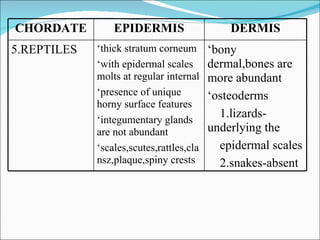
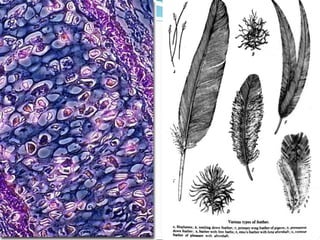
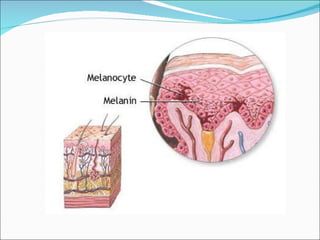
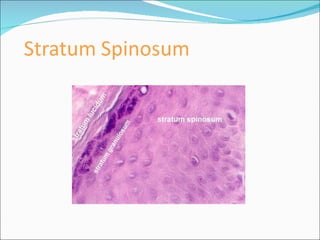
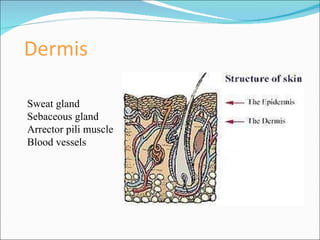
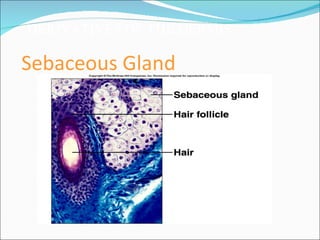
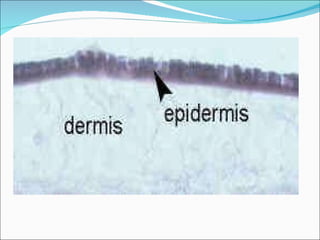
The document discusses the structure, composition, and functions of the integumentary system. It describes the three main layers of skin - the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. It details the differences between these layers and lists the skin's main functions like protection, temperature regulation, and sensory functions. The document also examines glands associated with the skin like sweat glands and sebaceous glands. It discusses skin derivatives like hair, nails, scales and compares skin structures across different chordates.









![3.OIL/ SEBACEOUS GLANDS secretes oilo/sebum;for lubrication/mare skin moist/shiny 4.UROPYGIAL GLAND [BIRDS] tail of uroryogium secretes oil,oiling the beark;shiny feathers/preening by beaks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theintegumentarysystem-100430042335-phpapp02/85/The-integumentary-system-11-320.jpg)
![5.SEROUS GLANDS [SNAKE] secretes poison/toxic alkaloids 6.CERUMINOUS GLANDS [MAN] -secretes cerumen 7.GLANDS OF ZELS -moits the eyelashes 8.MELBOMIAN GLANDS -moists the eyelids](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theintegumentarysystem-100430042335-phpapp02/85/The-integumentary-system-12-320.jpg)
![TYPES OF GLANDS ACCDG. TO MANNER OF SECRETION 1.MEROCRINE GLANDS [TRUE GLAND] release secretion thought memrbrane/cells remain intact. ex.unicellular integumentary glands sweat glands 2.HOLOCRINE GLANDS cells themselves constitute the secretion cells goes with secretion ex.sebaceous gland](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theintegumentarysystem-100430042335-phpapp02/85/The-integumentary-system-13-320.jpg)