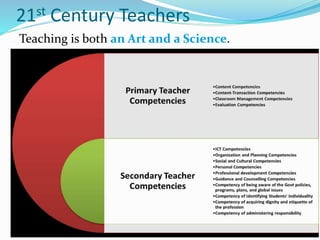
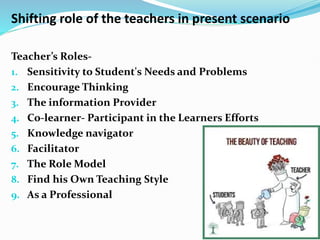
The document discusses the evolution of the Indian teaching-learning system from the guru-shishya tradition to contemporary pedagogical practices, emphasizing the integration of traditional value-based education with modern technology as outlined in the National Education Policy 2020. It highlights the diverse pedagogical approaches necessary for effective learning, including experiential, inquiry-driven, and learner-centered methods, while also addressing the roles of teachers in fostering a supportive learning environment. The document advocates for inclusivity and the development of 21st-century skills, underlining the importance of adapting teaching methods to meet the varied learning needs of students.