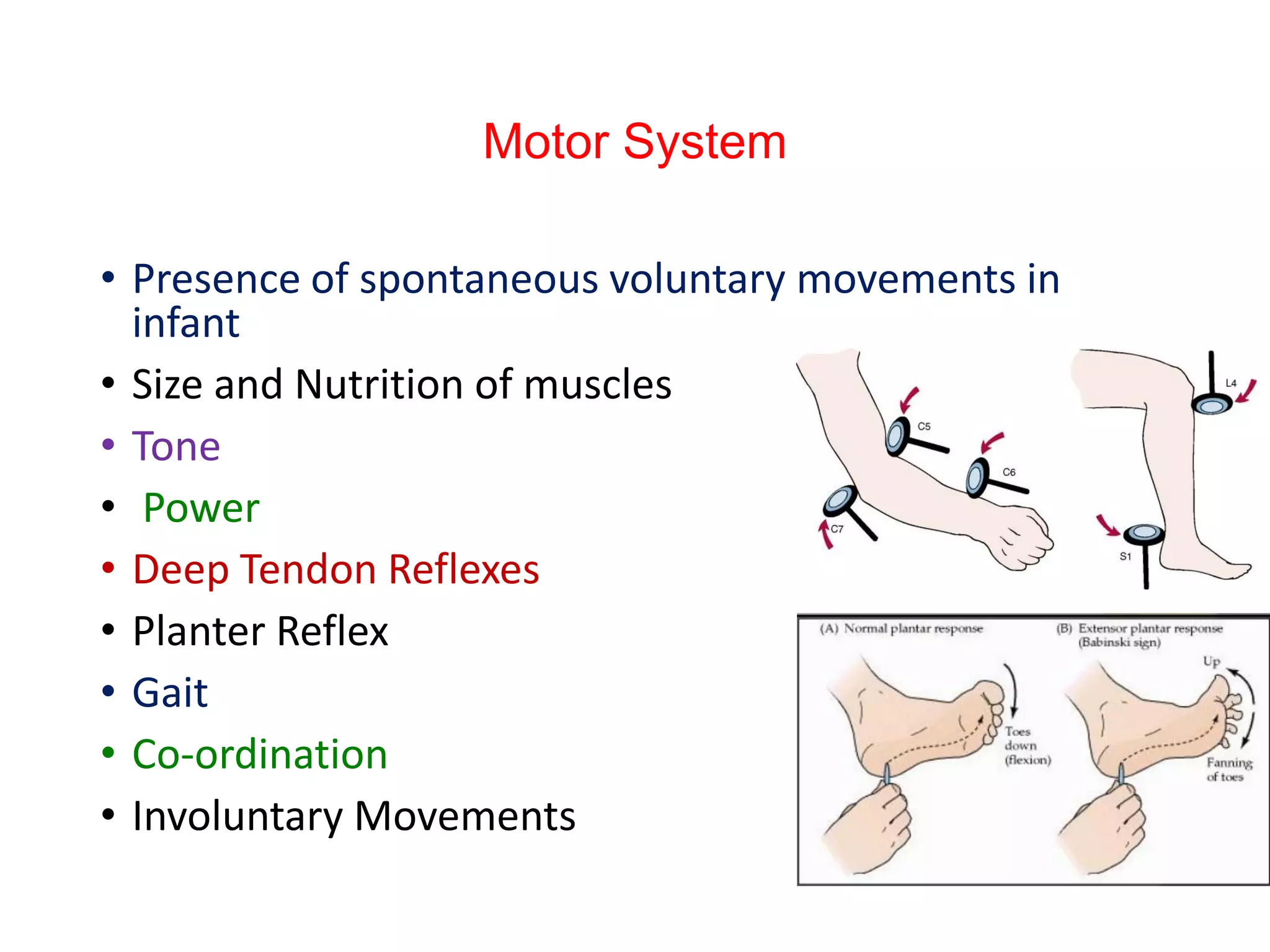
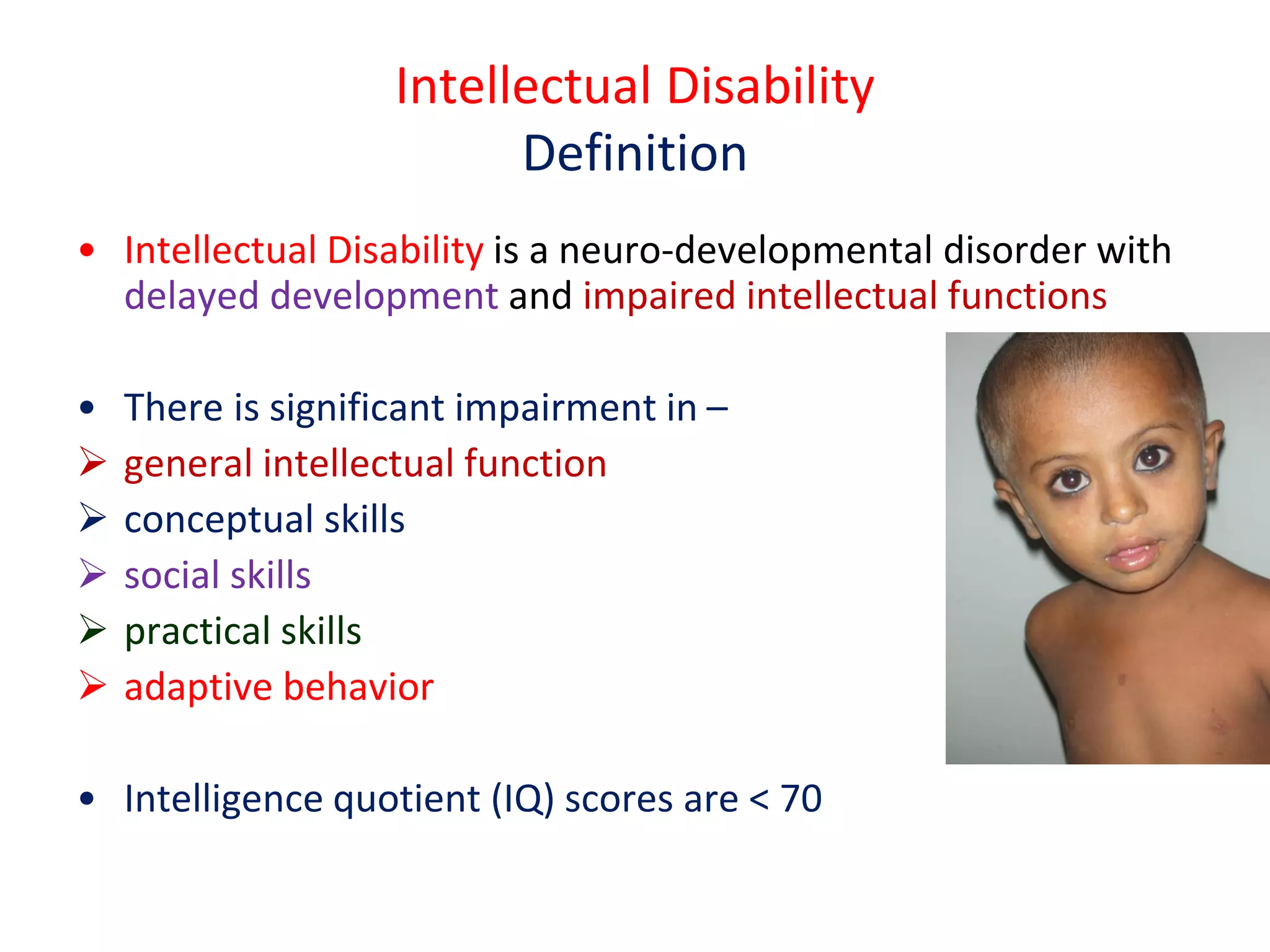
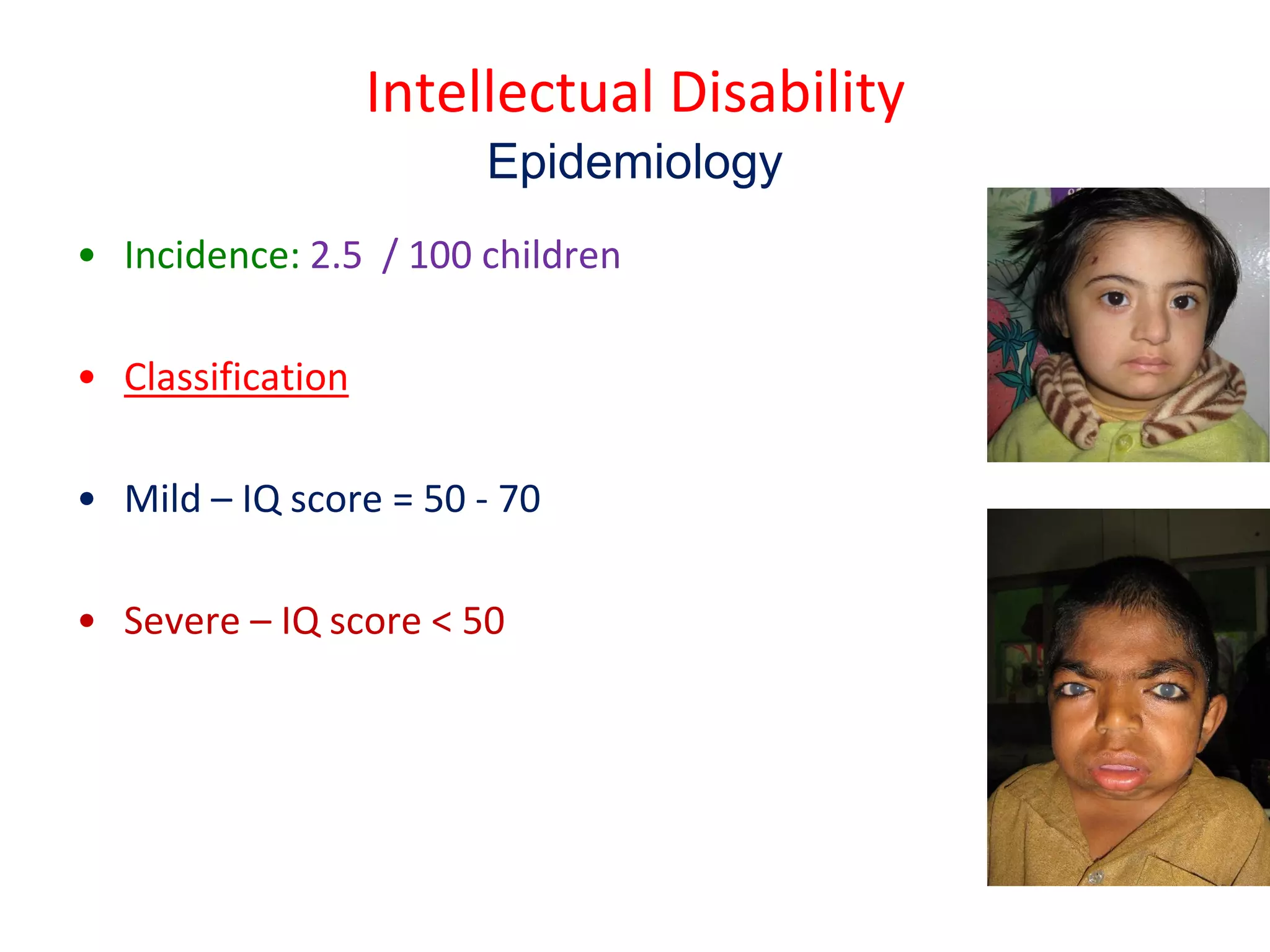
This document discusses intellectual disability in children. It defines intellectual disability as a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by delayed development and impaired intellectual functioning, with an IQ below 70. The causes include genetic conditions, brain malformations, perinatal or postnatal brain injuries, nutritional deficiencies, and child abuse or neglect. Intellectual disability has a prevalence of about 2.5 per 100 children. Diagnosis involves developmental and cognitive assessments, as well as medical tests to identify the underlying cause. Management focuses on family support, special education, behavior management, and medications. The goal is to help children with intellectual disabilities develop skills and participate fully in community life.