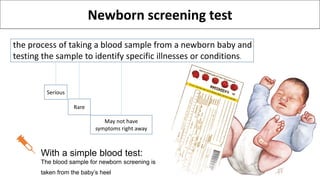
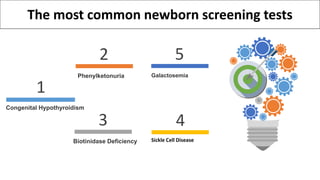
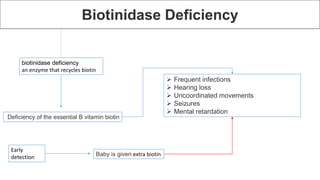
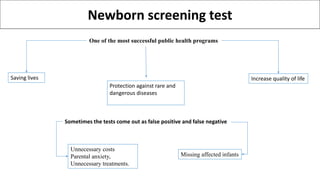
Newborn screening is a test performed on infants 24 to 48 hours after birth to identify serious genetic, metabolic, and endocrine disorders through a blood sample taken from the heel. Common disorders screened include congenital hypothyroidism, phenylketonuria, biotinidase deficiency, galactosemia, and sickle cell disease, with early detection allowing for effective treatments to prevent severe consequences. Although the program has saved many lives, there are challenges such as false positives and negatives that can lead to unnecessary treatments and parental anxiety.