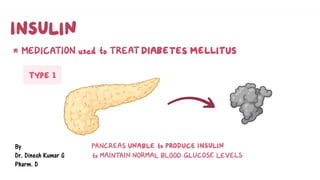
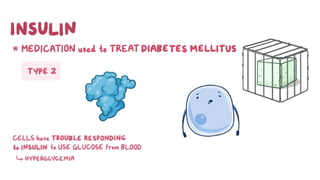
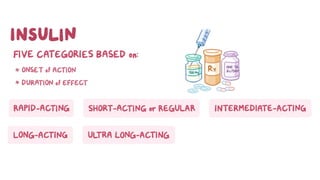
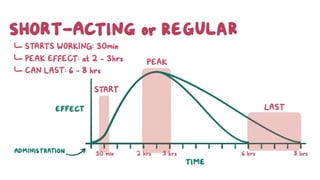
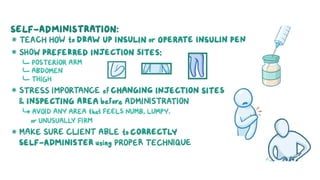
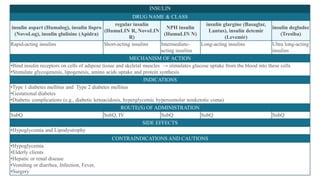
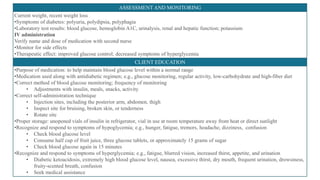
This document provides information about different types of insulin, including their classification, mechanisms of action, indications, routes of administration, side effects, contraindications, assessment and monitoring considerations, and important points for patient education. It discusses rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulins. The key points are that insulin works by stimulating glucose uptake and use, is used to treat diabetes and its complications, is administered via subcutaneous injection or intravenous routes, and careful monitoring and education of patients is important to safely manage insulin therapy and avoid hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.