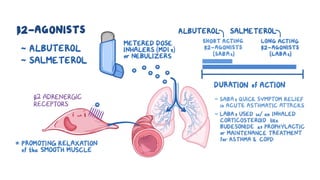
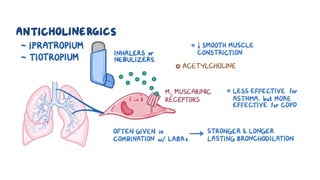
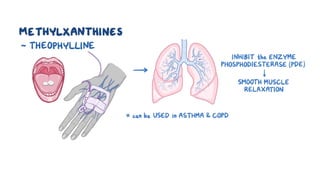
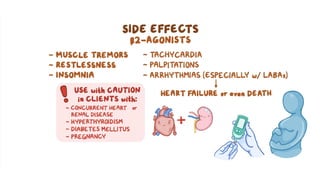
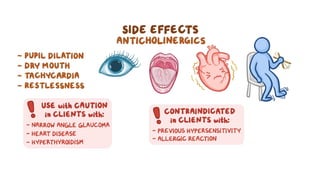
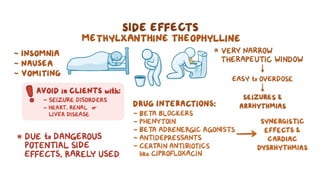
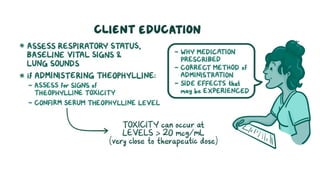
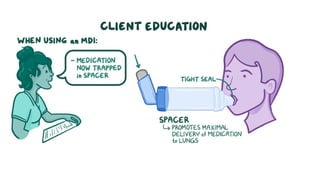
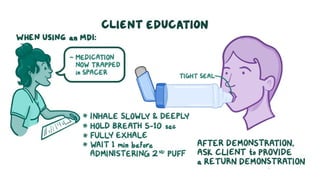
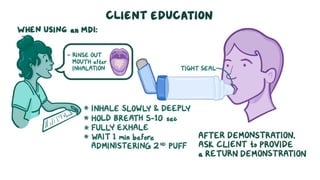
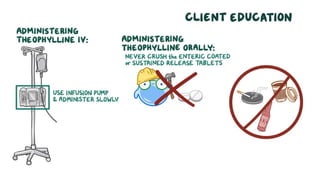
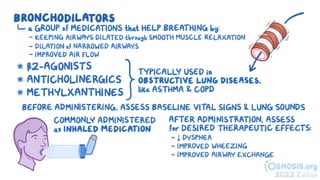
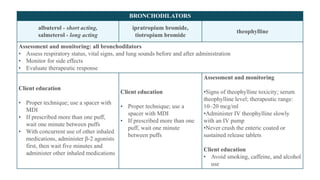
The document discusses bronchodilators, including short-acting (albuterol) and long-acting (salmeterol) drugs, their mechanisms, uses, side effects, contraindications, and necessary assessments for patients. It highlights the importance of proper administration techniques and monitoring for potential side effects or drug interactions. Patient education also emphasizes avoiding smoking and certain substances to ensure effective treatment.