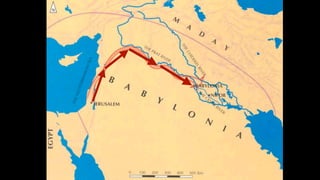
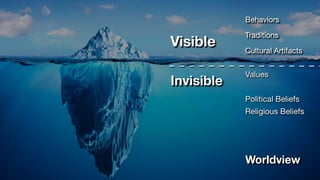
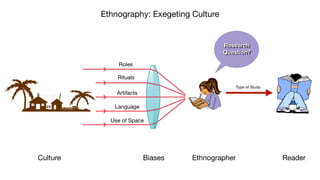
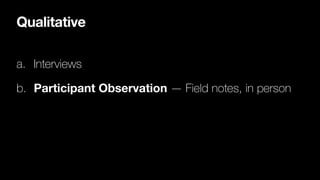
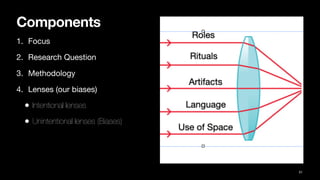
The document discusses the discipline of ethnography, which involves analyzing and describing a culture through immersive fieldwork research methods like interviews and participant observation. It provides context on how Daniel was trained in intercultural competence when he and other Israelites were taken to Babylon and given Babylonian names and education to serve in the king's palace. The purpose was to indoctrinate them in the language and literature of the Chaldeans to serve the king.