Integumentary Histology | skin |Histology of Skin| Histology of Integument | by Ali Asadullah
- 1. The Integumentary System-2 Ali Asadullah
- 2. Learning outcomes Keratinocytes and non-keratinocytes Layers of Dermis Hypodermis Thick and thin skin Appendages
- 3. Tactile epithelioid cells, also known as Merkel cells, are located in the basal region of the epidermis in both hairless and hairy skin. Its nucleus is lobulated and irregular, and the cytoplasm is clear .
- 4. Tactile epithelioid cells are connected to adjacent keratinocytes by desmosomes. When associated with an axon, a tactile epithelioid cell–neurite complex or non-encapsulated tactile corpuscle is formed. Specialized areas of skin containing these complexes are known as tactile hair discs. Tactile epithelioid cells can also stimulate keratinocyte growth. In addition, tactile epithelioid cells can function as receptors for touch.
- 5. The dendritic cells located in the epidermis are called intraepidermal macrophages (Langerhans cells). Intraepidermal macrophages are most commonly found in the upper spinous layer of the epidermis. Reported in adult pigs, cats, dogs, human and rodents.
- 6. Langerhans cells Also identified in the stratified squamous epithelium of the upper digestive tract, female genital tract and sheep rumen.
- 7. Langerhan cell (cont.. At the ultrastructural level, intraepidermal macrophages have a depressed nucleus and the cytoplasm contains typical organelles. A unique feature of this cell is distinctive rod- or racket-shaped granules in the cytoplasm that are known as intraepidermal macrophage (Birbeck) granules. Langerhans cells are capable of presenting antigen to lymphocytes .
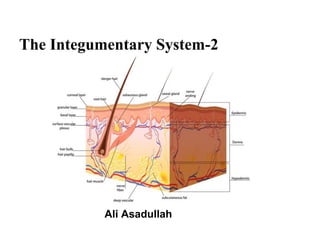
- 9. Dermis Strong, flexible connective tissue Cells: fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, WBCs Fiber types: collagen, elastic, reticular Rich supply of nerves and vessels Critical role in temperature regulation (the vessels) Two layers (see next slides) Papillary – areolar connective tissue; includes dermal papillae Reticular – “reticulum” (network) of collagen and reticular fibers
- 10. Layers of the dermis Papillary layer Reticular layer
- 12. thin skin thick skin Thin (hairy) skin vs Thick (hairless) skin
- 13. Epidermis and dermis of (a) thick skin and (b) thin skin (which one makes the difference?)
- 14. Hypodermis “Hypodermis” (Gk) = below the skin “Subcutaneous” (Latin) = below the skin Also called “superficial fascia” “fascia” (Latin) =band; in anatomy: sheet of connective tissue Fatty tissue which stores fat and anchors skin (areolar tissue and adipose cells)
- 15. Skin appendages Derived from epidermis but extend into dermis Include Hair and hair follicles Sebaceous (oil) glands Sweat (sudoriferous) glands Nails
- 16. Nails Of hard keratin Corresponds to hooves and claws Grows from nail matrix
- 17. Hair and hair follicles: complex Derived from epidermis Everywhere but palms, soles, nipples, parts of genitalia *“arrector pili” is smooth muscle * Hair papilla is connective tissue________________ Hair bulb: epithelial cells surrounding papilla
- 18. Functions of hair Warmth – less in man than other mammals Sense light touch of the skin Protection - scalp Parts Root imbedded in skin Shaft projecting above skin surface Make up of hair – hard keratin Three concentric layers Medulla (core) Cortex (surrounds medulla) Cuticle (single layers, overlapping)
- 19. Hair color Amount of melanin for black or brown; distinct form of melanin for red White: decreased melanin and increase air bubbles in the medulla
- 20. Epidermal Appendages Hair follicle Apocrine Sweat gland Eccrine Sweat gland Sebaceous gland Arrector pili muscle *also nails and mammary glands
- 21. Hair Follicles
- 23. Hair Follicles
- 24. Sebaceous (oil) glands Entire body except palms and soles Produce sebum by holocrine secretion Oils and lubricates
- 25. Epidermal Appendages Hair follicle Apocrine Sweat gland Eccrine Sweat gland Sebaceous gland Arrector pili muscle *also nails and mammary glands
- 26. Sebaceous glands sebocytes secrete sebum: triglycerides, fatty acids, waxes
- 27. Sebaceous gland
- 28. Sweat glands Entire skin surface except nipples and part of external genitalia Prevent overheating Produced in response to stress as well as heat
- 29. Types of sweat glands Eccrine or merocrine Most numerous True sweat: 99% water, some salts, traces of waste Open through pores Apocrine Axillary, anal and genital areas only Ducts open into hair follicles The organic molecules in it decompose with time - odor Modified apocrine glands Ceruminous – secrete earwax Mammary – secrete milk
- 30. Epidermal Appendages Hair follicle Apocrine Sweat gland Eccrine Sweat gland Sebaceous gland Arrector pili muscle *also nails and mammary glands
- 31. Apocrine Sweat Glands secrete a mixture of carbs, lipids, protein and ammonia
- 32. Apocrine Sweat Glands simple cuboidal or columnar secretory cells and myoepithelial cells
- 33. Epidermal Appendages Hair follicle Apocrine Sweat gland Eccrine Sweat gland Sebaceous gland Arrector pili muscle *also nails and mammary glands
- 36. The mammary gland is a compound- tubuloalveolar gland. The secretory units form lobules separated by connective-tissue septa. Mammary Gland
- 37. Alveoli Secretory alveoli of the mammary gland are spherical to ovoid in shape with a large lumen. Adjacent alveoli may fuse partially. The lumen is partially collapsed and irregular in outline. Clusters of alveoli form lobules within the gland.
- 39. Alveoli The epithelium of the alveoli varies markedly in height during various stages of secretory activity. During active secretion, the basal portion of the columnar epithelial cells contains a well-developed rough endoplasmic reticulum. At the end of the secretory cycle, the epithelial cells are low cuboidal in shape.
- 40. Interstitium The interstitial tissue of the mammary gland provides important structural support for the secretory units and contains the blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves. Each secretory unit is surrounded by loose connective tissue with an extensive plexus of blood and lymph capillaries. The interlobular connective tissue is thick and contains the interlobular ducts and larger blood and lymph vessels.
- 41. Ducts The duct system begins with an intralobular duct which drains into an interlobular duct. The interlobular duct, in turn, drains into a lactiferous duct, which is the primary excretory duct for a lobe. The intralobular duct epithelium is simple cuboidal. Spindle-shaped myoepithelial cells may be associated with these ducts.
- 43. Teat The teat, or nipple, contains the terminal part of the duct system. The lactiferous sinus is continuous with the teat sinus (teat cistern, cavity of the teat), which is lined by stratified cuboidal epithelium. The teat sinus empties into one or more papillary ducts (teat canal, streak canal) leading to the external surface of the teat. A single papillary duct is present in ruminants while multiple papillary ducts open separately onto the teat surface of other species. Horses have 2 papillary ducts, pigs have 2 to 3, cats have 4 to 7, and dogs have 7 to 16. The papillary duct is lined with stratified squamous epithelium.
- 44. Teat The skin of the teat in cows and sows is composed of a thick, keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and dermis without hair follicles and sweat or sebaceous glands. However, in some domestic species, such as sheep and goats, the teat may contain fine hairs and sweat and sebaceous glands.
- 45. Hypodermis
- 47. Major Points The dermis is a dense irregular connective tissue with dermal papillae that contain capillaries Many types of nerve endings are found in different parts of the skin Epidermal appendages are derived from the epidermis and include hair follicles, apocrine sweat glands, eccrine sweat glands, and sebaceous glands The hypodermis is a fatty connective tissue layer that surrounds some epidermal appendages
