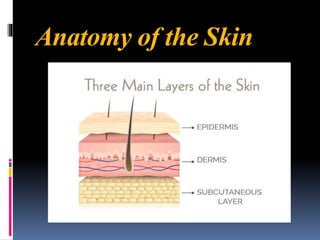
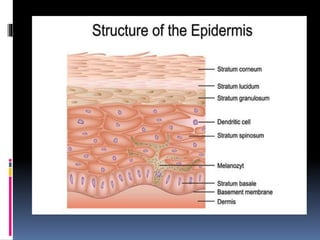
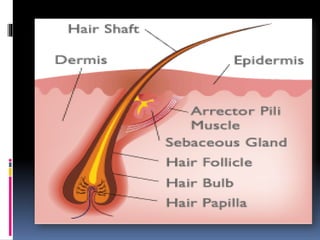
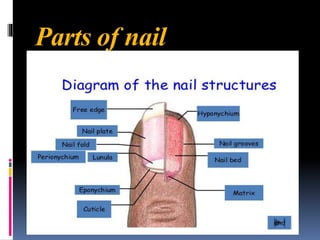
The integumentary system includes the skin, hair, nails, and glands. The skin is made up of three layers - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. The epidermis is made of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium and provides protection. Below this lies the dermis, made of dense connective tissue containing collagen, elastin, and blood vessels. The deepest layer is the hypodermis, made of adipose tissue. Skin functions include protection, sensation, synthesis, and temperature regulation. Accessory structures include hair, nails, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands.