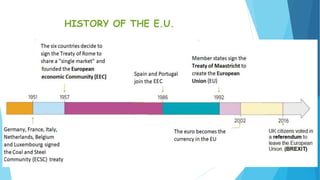
Spain is a democratic country based on its 1978 constitution. It has a separation of powers between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The legislative branch includes the Congress and Senate, which make laws. The executive branch is the national government including the prime minister and ministers. The judicial branch interprets laws through courts and tribunals. Spain is also divided into 17 autonomous communities and 2 autonomous cities, each with their own regional government. The European Union aims to promote peace, security, and economic integration between countries through institutions like the European Parliament, Council, and Commission.