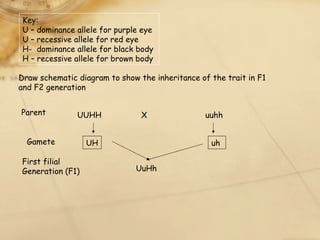
This document discusses Mendelian genetics and inheritance patterns. It introduces key concepts such as:
- Traits being controlled by genes which consist of allele pairs
- Dominant and recessive alleles and how they determine phenotypes
- The use of Punnett squares to predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes from parent crosses
- Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment, which describe how alleles separate and assort independently during gamete formation and fertilization.
Several examples are provided to illustrate Mendelian crosses involving one or two traits, and how the expected phenotypic ratios in offspring can be determined. Questions are also included to test understanding of genetic terminology and inheritance patterns.