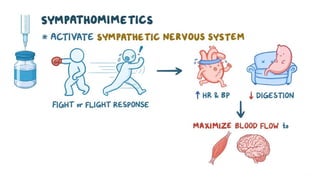
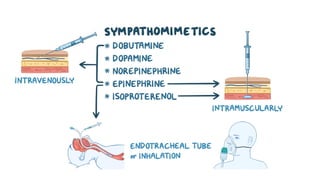
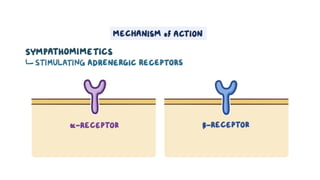
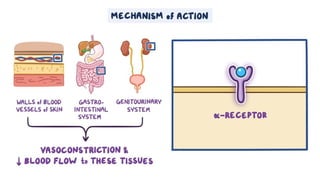
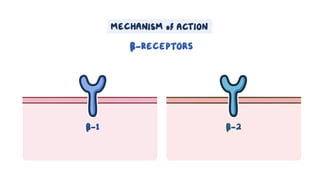
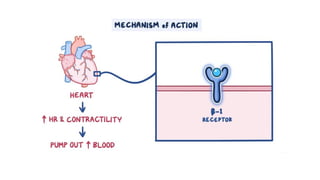
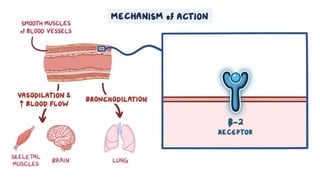
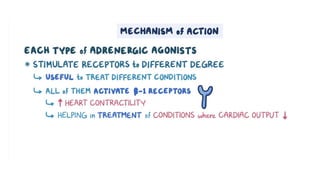
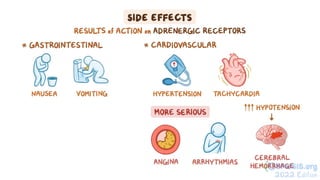
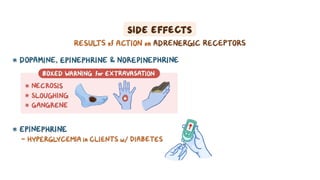
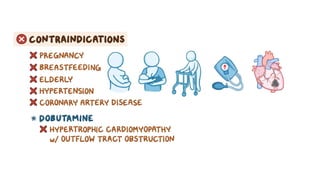
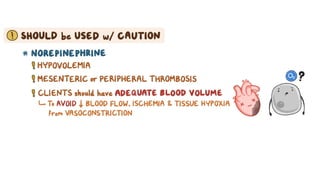
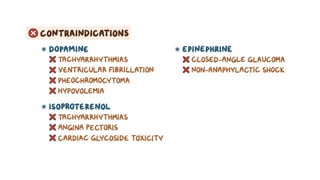
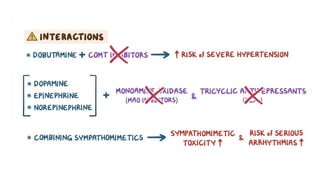
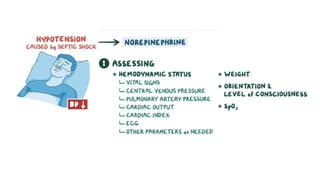
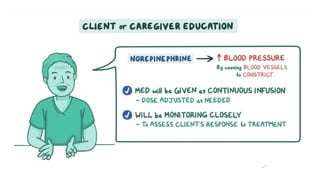
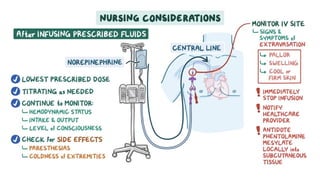
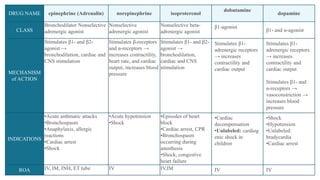
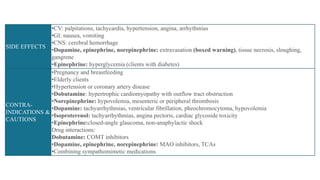
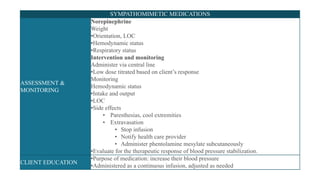
The document provides an overview of various adrenergic medications, including epinephrine, norepinephrine, isoproterenol, dobutamine, and dopamine, detailing their classifications, mechanisms of action, indications, routes of administration, and side effects. It outlines contraindications, cautions, and drug interactions for each medication and emphasizes the importance of proper assessment and monitoring during their use. Client education focuses on the purpose of these medications, particularly in managing blood pressure through continuous infusion.