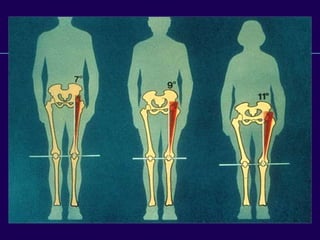
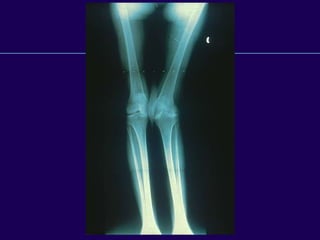
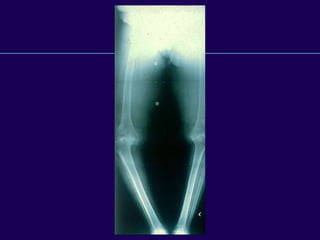
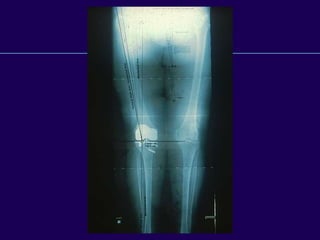
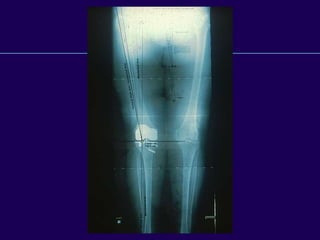
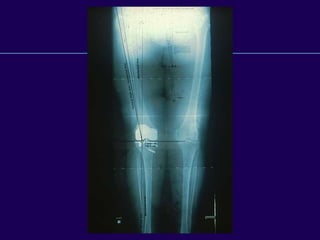
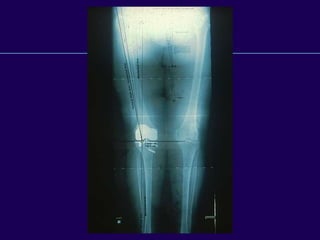
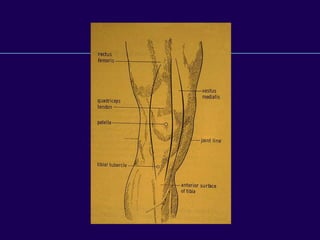
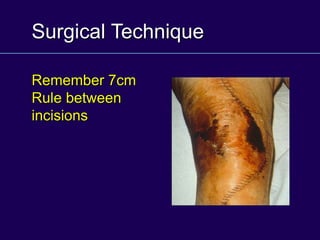
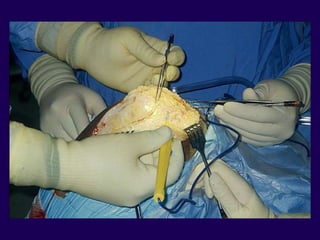
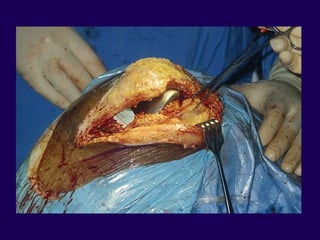
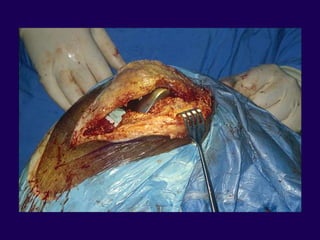
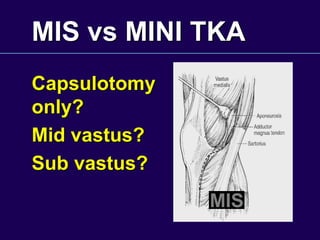
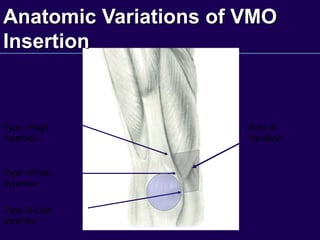
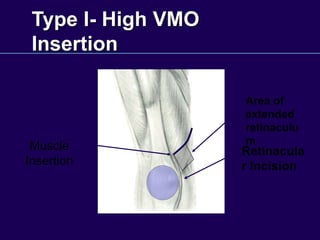
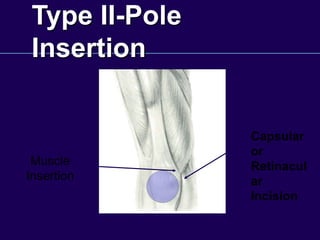
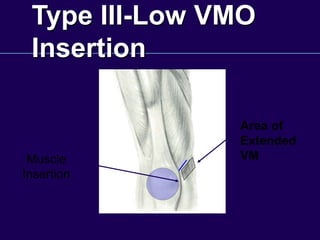
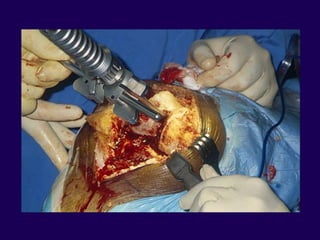
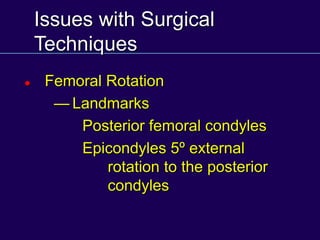
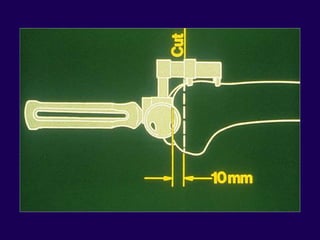
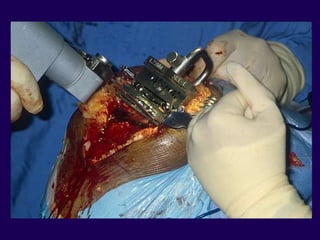
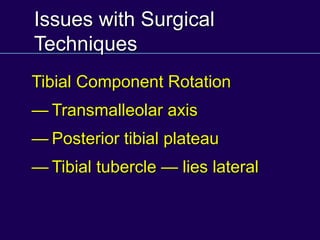
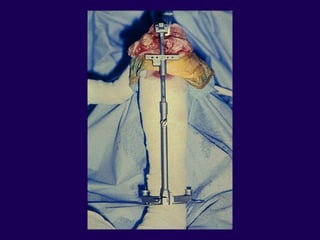
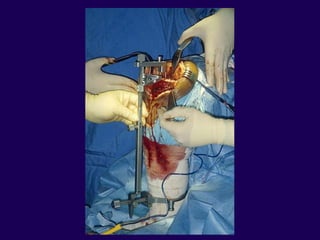
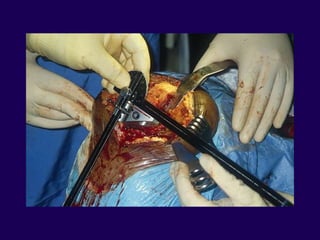
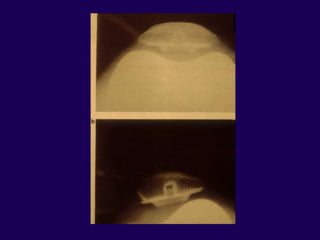
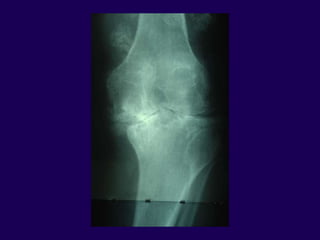
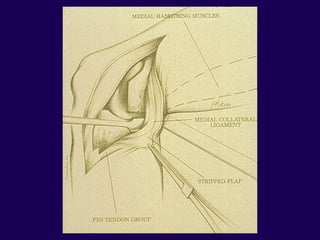
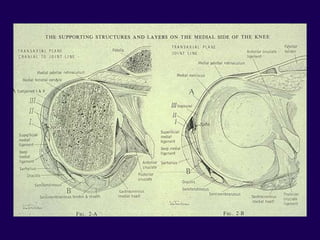
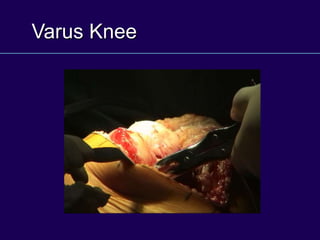
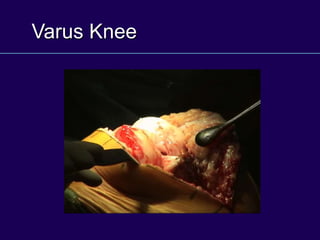
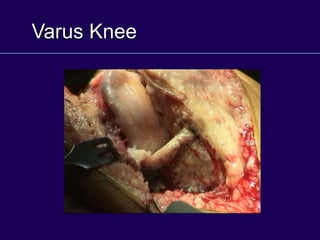
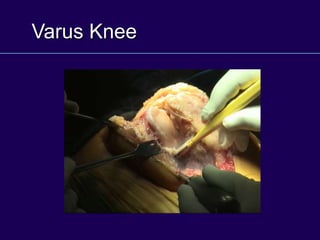
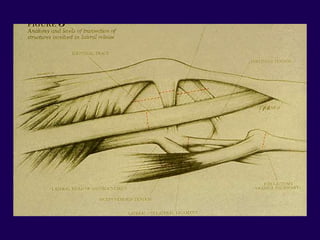
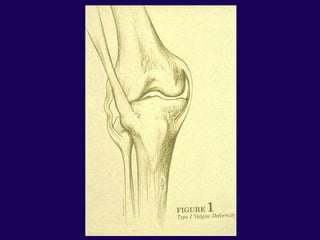
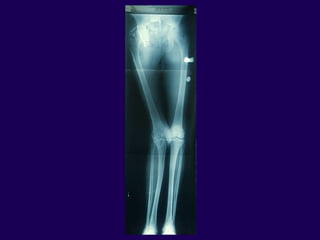
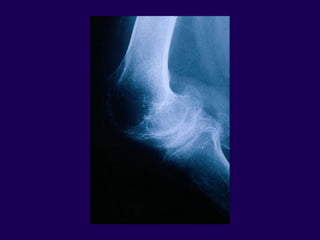
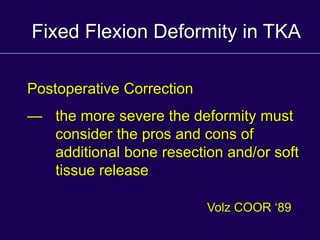
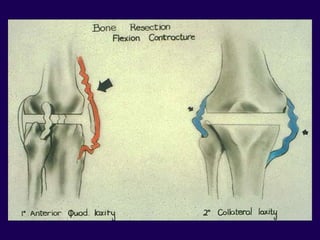
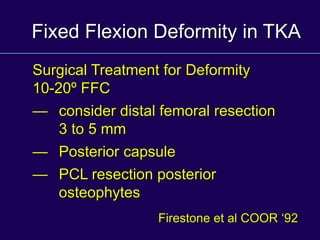
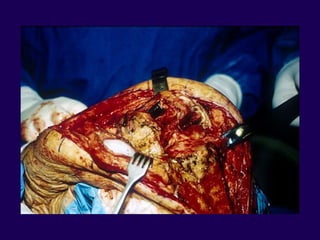
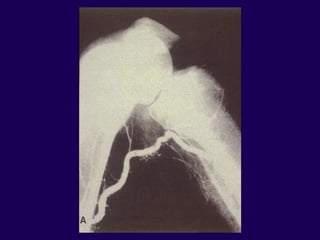
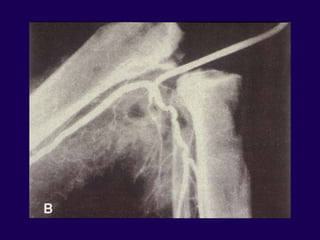
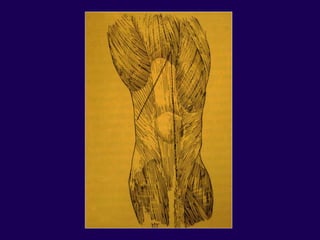
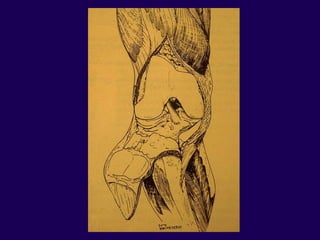
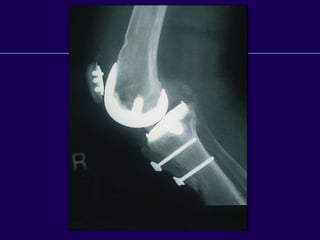
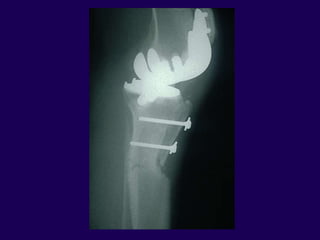
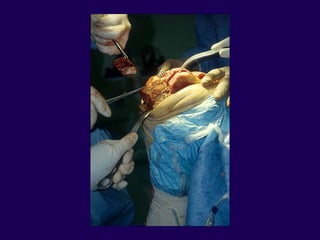
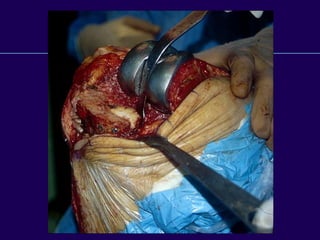
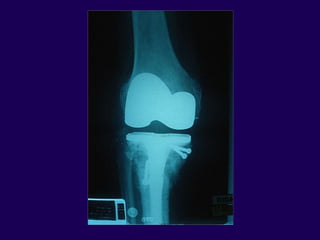
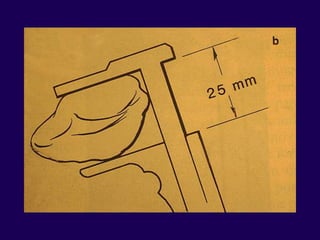
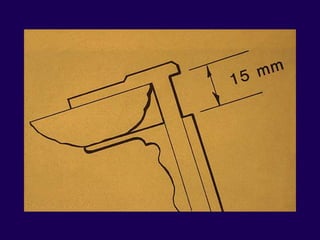
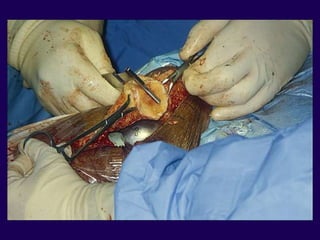
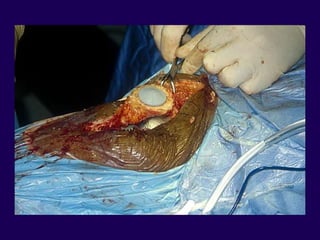
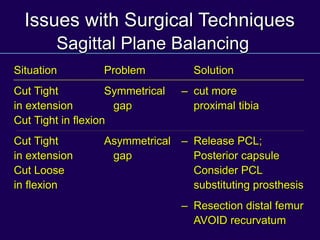
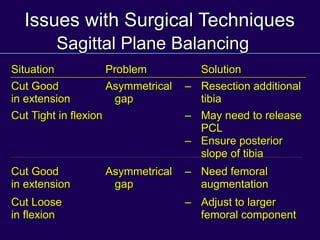
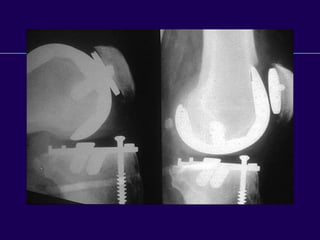
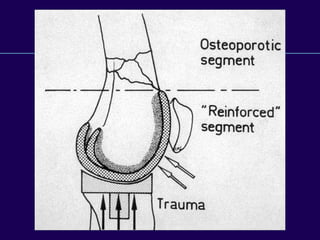
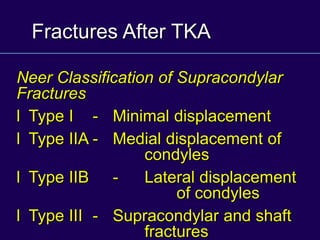
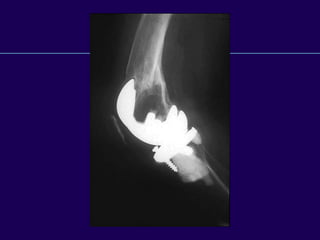
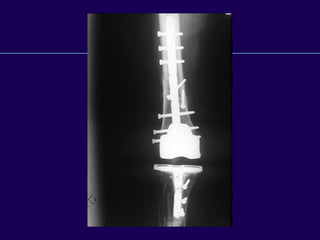
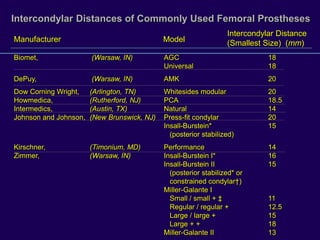
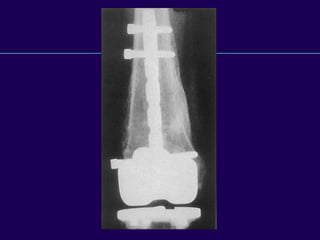
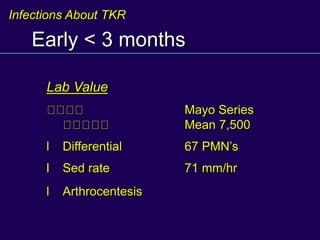
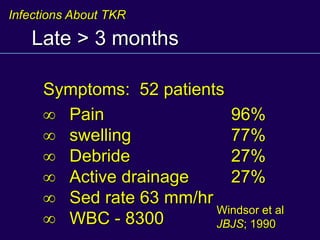
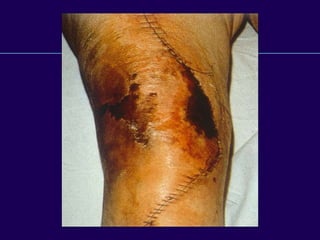
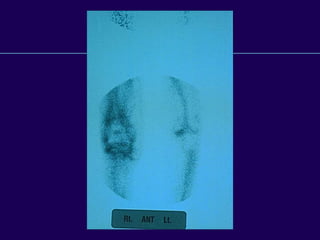
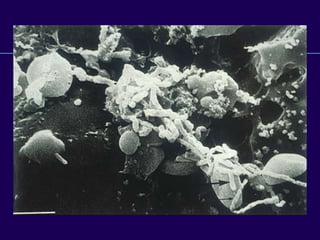
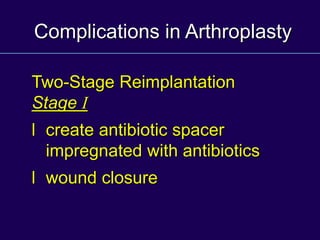
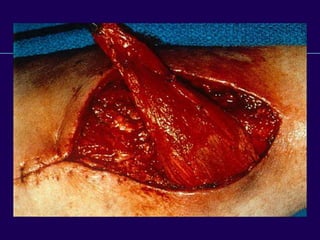
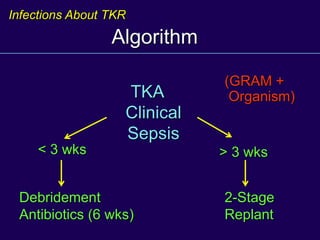
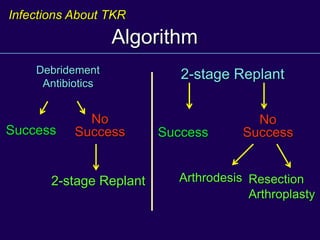
This document discusses total knee arthroplasty (TKA). It covers preoperative planning including radiographic evaluation, surgical techniques such as alignment and soft tissue balancing, and complications including supracondylar fractures. Key points include restoring mechanical alignment and joint line during TKA, use of extramedullary and intramedullary guides for alignment, balancing flexion-extension gaps, and treating supracondylar fractures nonoperatively when possible.