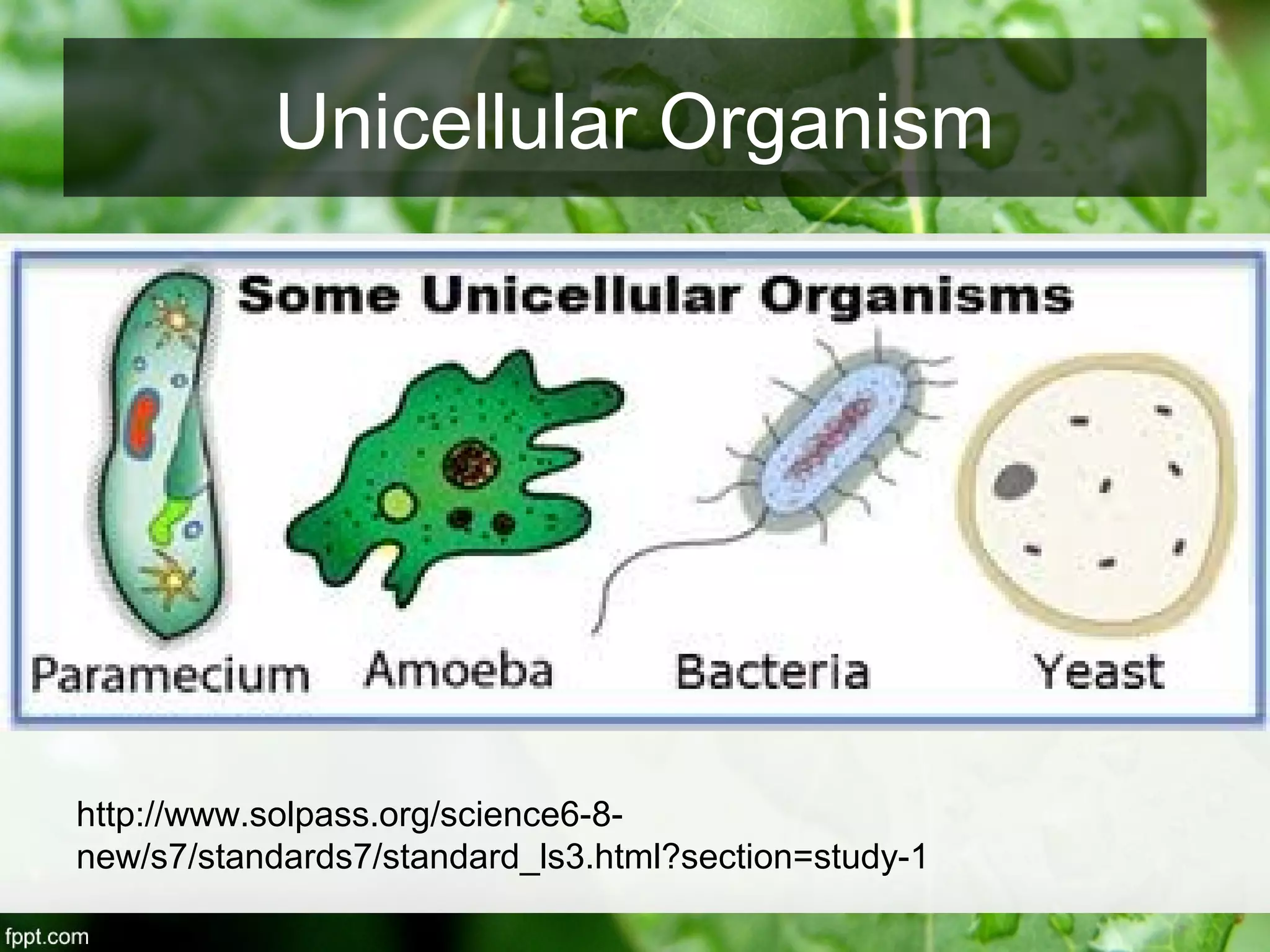
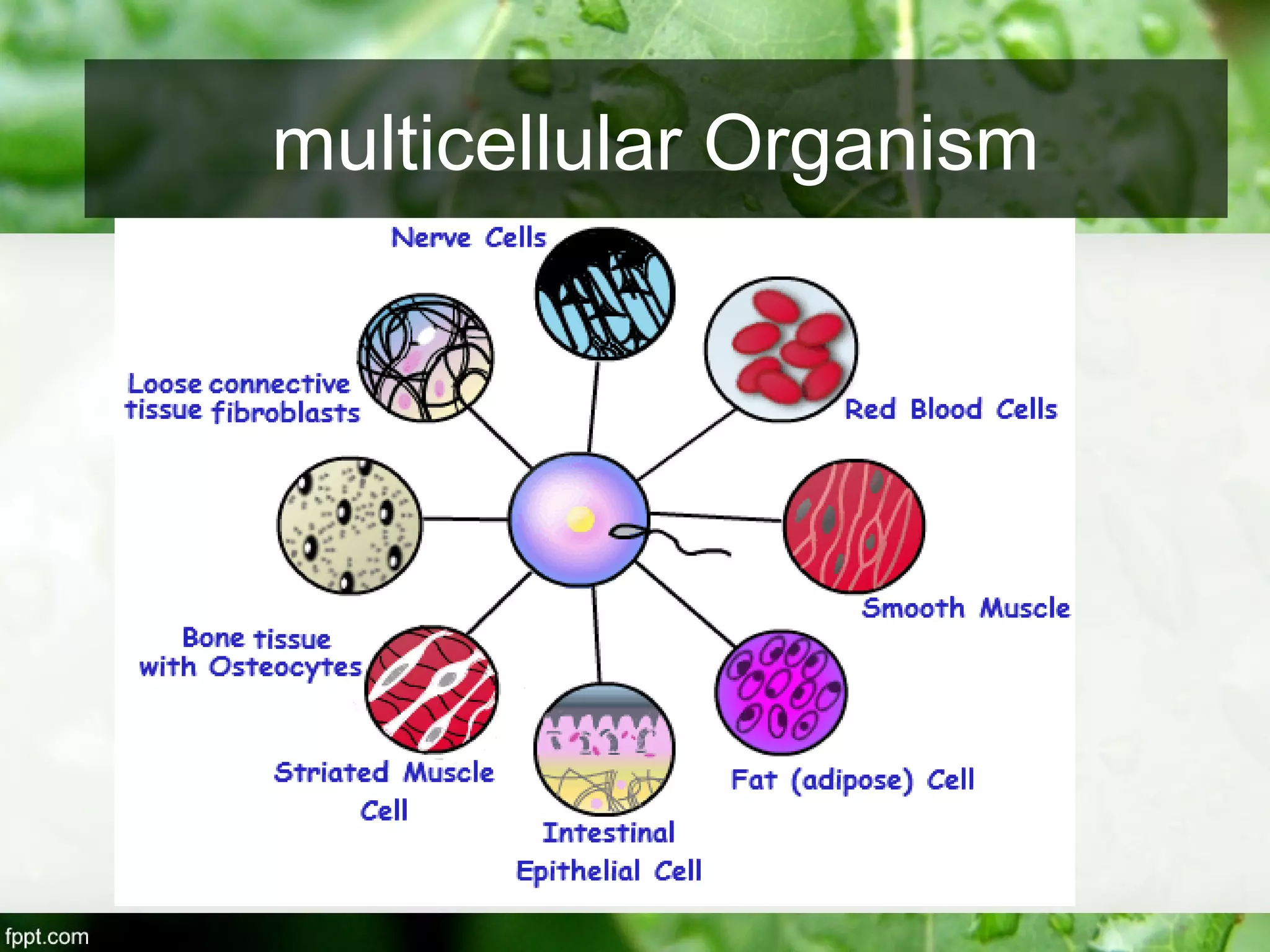
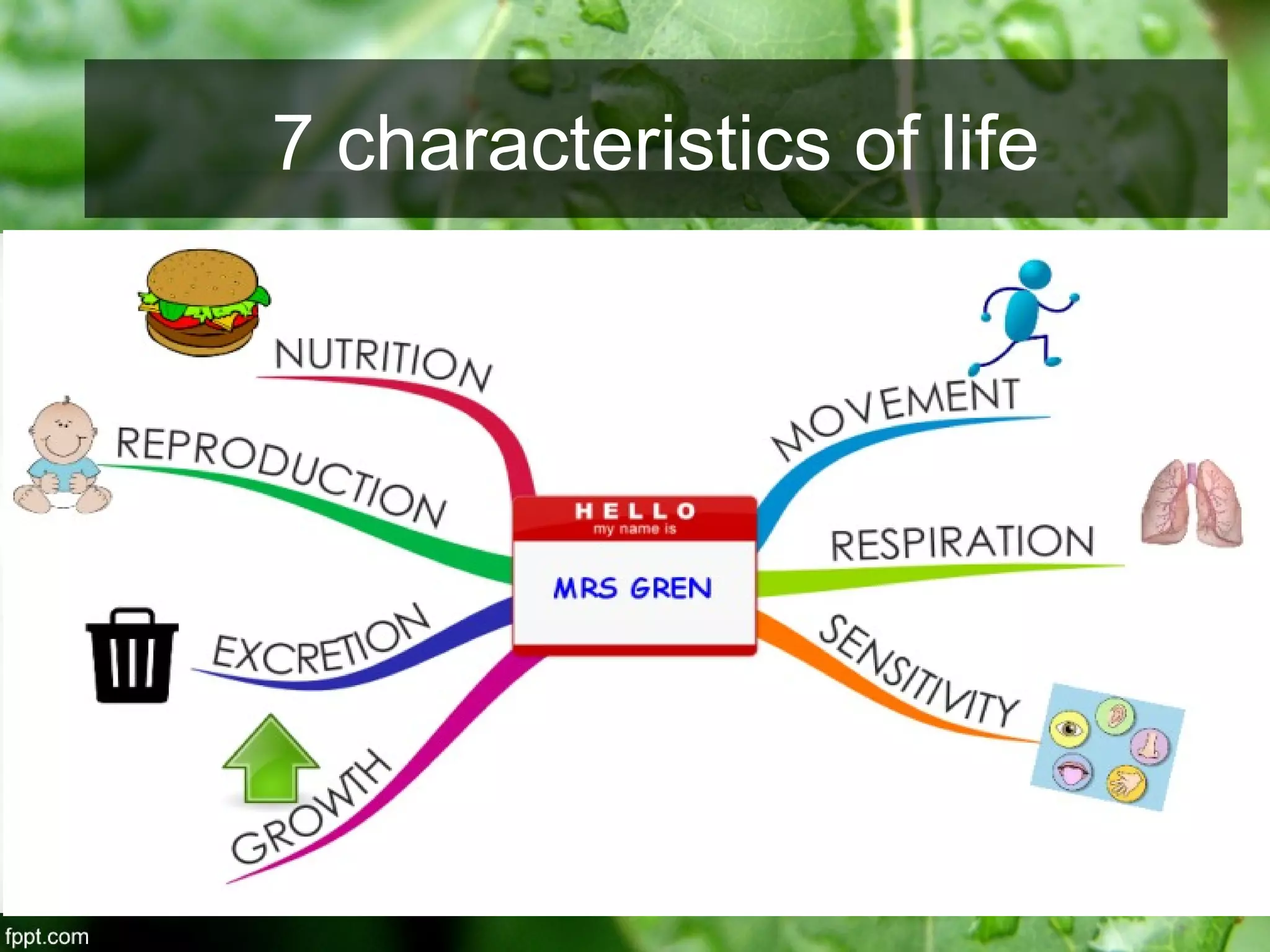
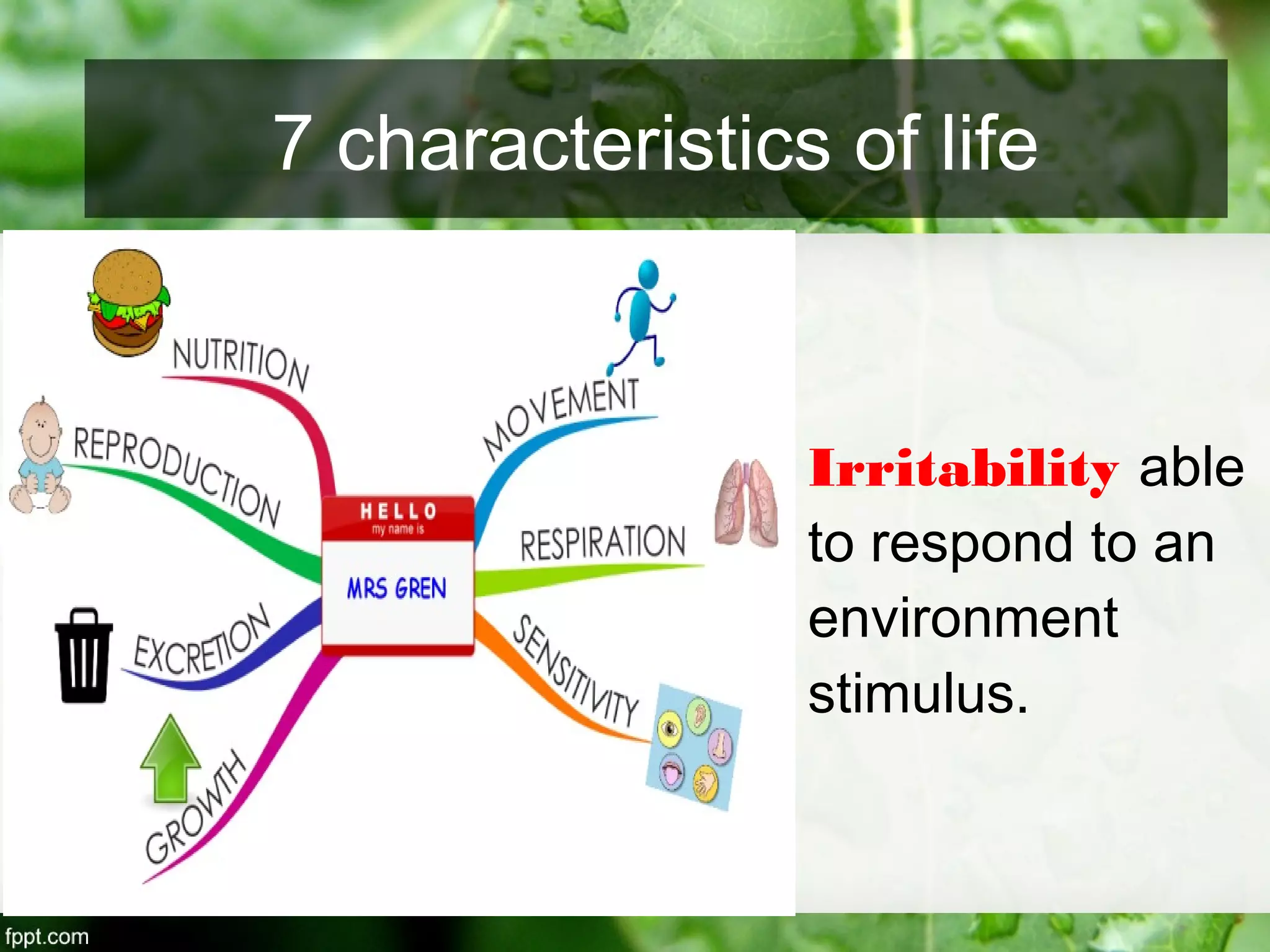
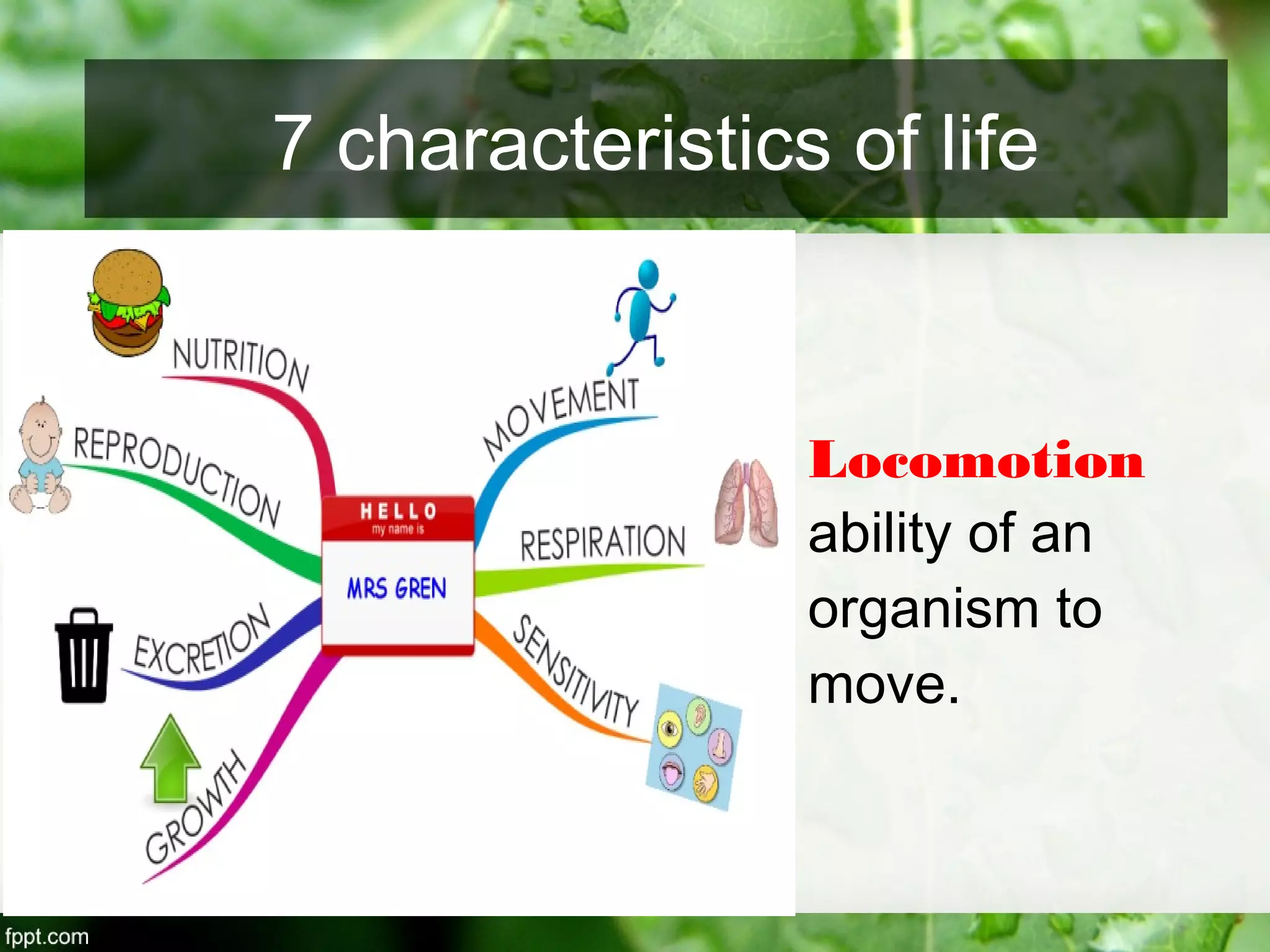
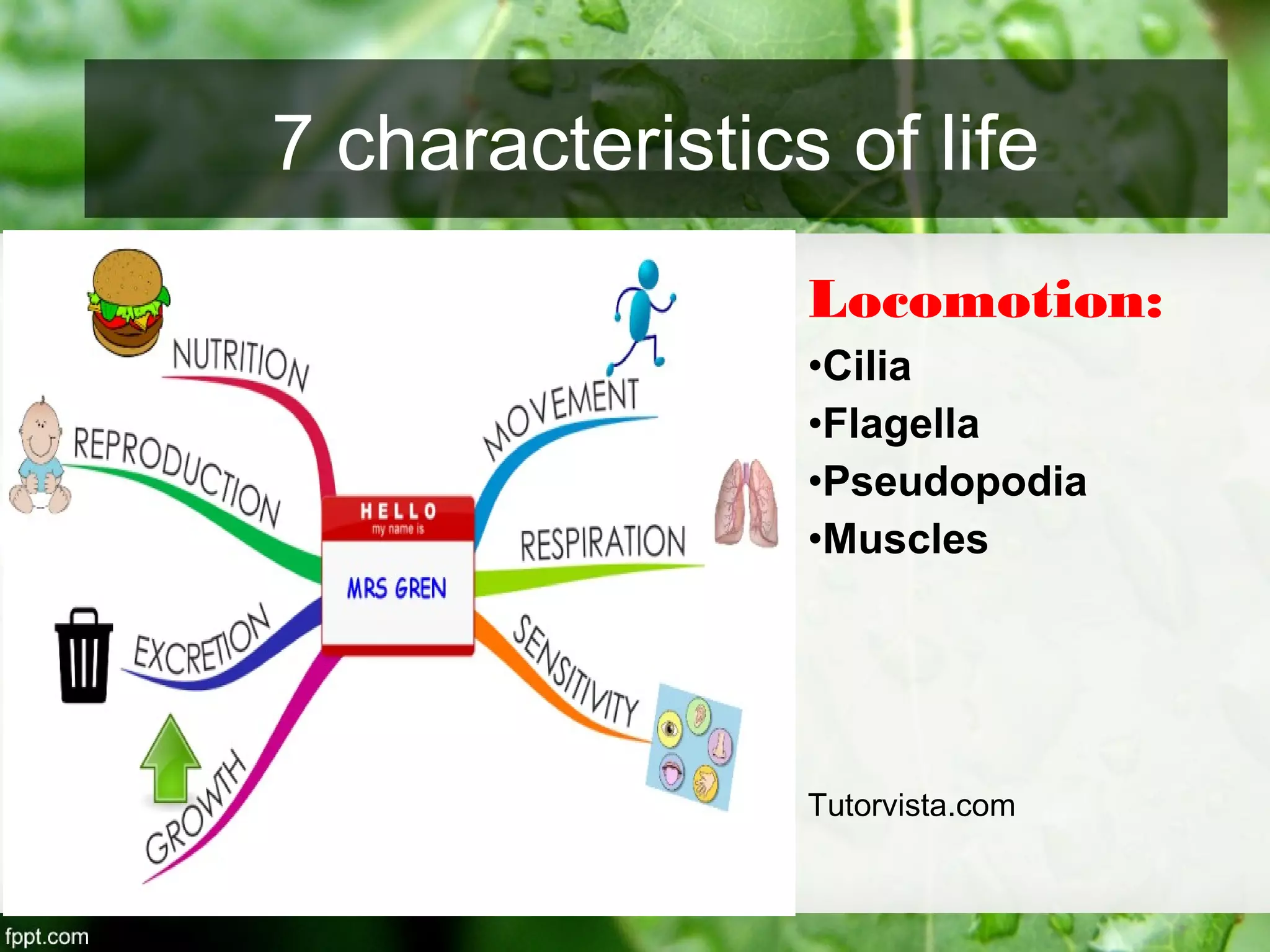
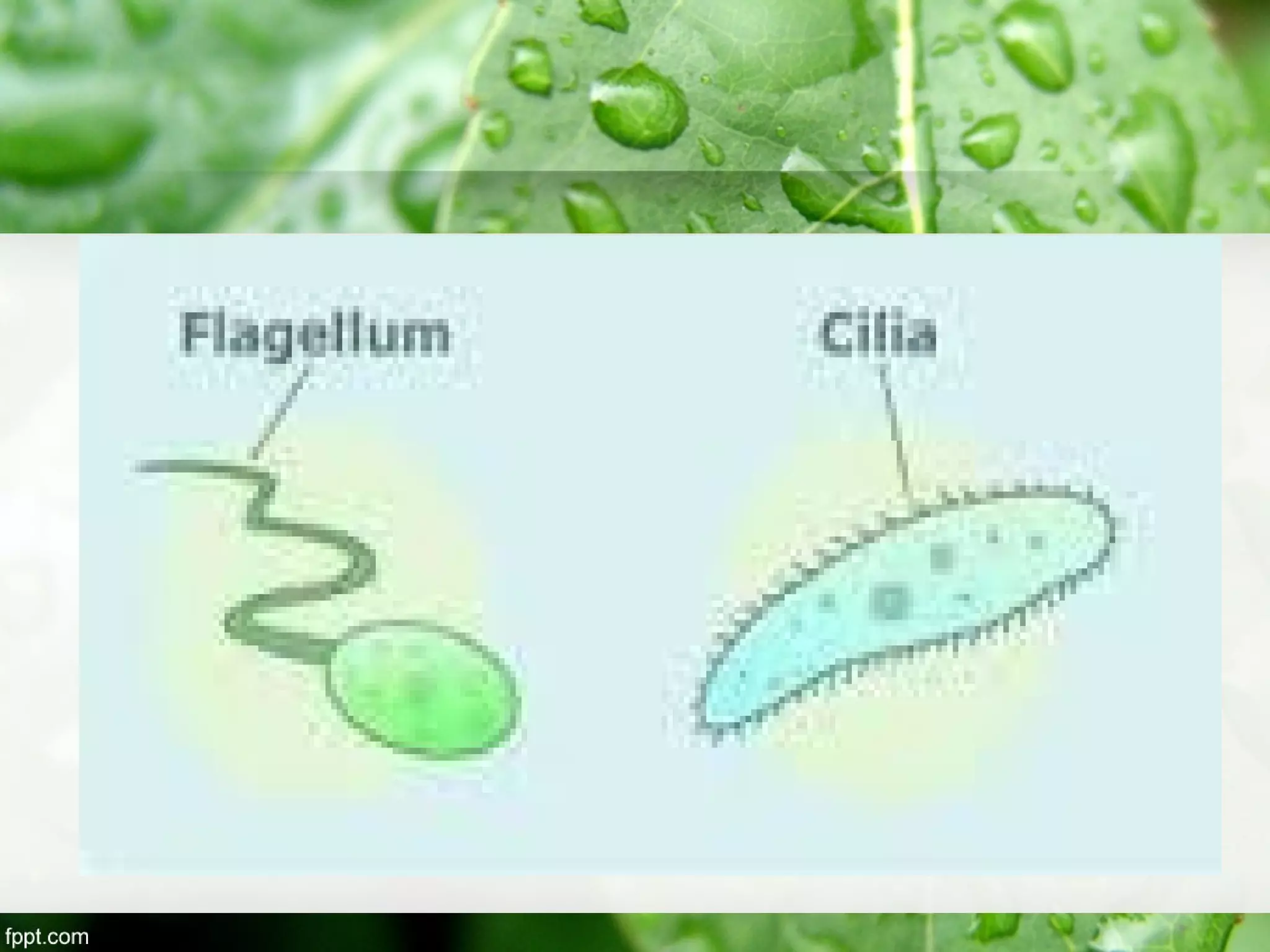
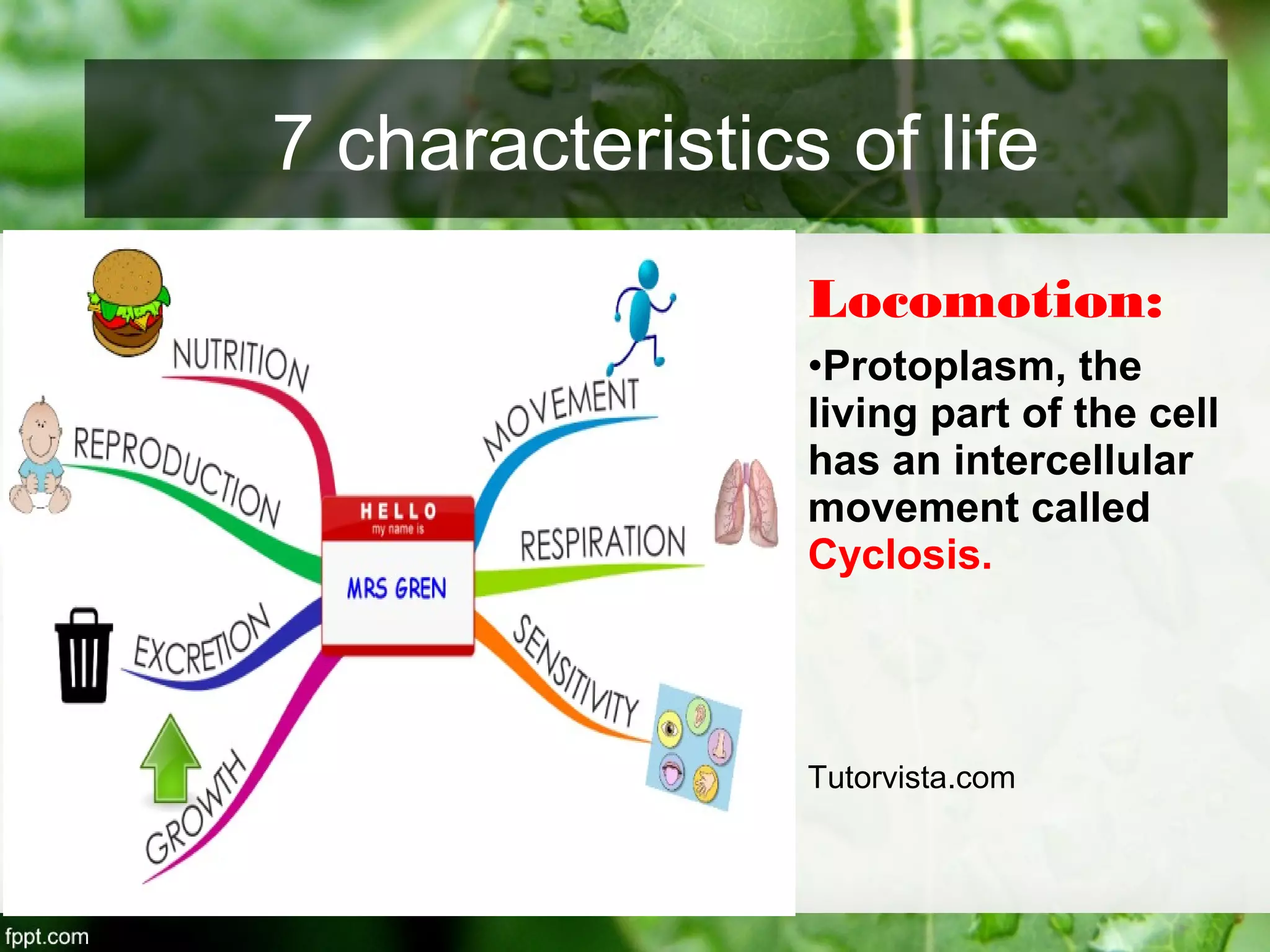
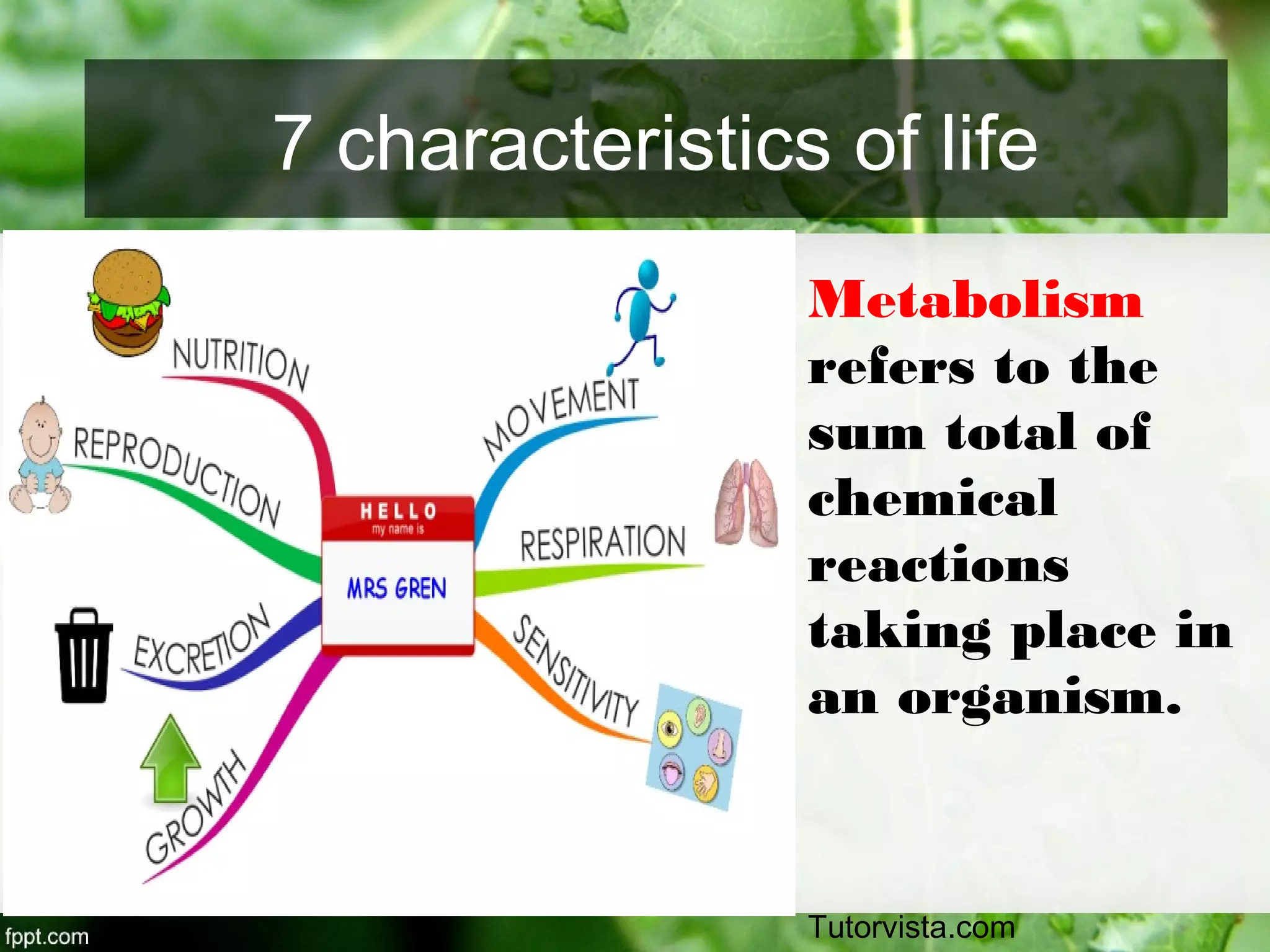
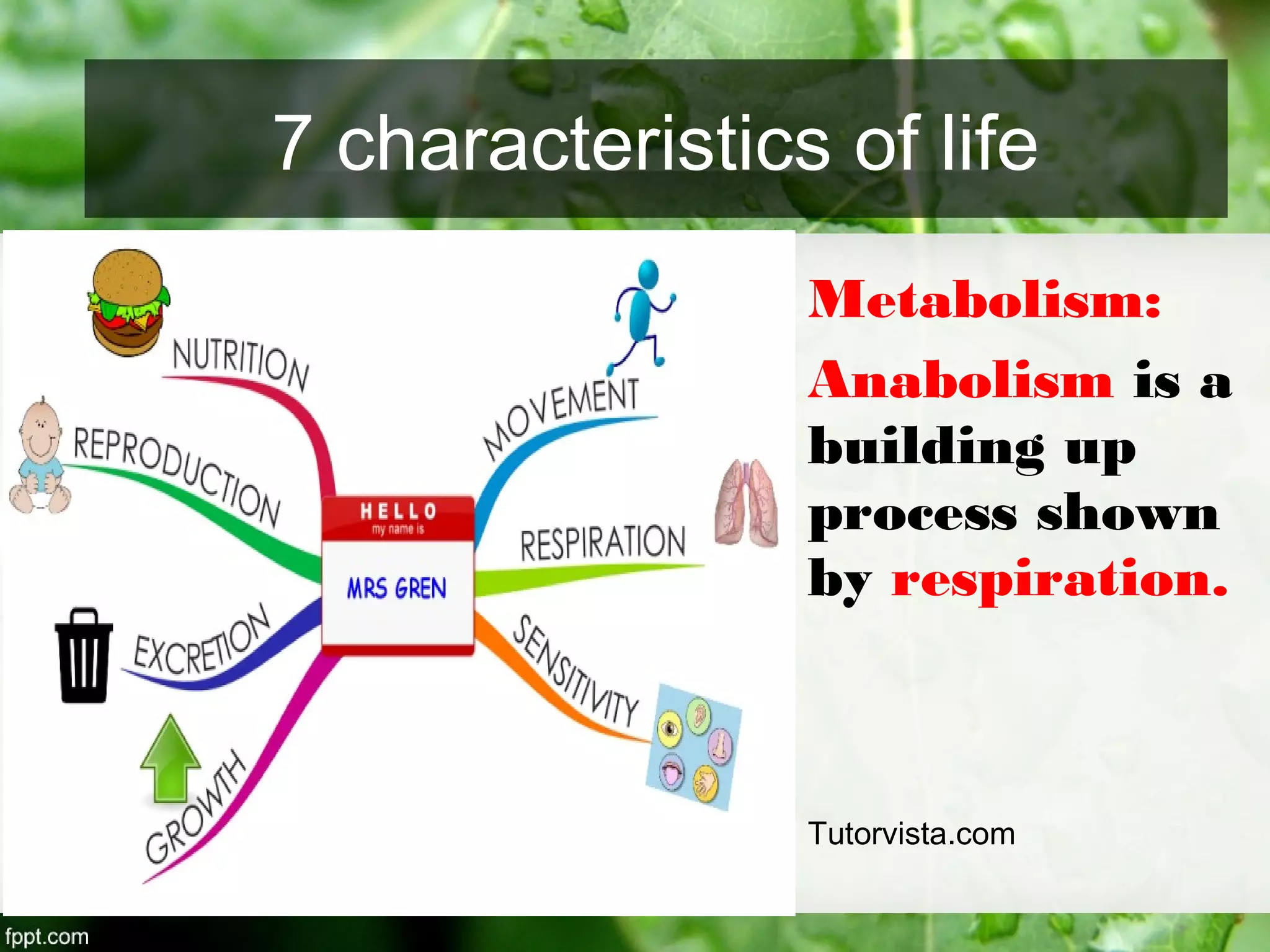
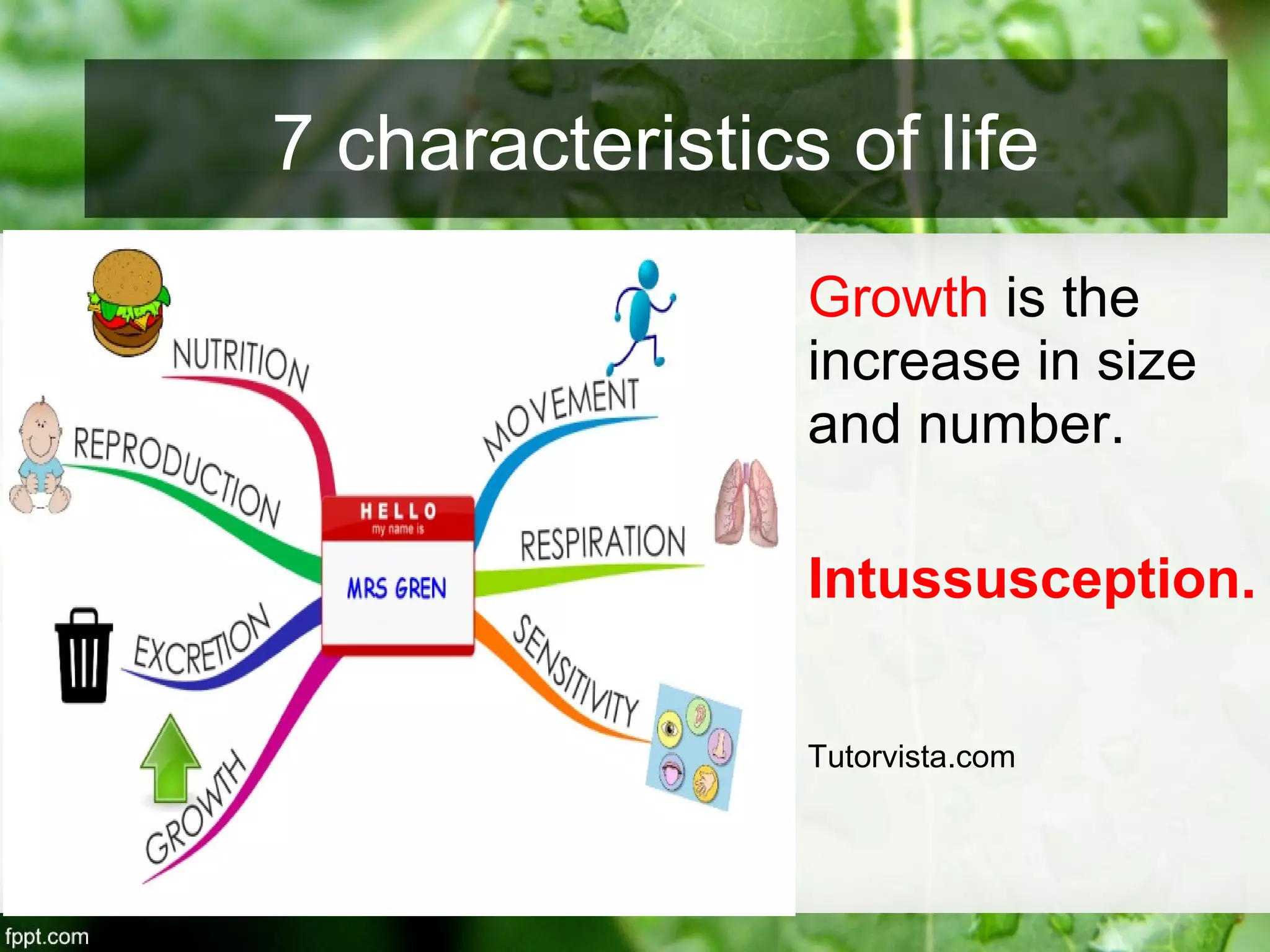
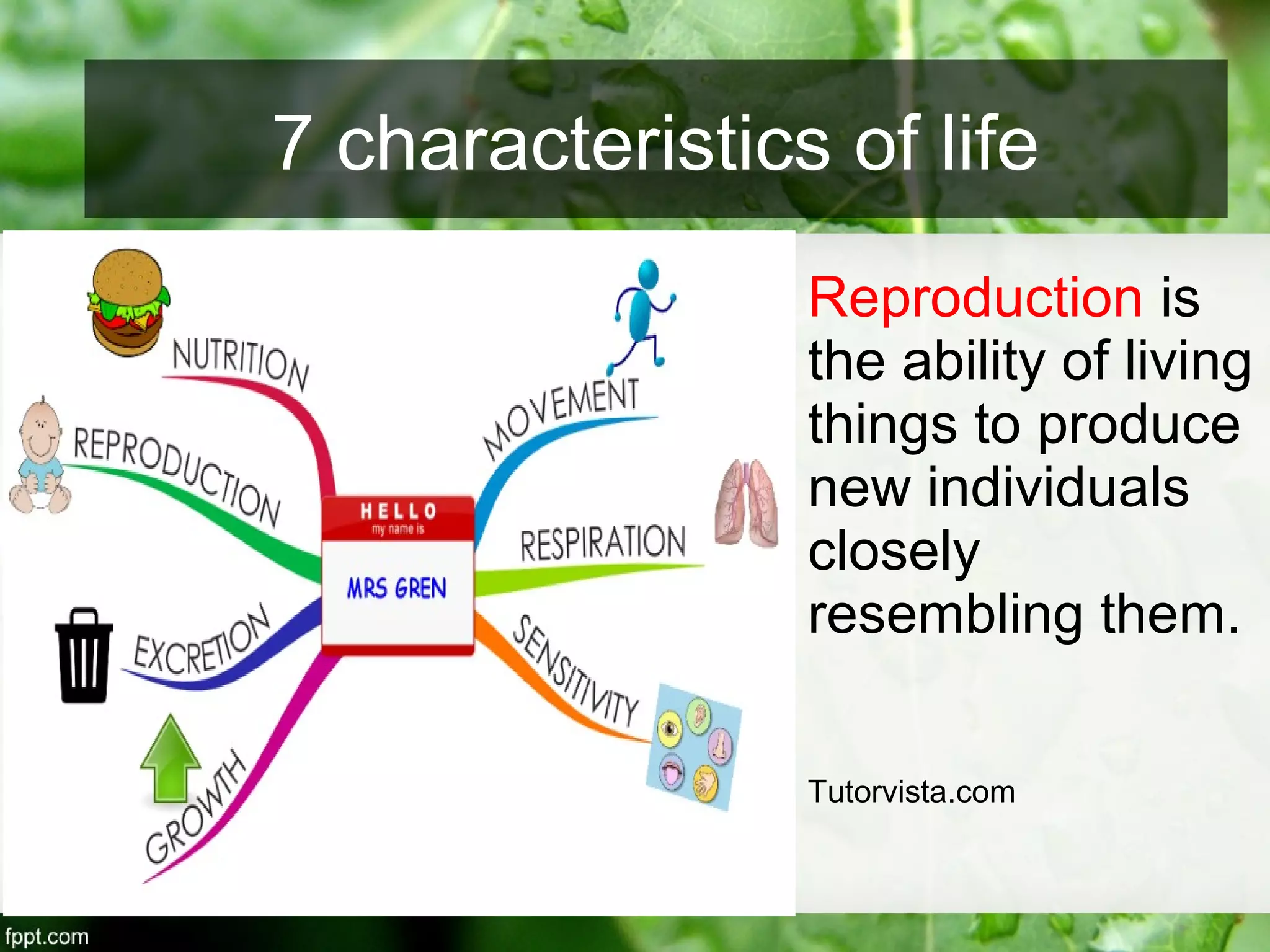
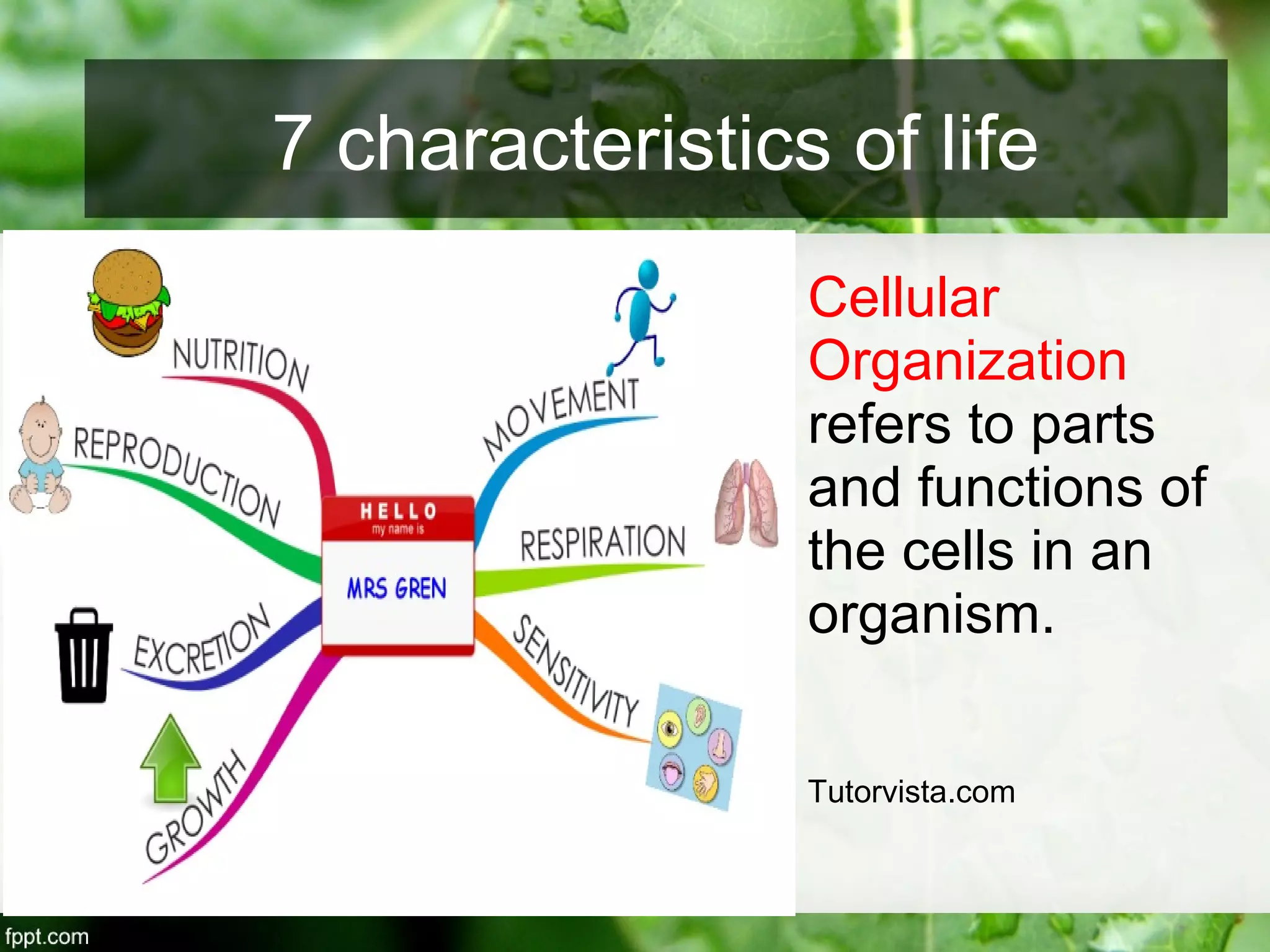
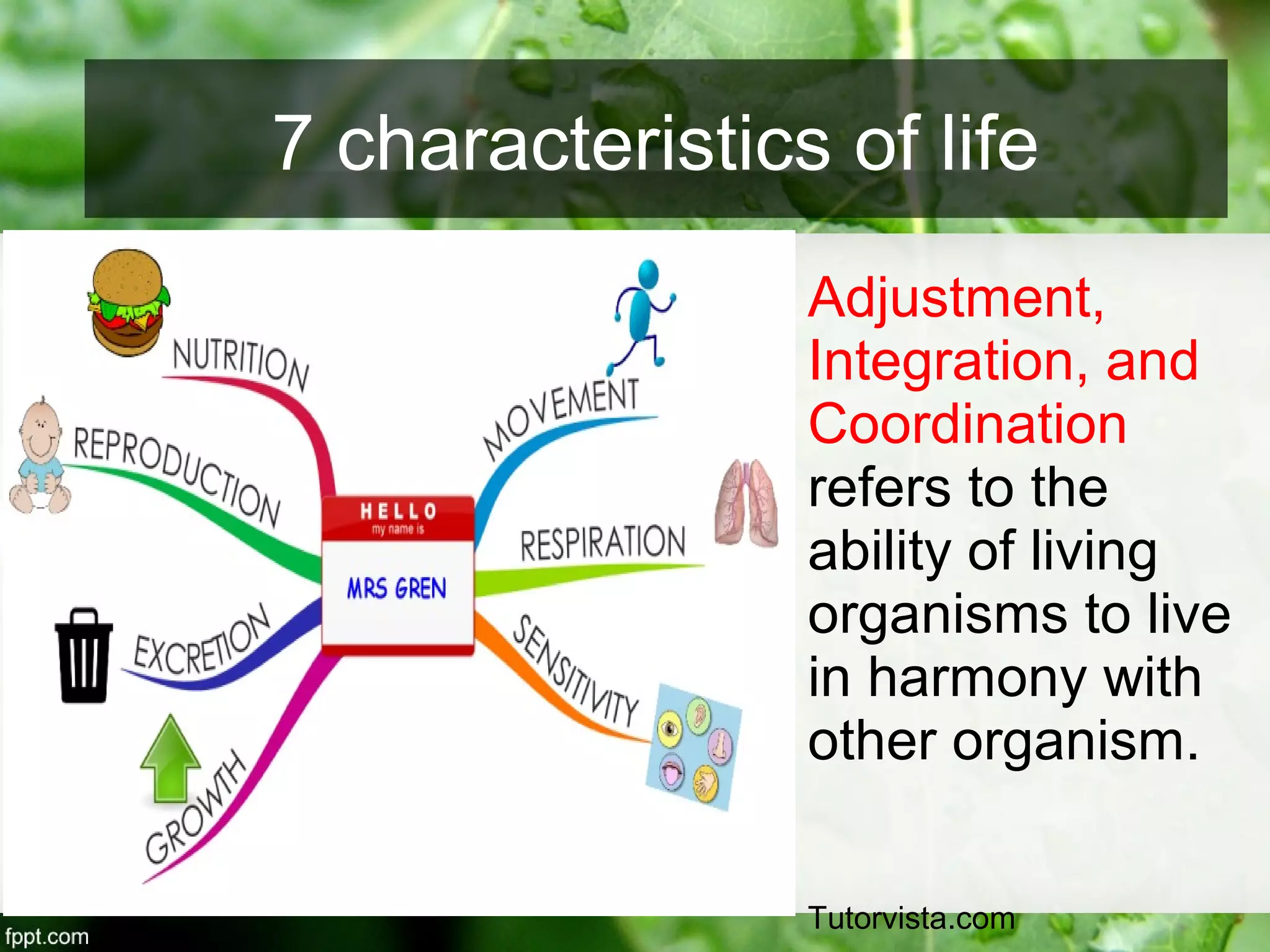
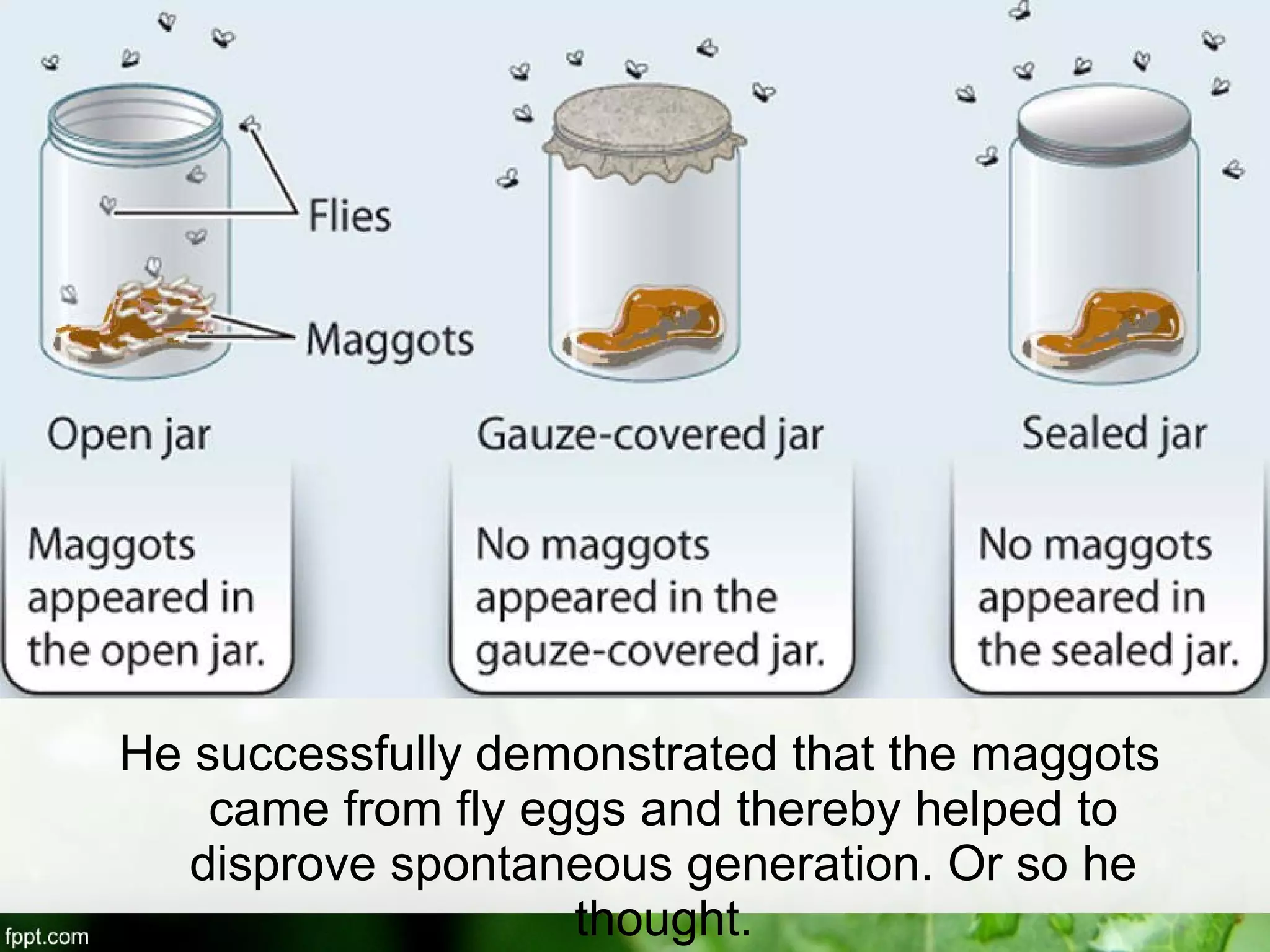
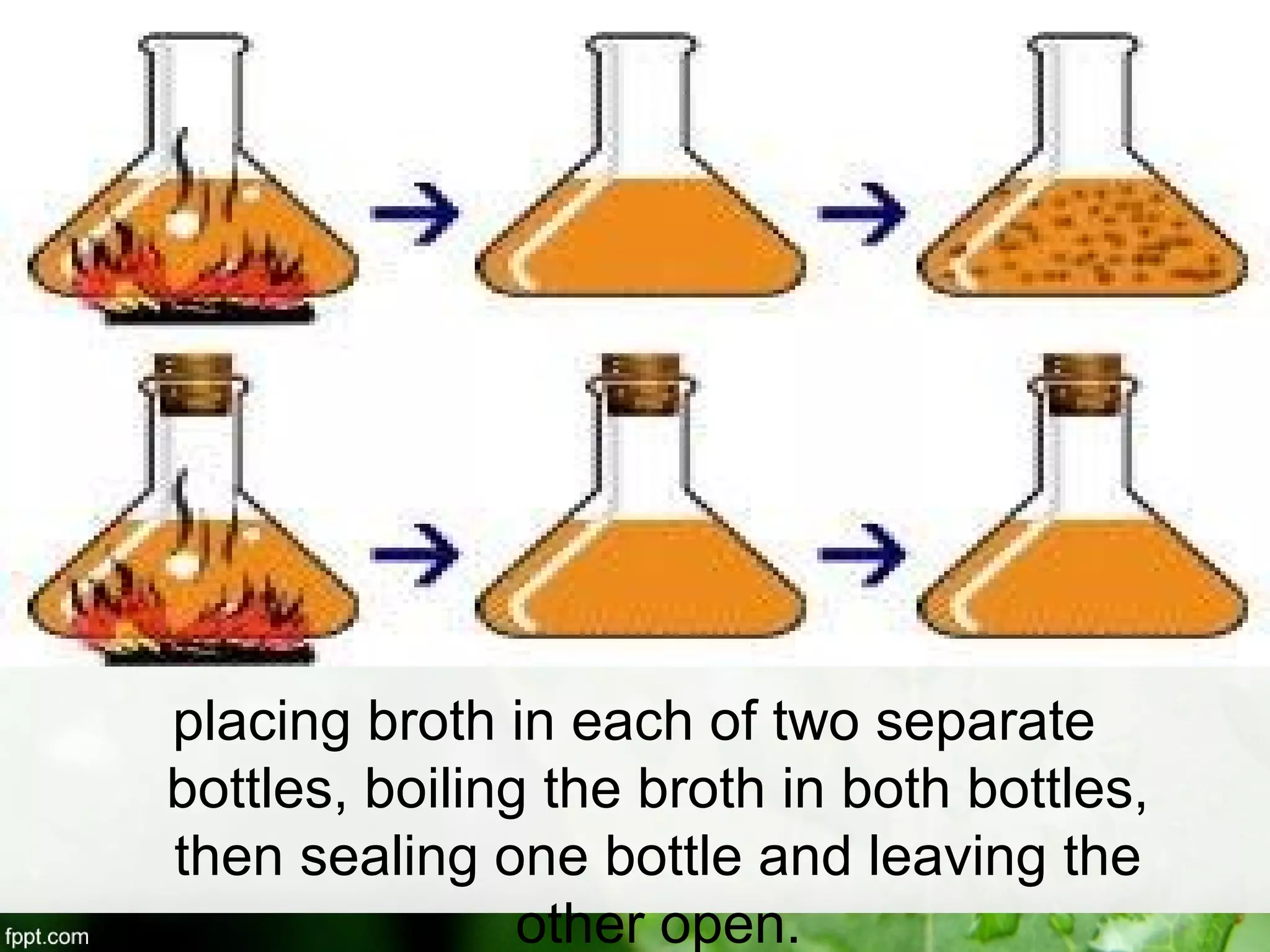
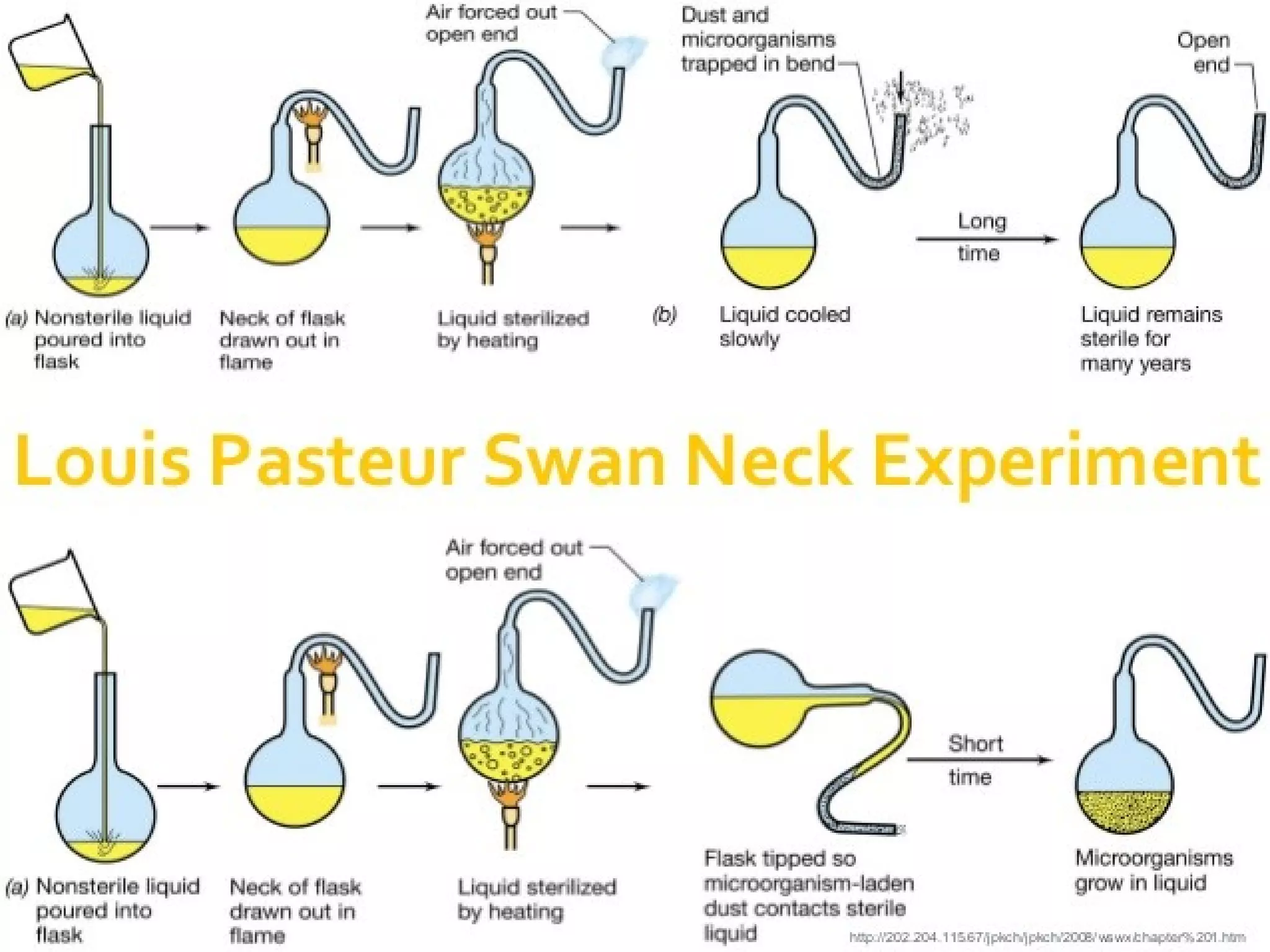
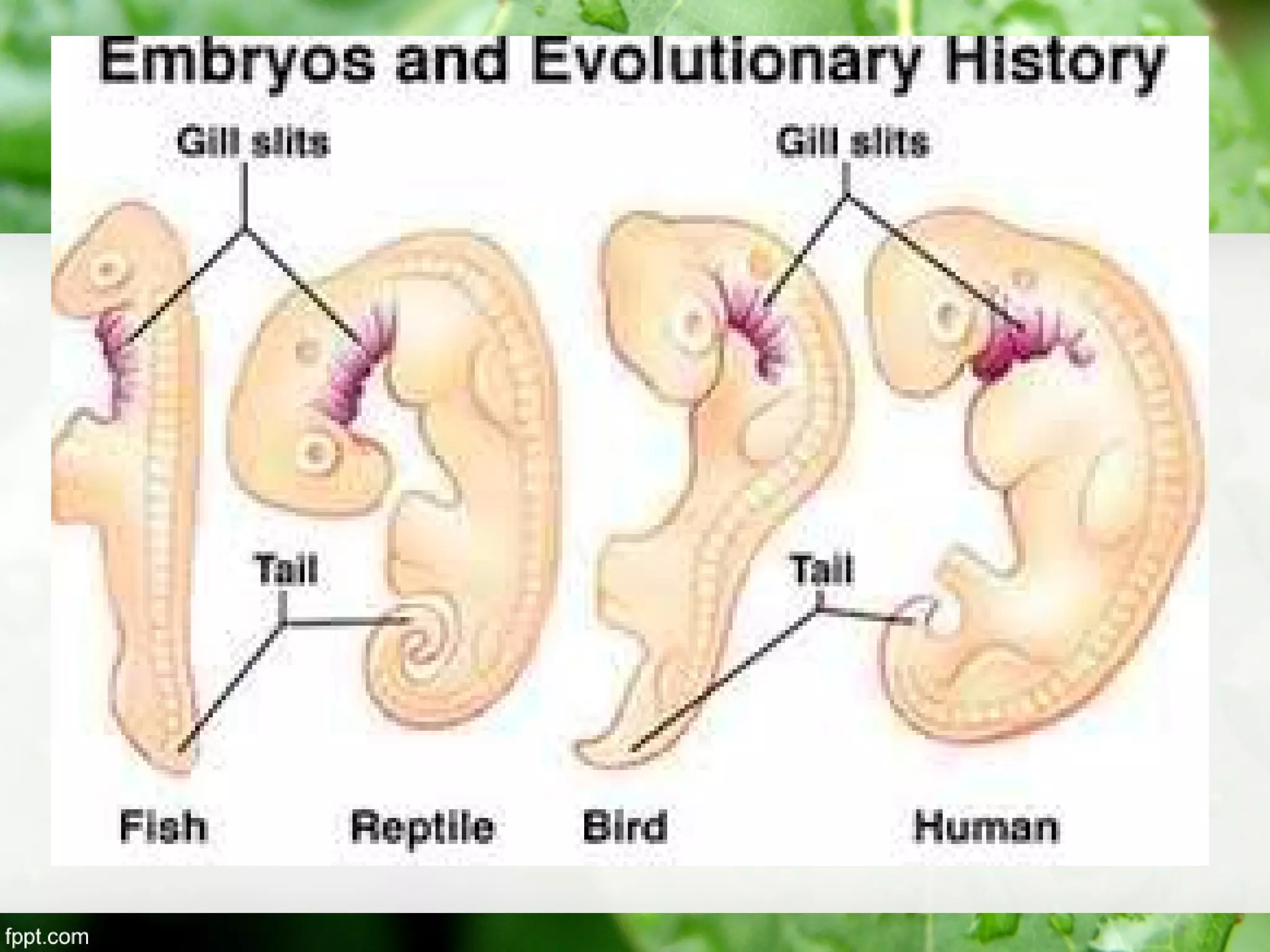
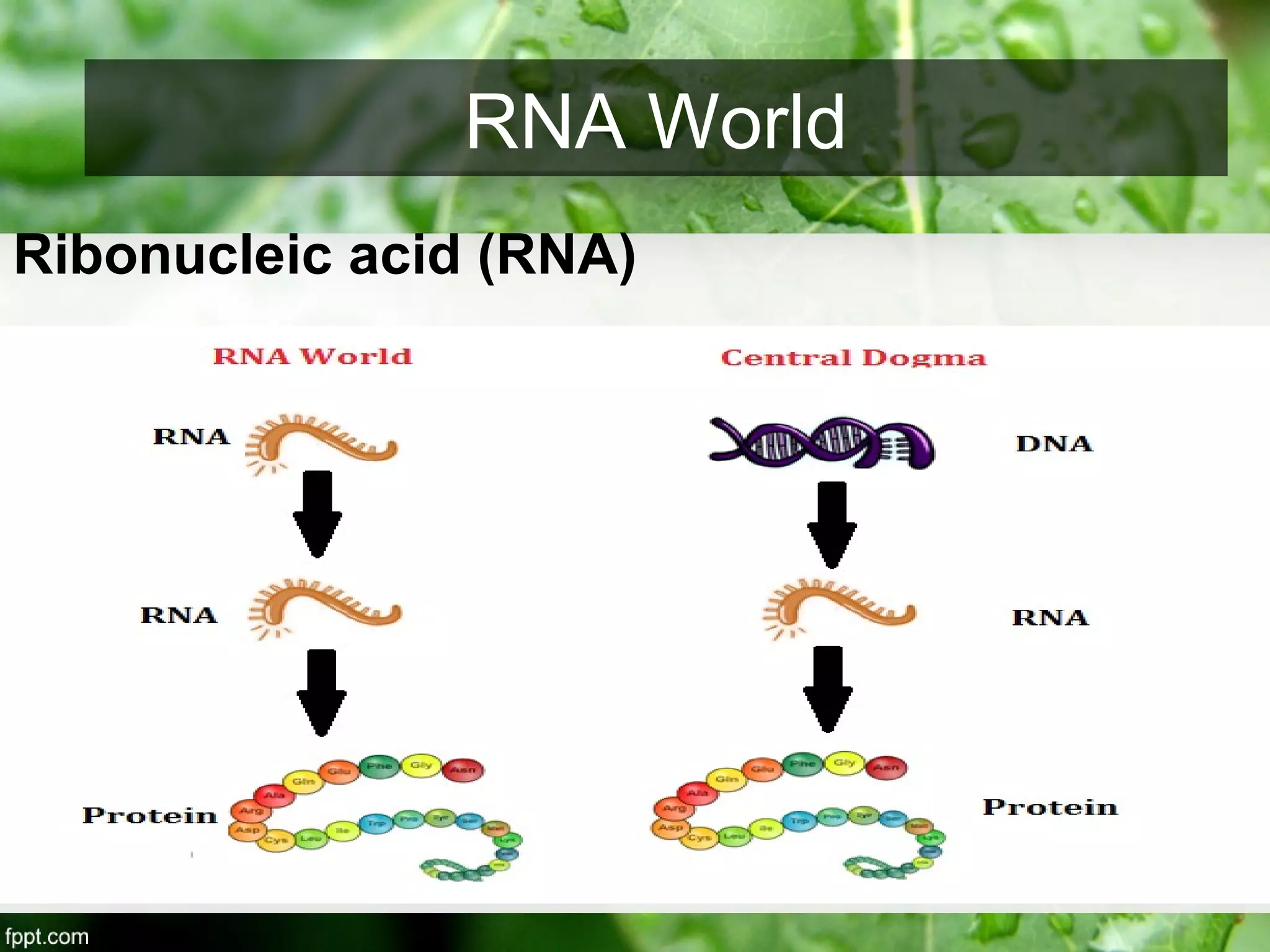
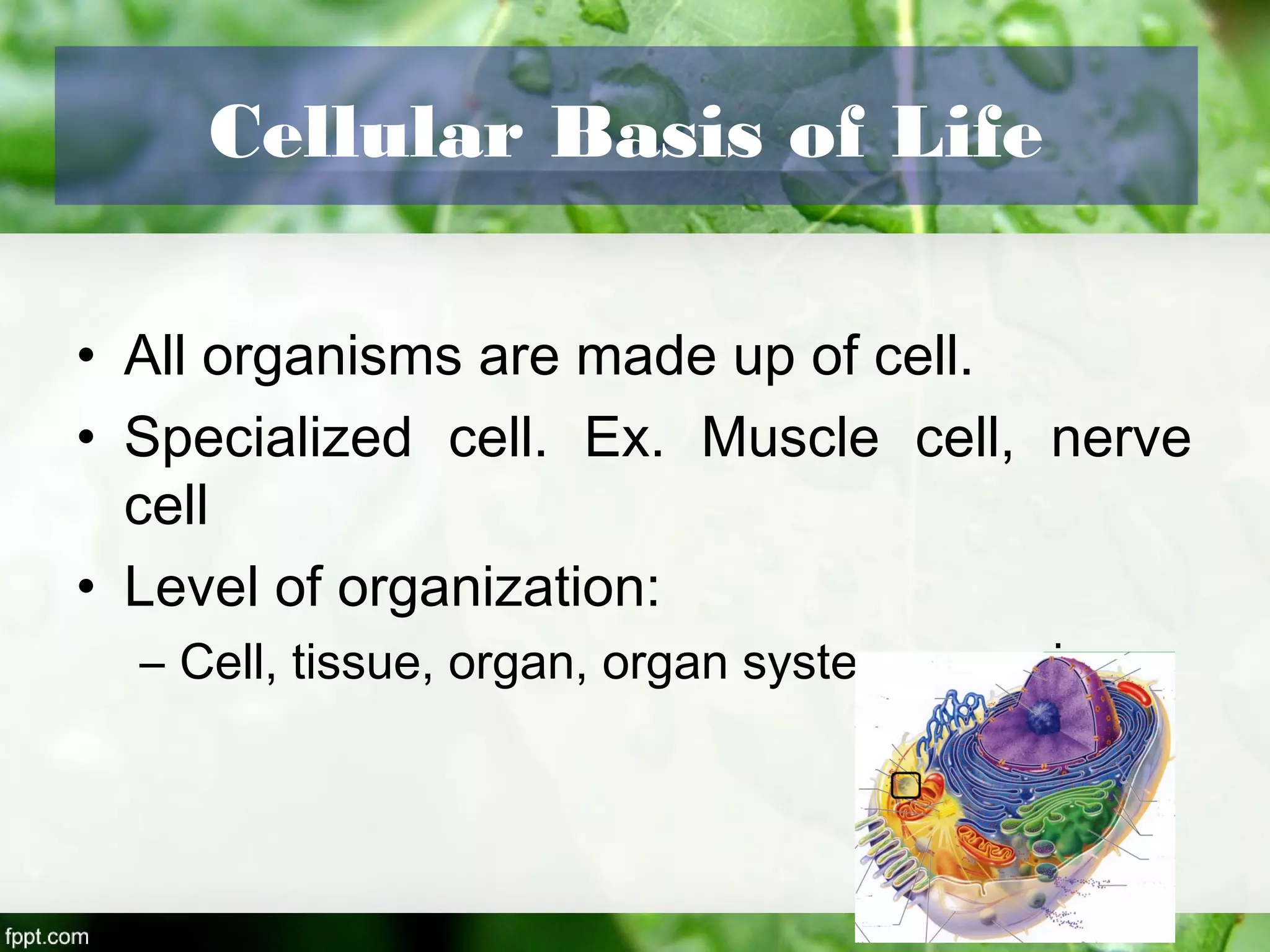
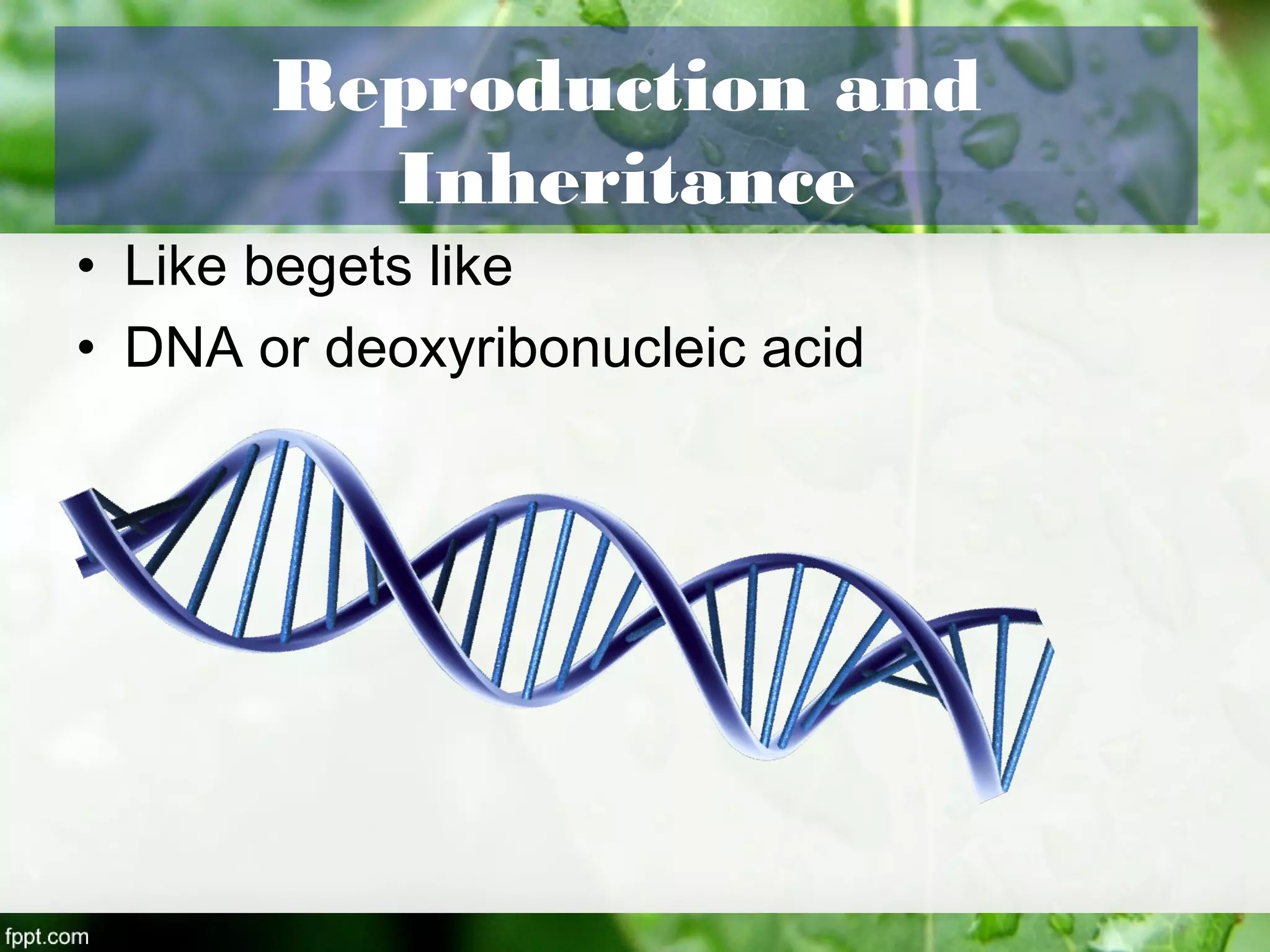
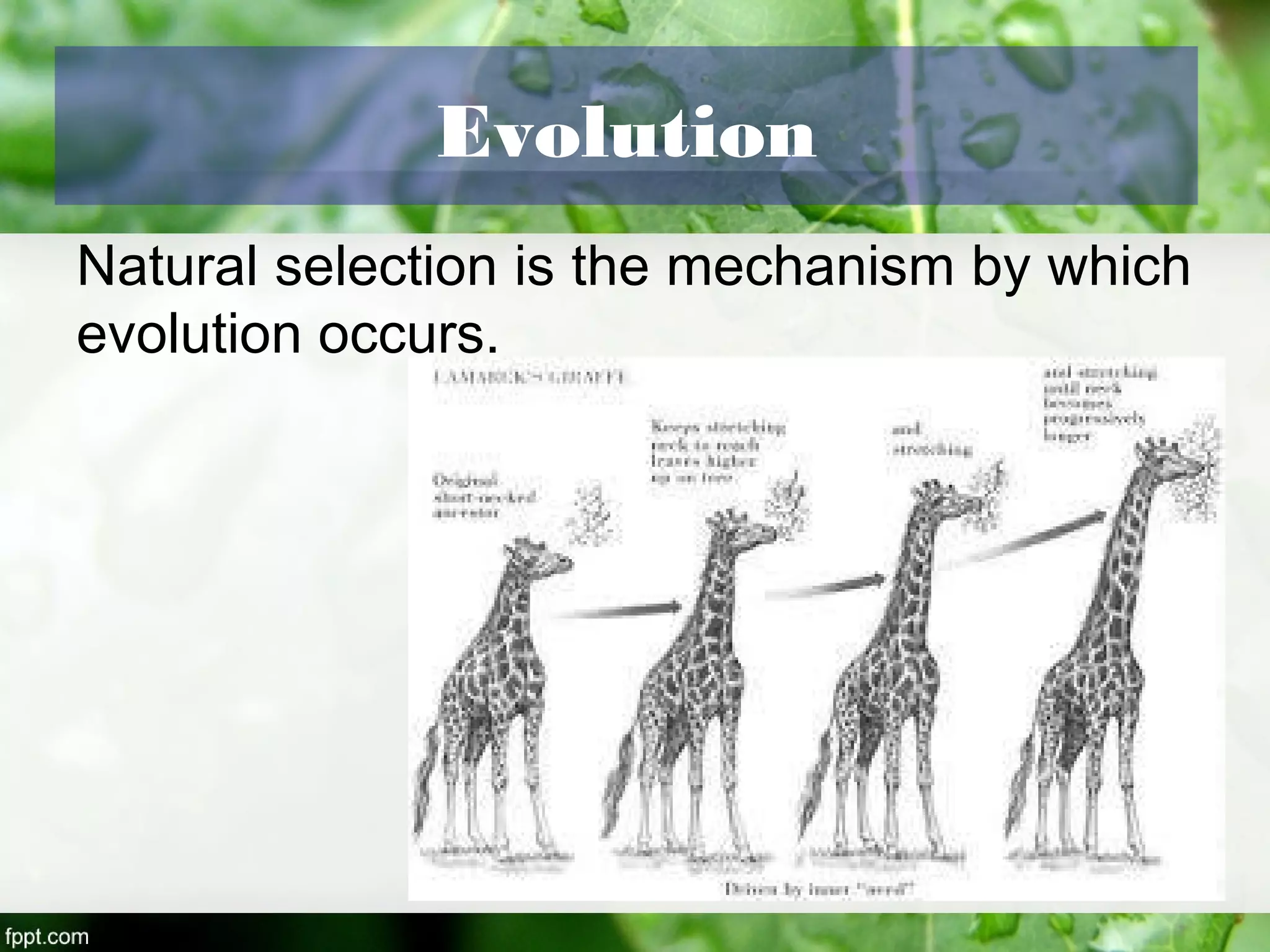
This document outlines an introduction to life science course, including learning competencies, topic outline, and content about the characteristics of life, cells, theories on the origin of life, and unifying themes in the study of life such as cellular organization, energy and life, homeostasis, adaptation, and evolution. The course will cover the historical development of the concept of life, the origin of the first life forms, and connections among living things through structure, function, and interactions with the environment and each other.