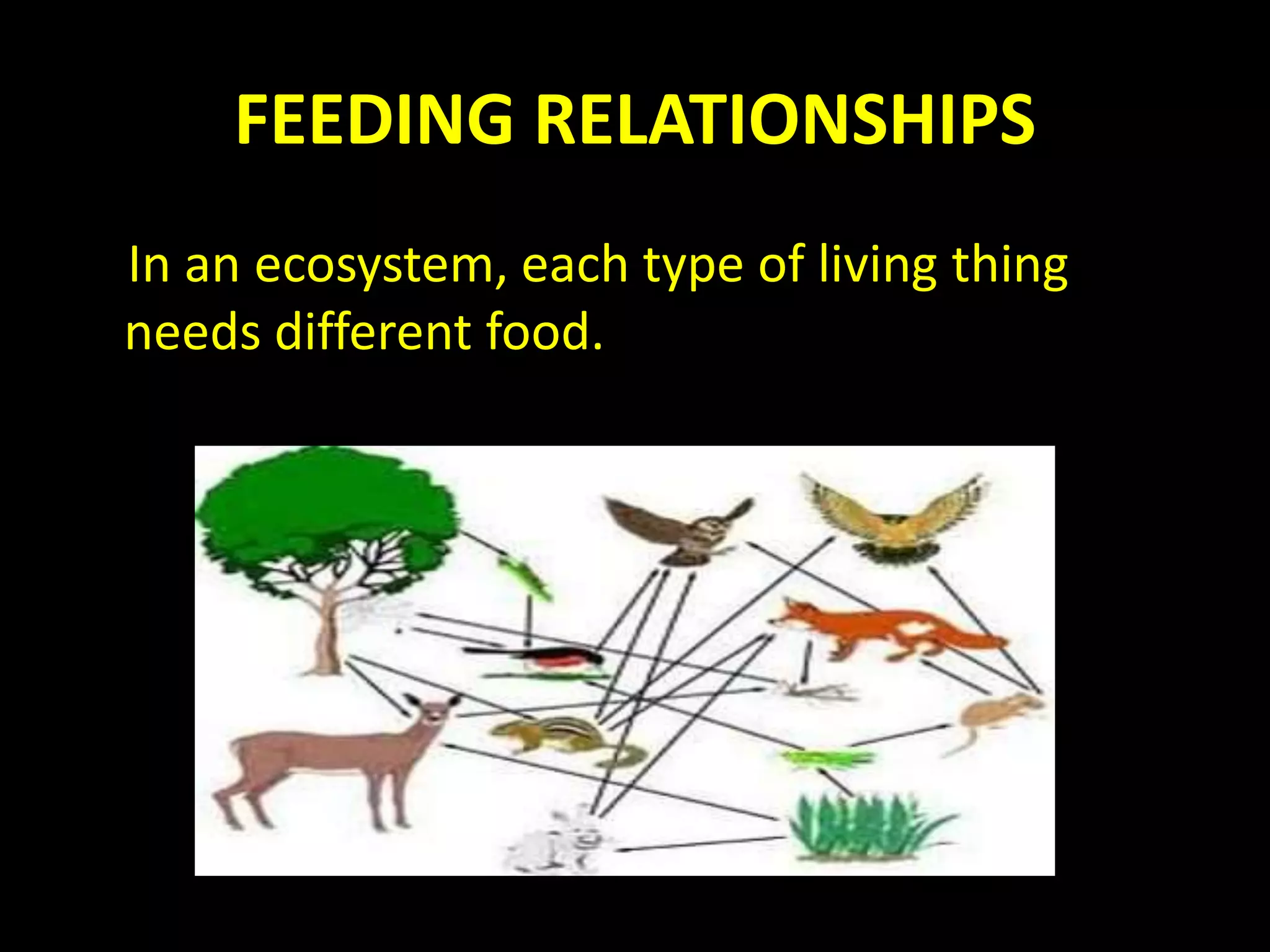
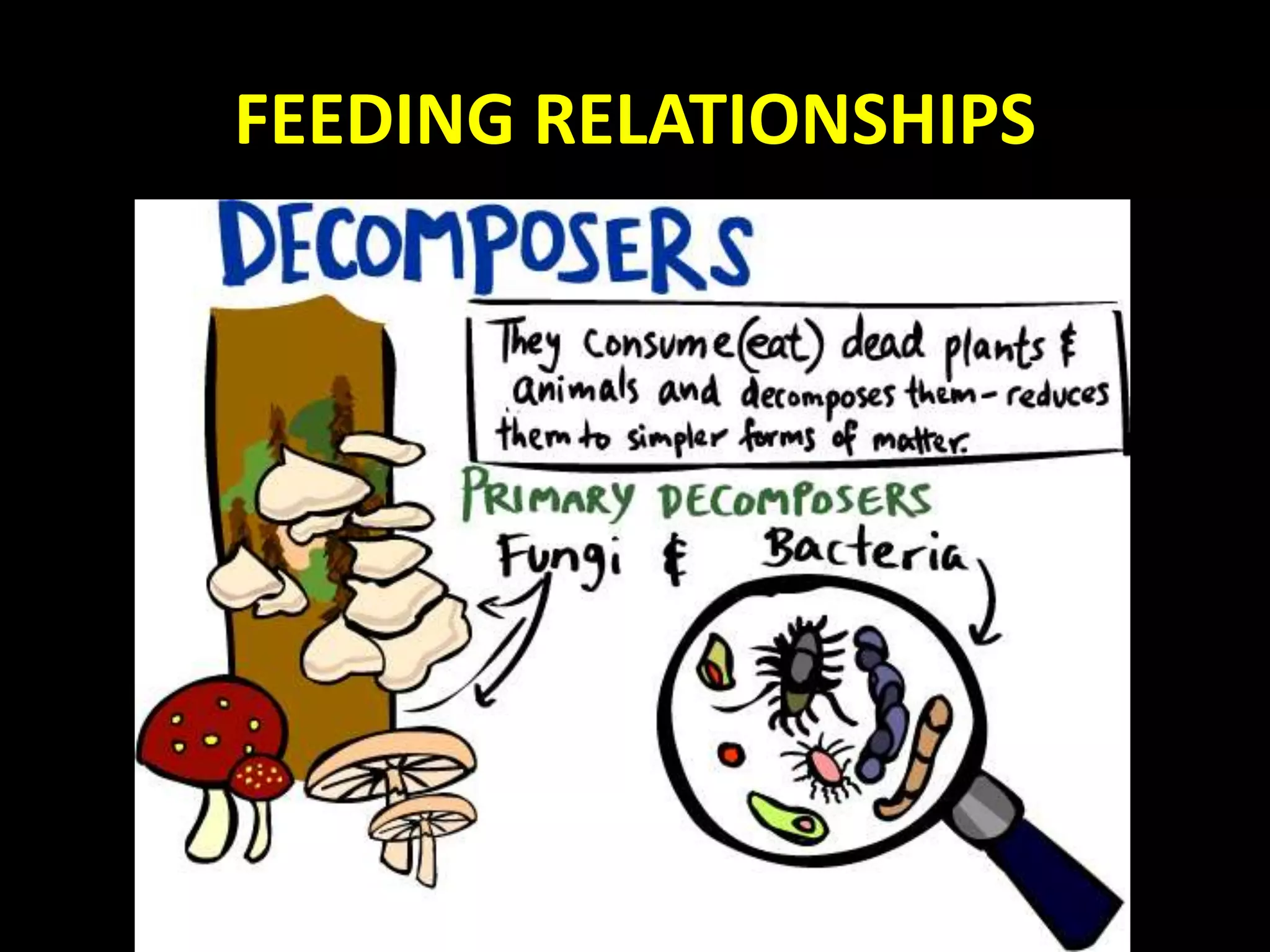
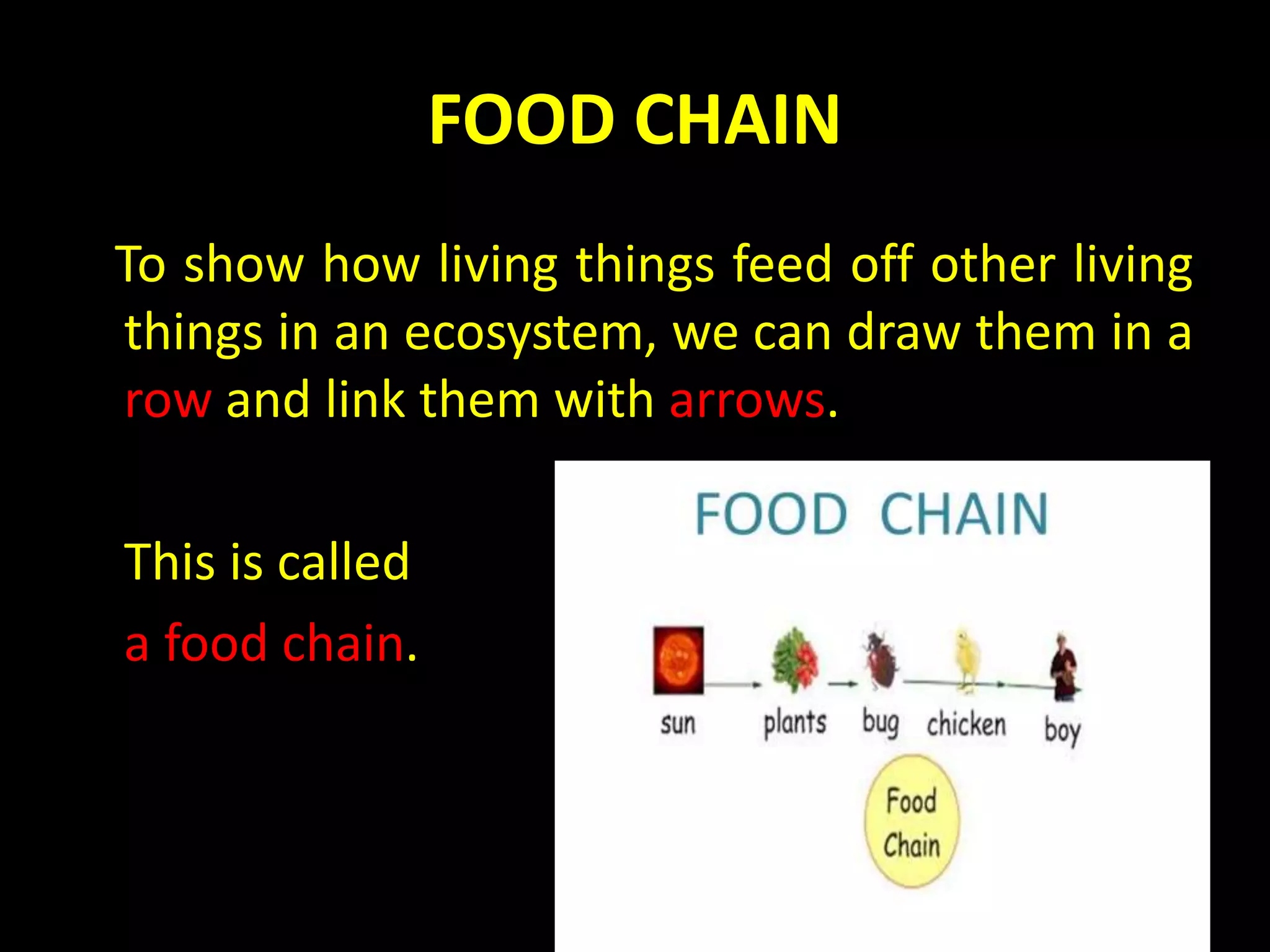
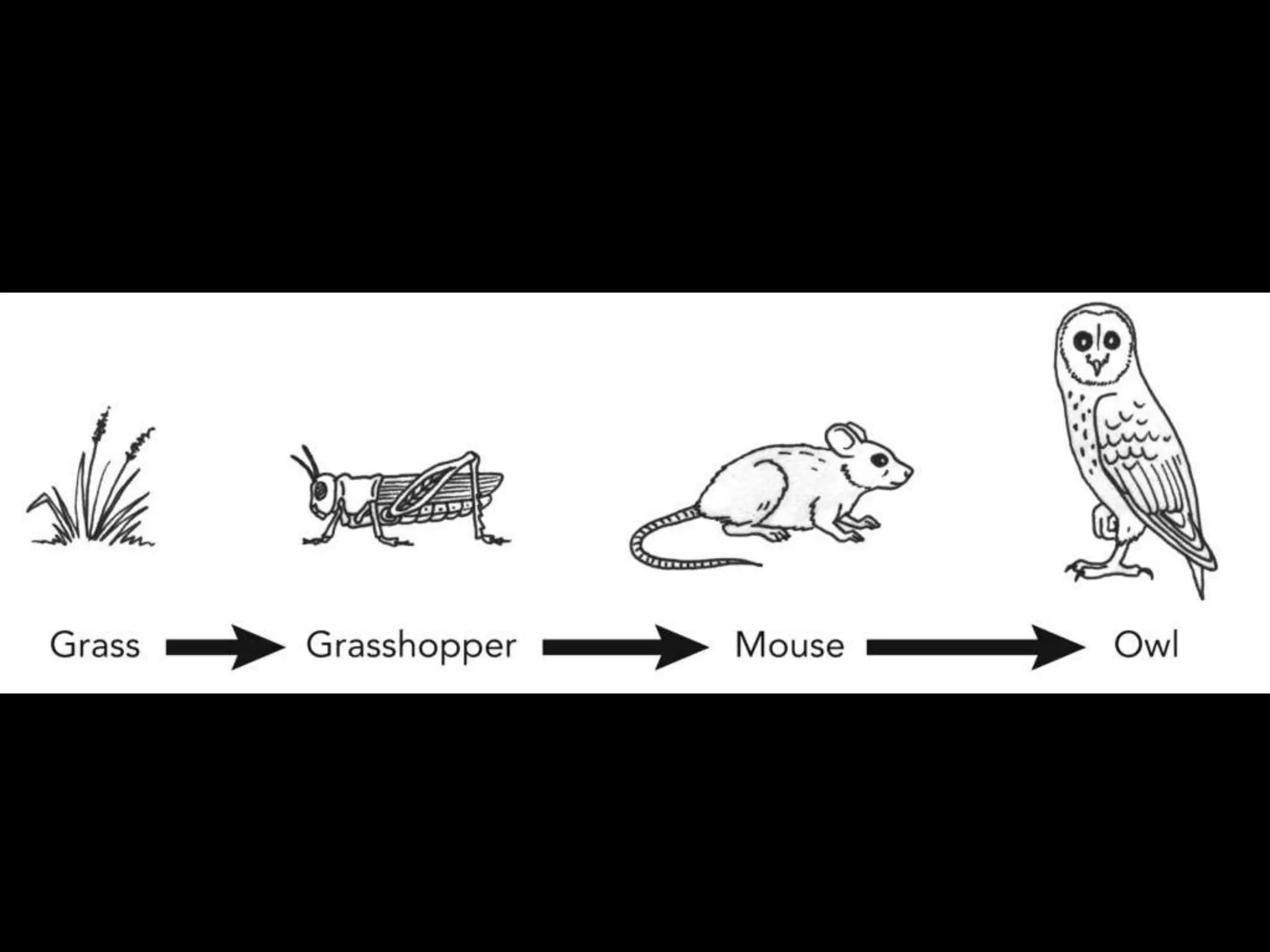
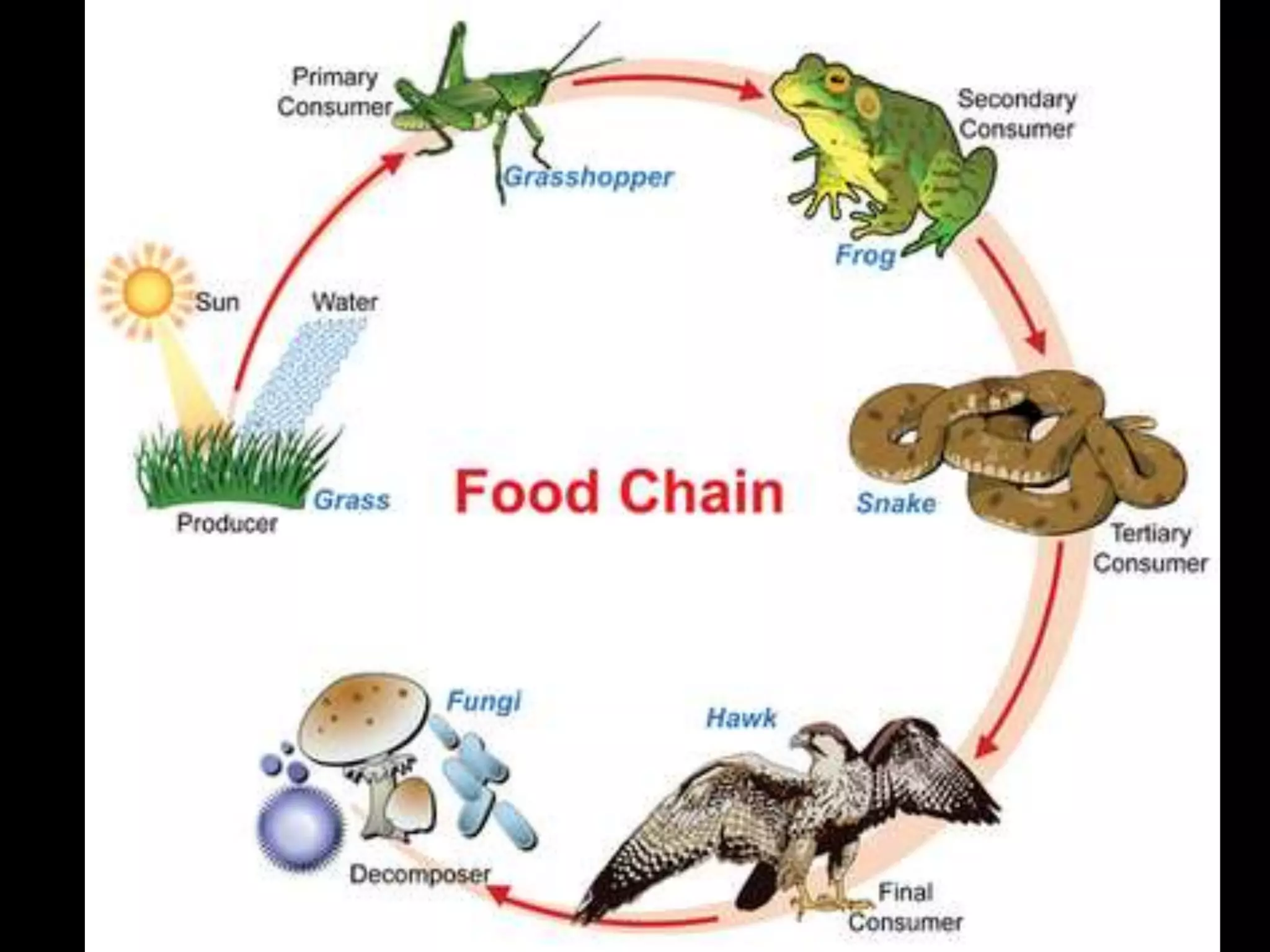
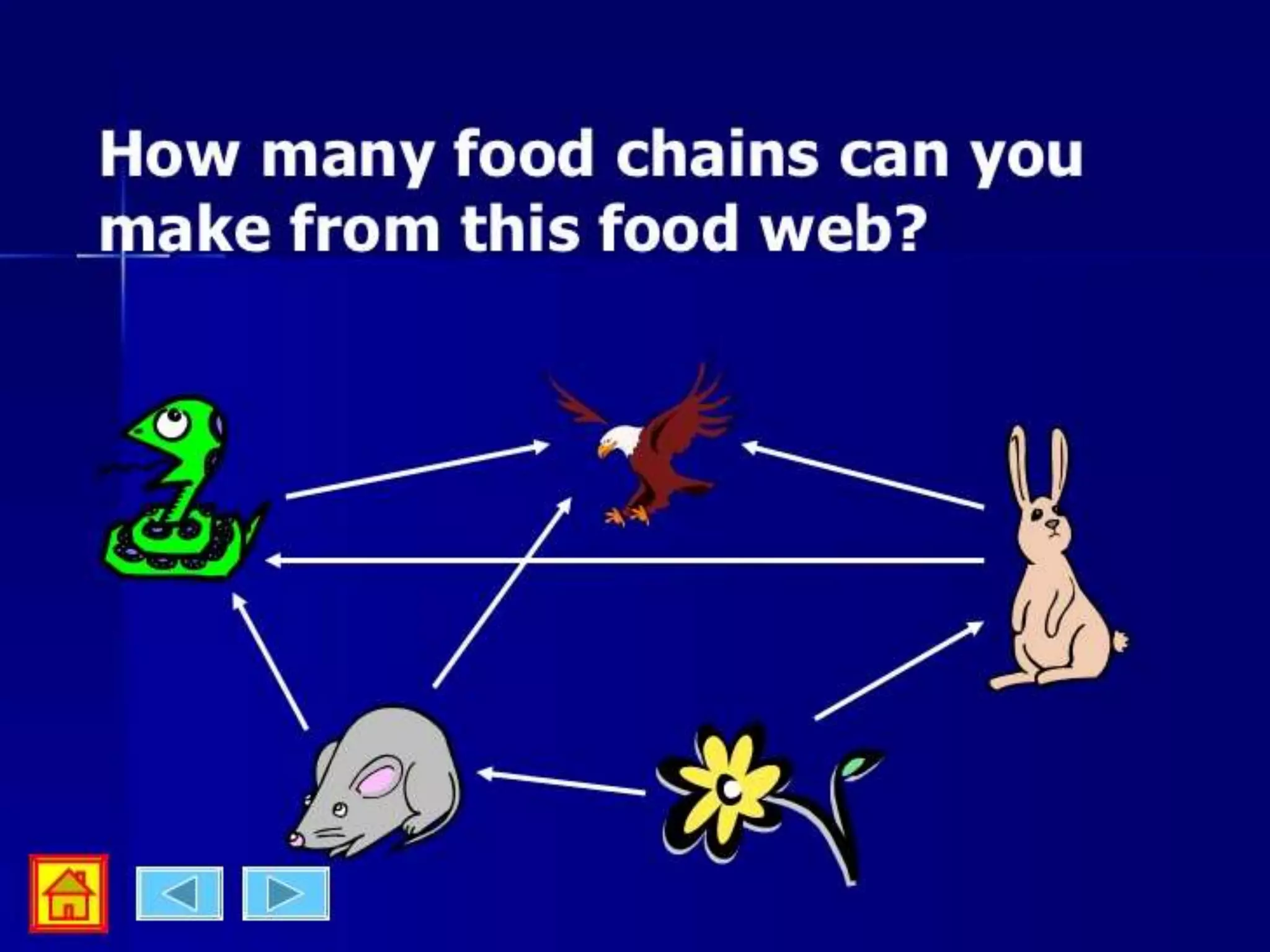
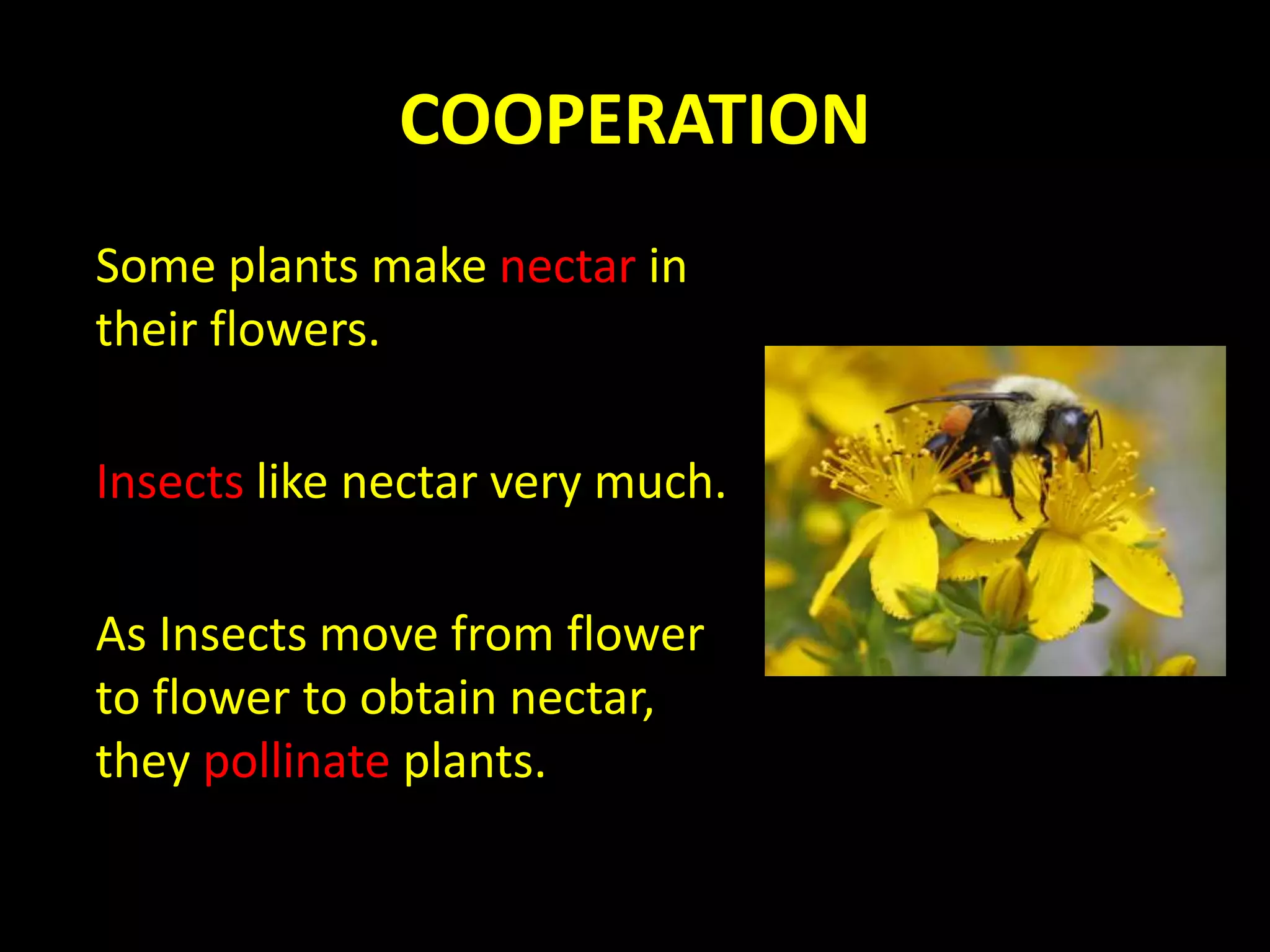
An ecosystem is made up of all living and non-living things that interact in a defined area. It contains biotic factors like plants and animals as well as abiotic factors such as temperature, water, soil and rocks. Living things have different needs that determine where they can survive, such as weeping willows needing water or cacti living in dry deserts. Within an ecosystem, plants produce food through photosynthesis while animals consume other organisms as herbivores, carnivores or omnivores. Food chains display the transfer of energy as organisms eat each other, and living things may compete for resources or cooperate, such as insects pollinating flowers in exchange for nectar.