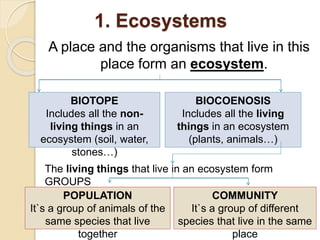
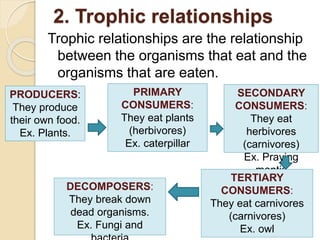
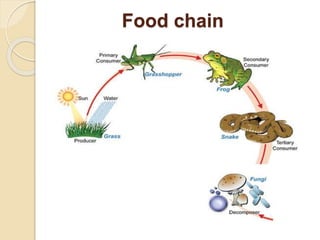
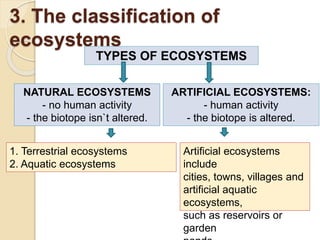
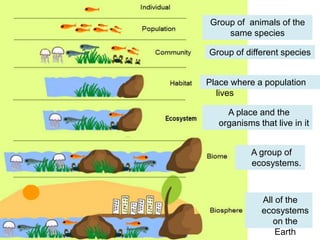
This document defines key terms and concepts related to ecosystems. It describes ecosystems as consisting of a biotope (non-living components) and biocoenosis (living components). Within ecosystems, organisms can be classified by their populations, communities, trophic relationships, and habitats. The document also categorizes different types of ecosystems as natural or artificial, and terrestrial or aquatic, providing examples. It defines related terms like biosphere, biome, and discusses natural and human-caused changes to ecosystems.