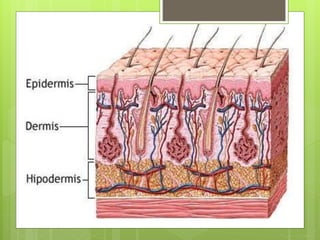
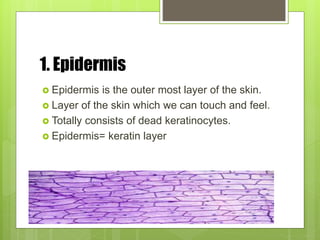
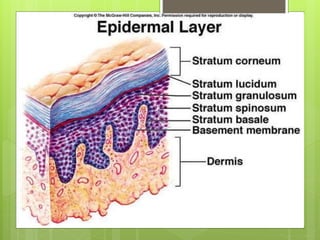
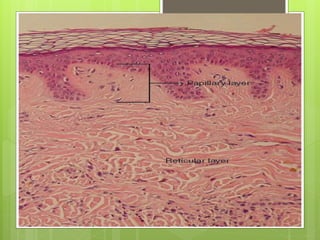
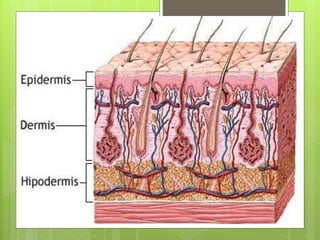
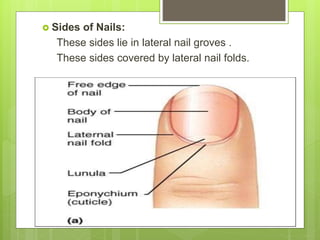
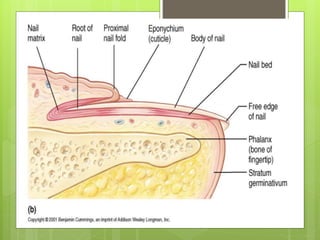
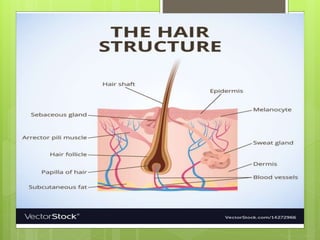
The integumentary system serves as a protective barrier between the body and the environment, consisting of skin, hair, nails, and exocrine glands. The skin has three layers: epidermis (with sub-layers based on keratin content), dermis (subdivided into papillary and reticular layers), and hypodermis. Nails and hair function in protection and sensory detection, while various glands in the skin secrete sweat and oils for regulation and protection.