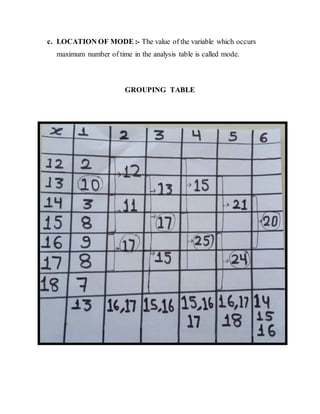
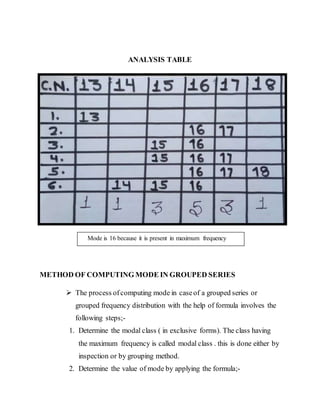
The document discusses the concept of mode in statistics. It defines mode as the value that occurs most frequently in a data set. It provides different methods to calculate the mode for individual data series, discrete series, and grouped series. These include inspection methods, making discrete series, using the mean and median formula, and grouping methods. The document also outlines some merits of using mode, such as being easily understood, as well as some demerits, such as it not being based on all observations. It concludes by discussing some uses of mode and providing a reference.