1. The document describes the key concepts of an ecosystem, including that an ecosystem is composed of all living and nonliving things that interact in a specific area.
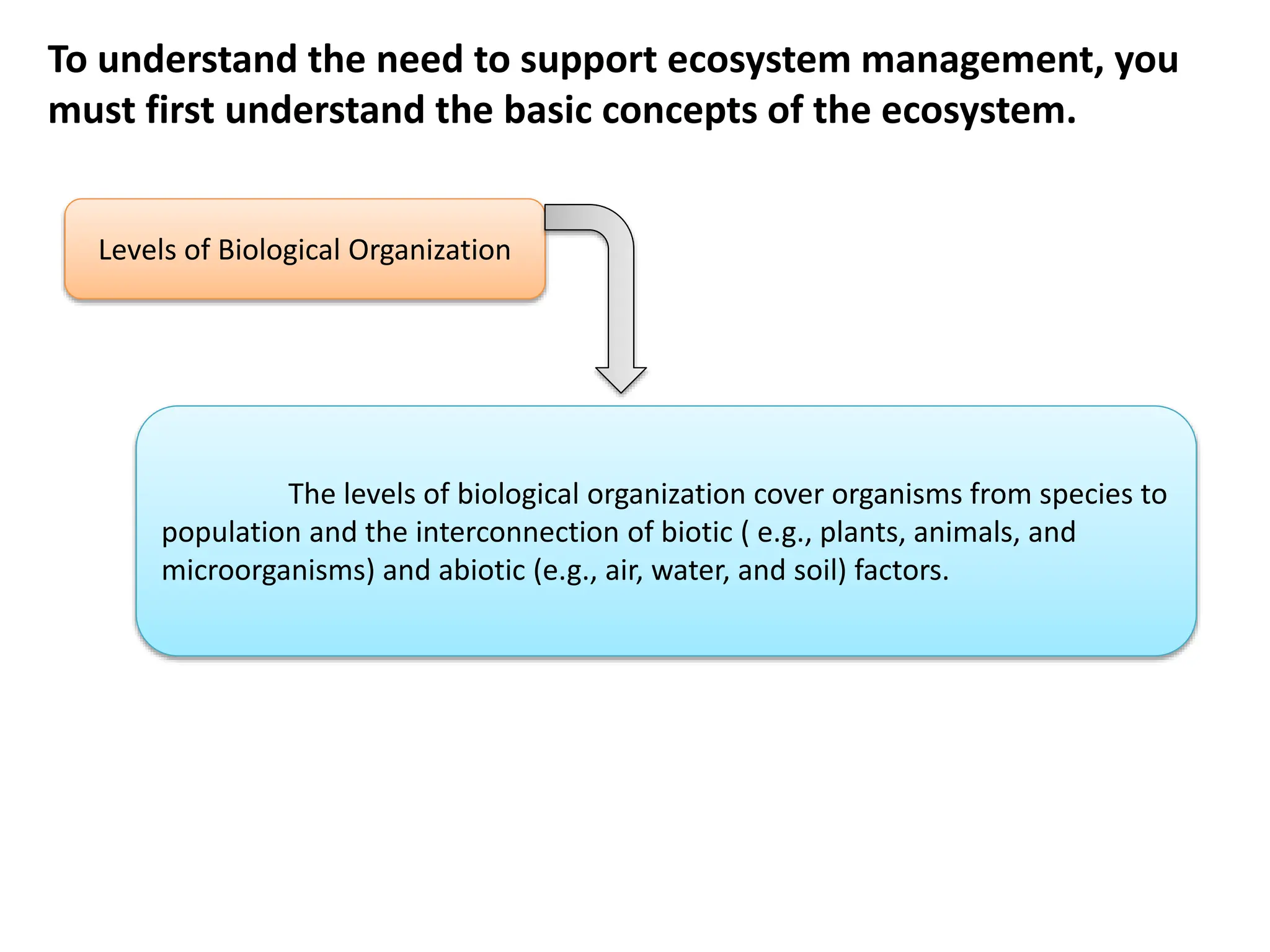
2. It explains the different levels of biological organization and how biotic and abiotic factors are interconnected within an ecosystem.
3. The document defines native, nonnative, and invasive species and their roles in an ecosystem. It also describes keystone species as those that help define an entire ecosystem such that it would be drastically different without that species.