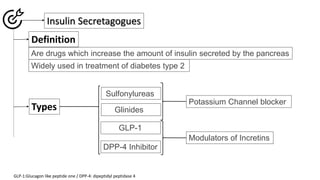
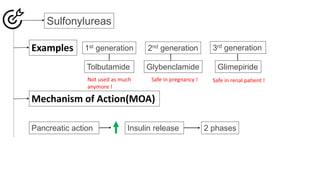
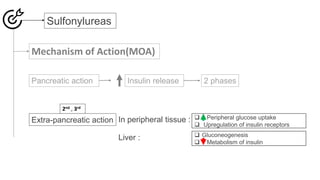
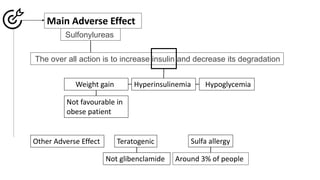
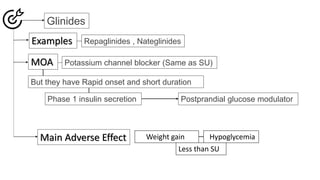
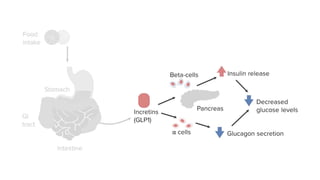
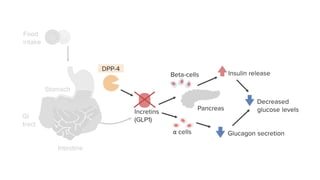
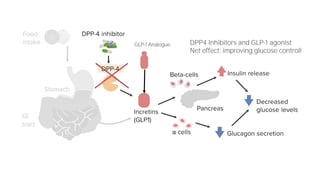
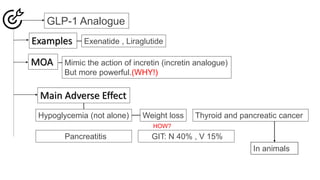
Insulin secretagogues are medications that enhance insulin secretion from the pancreas and are primarily used in treating Type 2 diabetes. There are several classes, including sulfonylureas, glinides, GLP-1 analogues, and DPP-4 inhibitors, each with unique mechanisms of action and associated adverse effects. Key concerns with these drugs include weight gain, hypoglycemia, and various other risks, including potential cancer links and teratogenic effects.