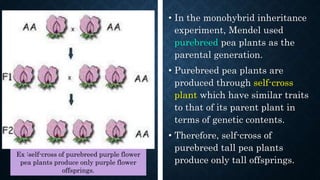
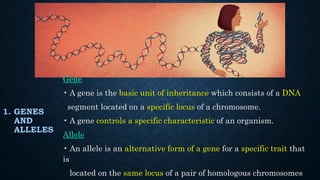
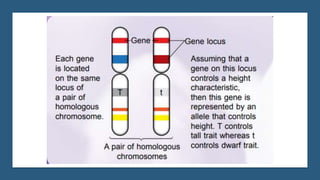
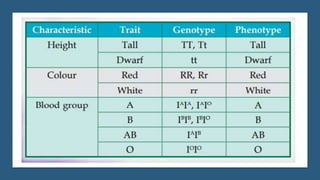
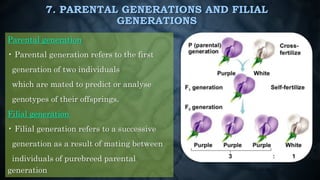
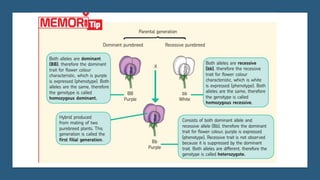
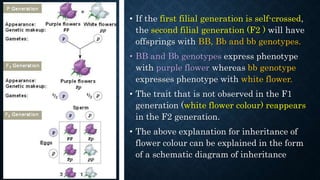
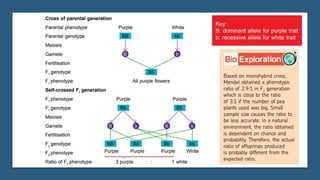
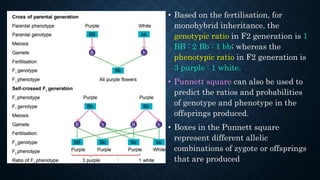
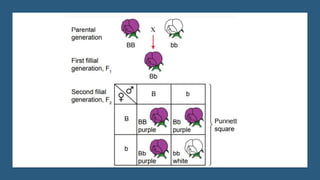
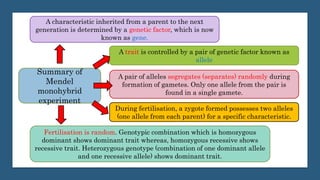
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments on pea plants to study inheritance of traits from parents to offspring. He found that traits are controlled by factors now known as genes and alleles. A characteristic has two alleles, and offspring inherit one allele from each parent. If one allele is dominant, it suppresses the effect of the recessive allele. In Mendel's monohybrid crosses, the F1 generation showed only the dominant trait, while the F2 generation had a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits. Mendel's experiments formed the basis of classical genetics and laws of inheritance.