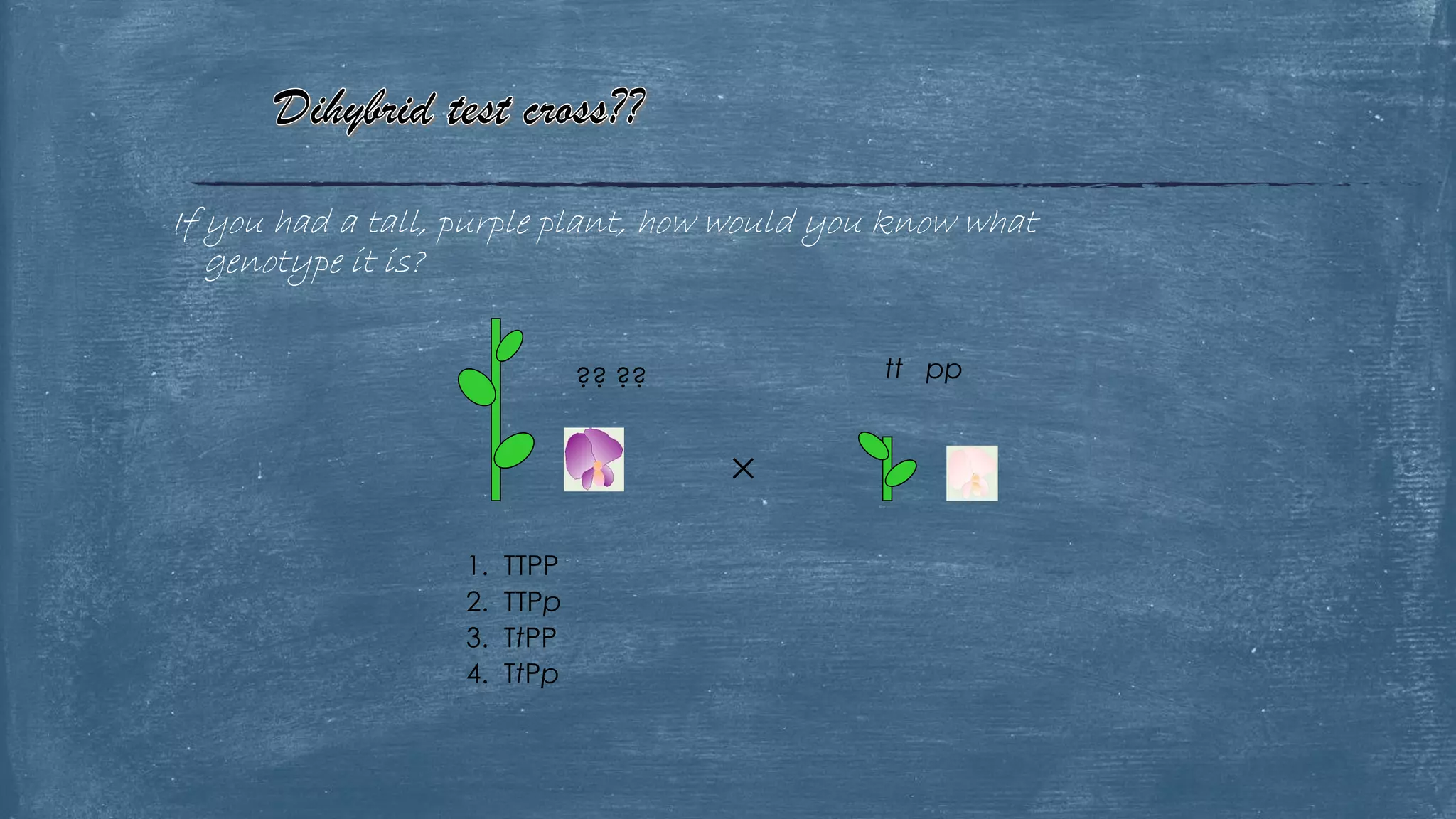
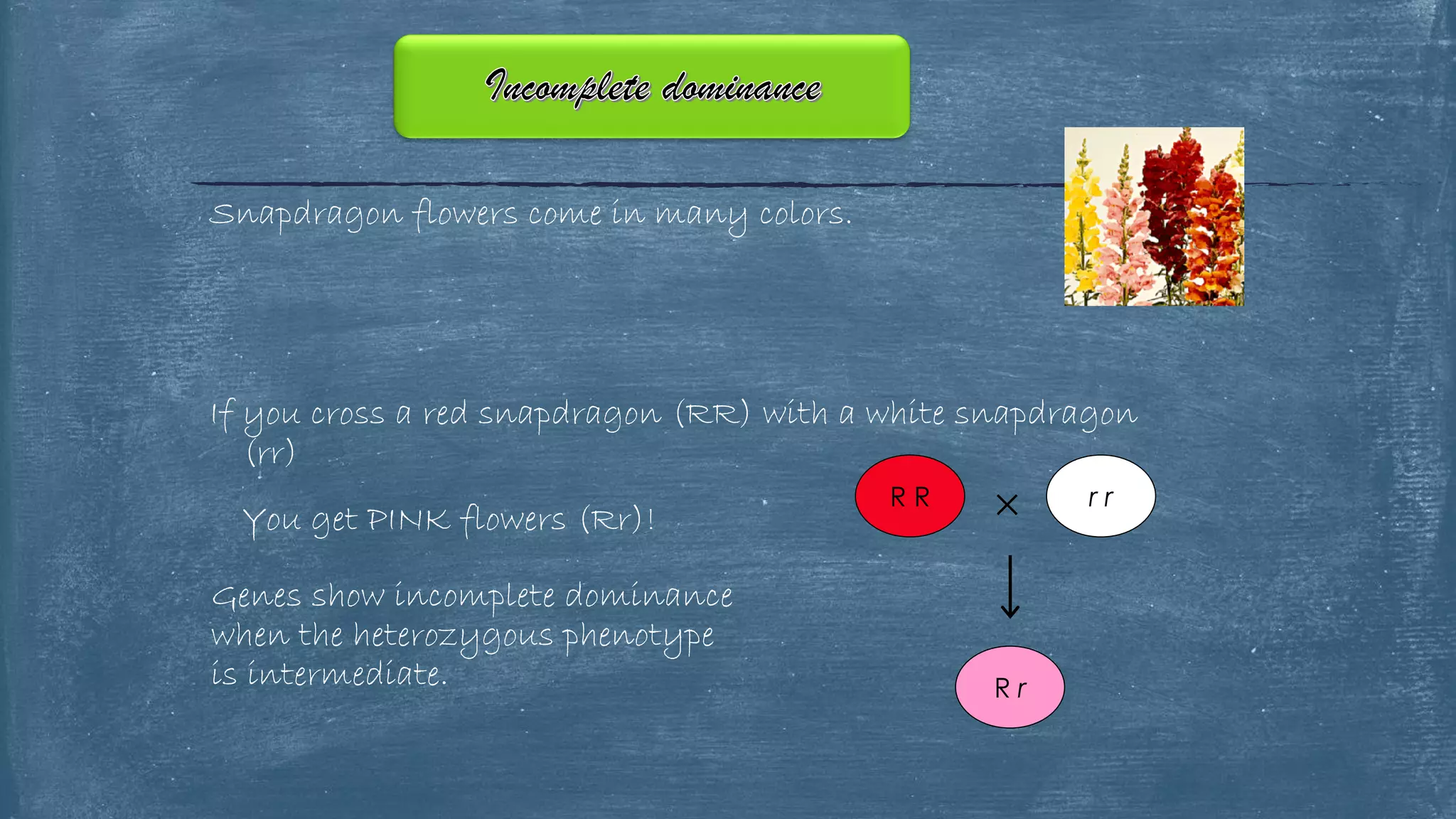
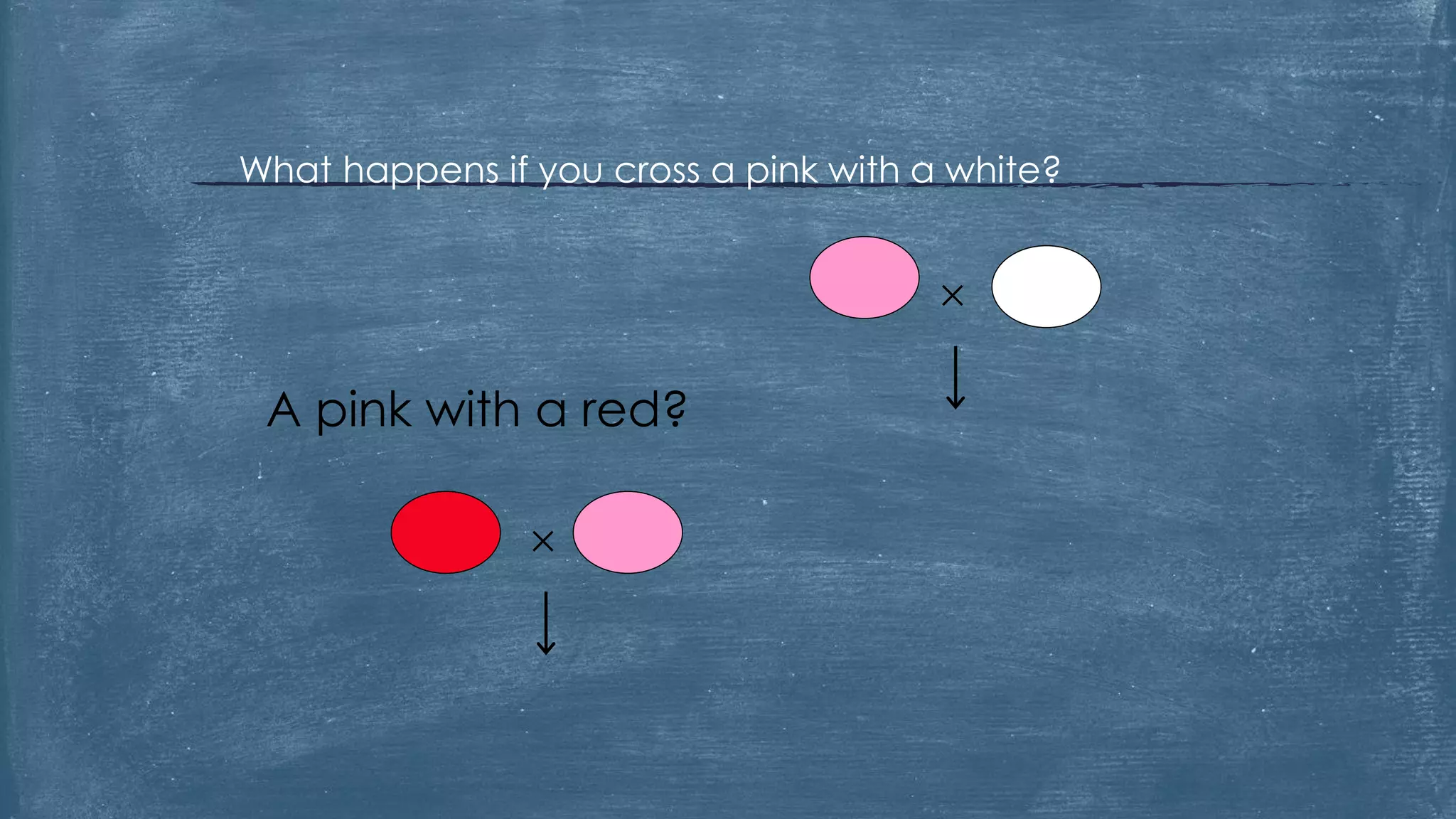
The document discusses several of Mendel's principles including independent assortment and how genes from one pair segregate independently from other gene pairs during gamete formation. It provides examples of test crosses using phenotypes like flower color to determine the genotype of unknown parents. The document also discusses incomplete dominance in snapdragons where the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate, appearing as pink flowers.