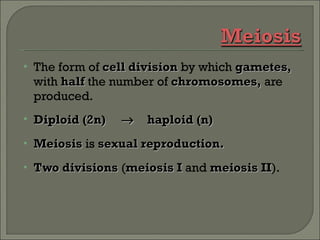
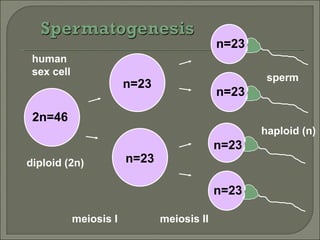
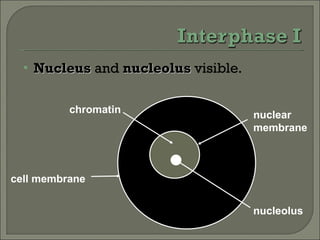
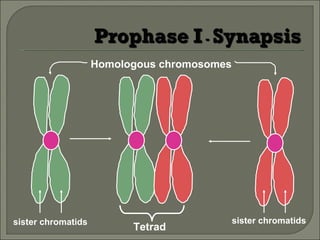
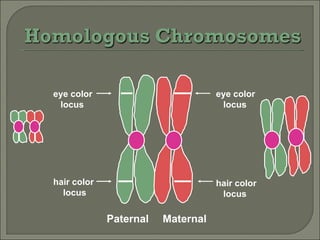
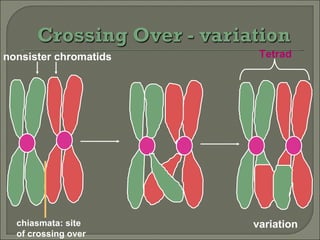
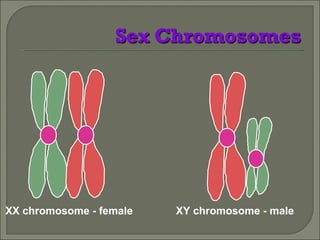
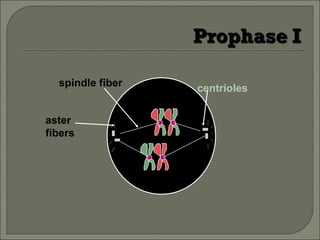
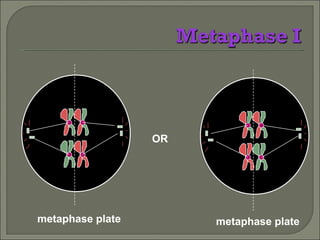
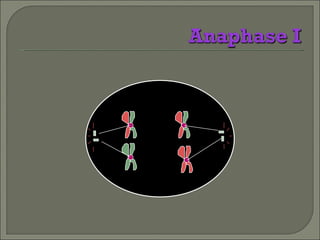
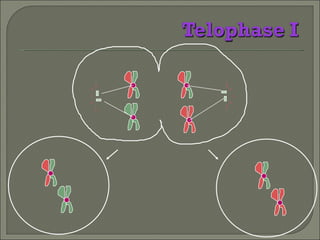
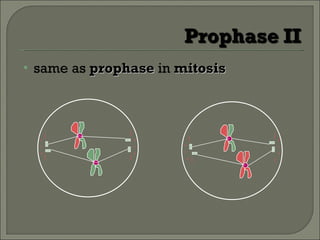
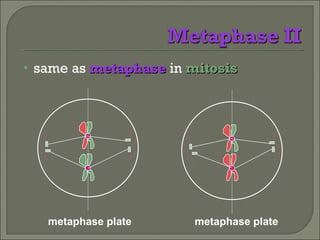
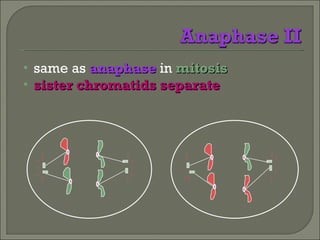
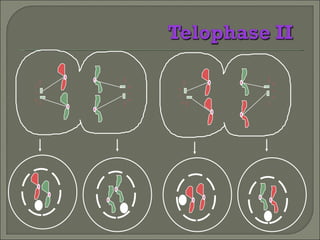
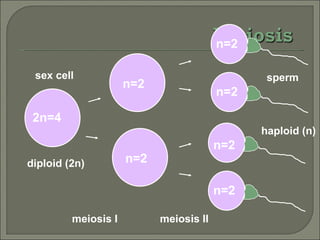
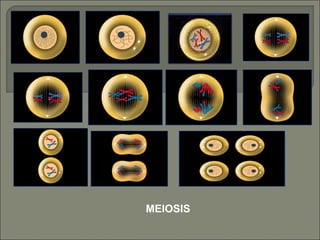
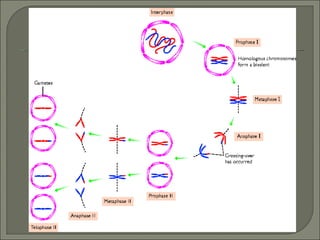
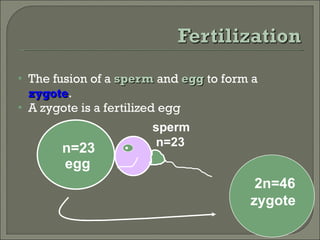
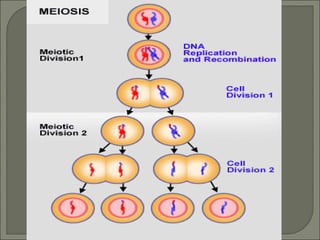
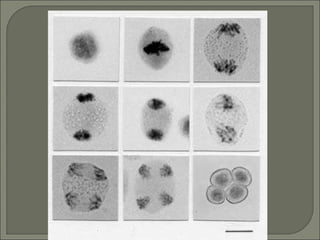
Meiosis is the type of cell division that produces gametes, such as sperm and egg cells, which have half the number of chromosomes as regular body cells. It involves two cell divisions - Meiosis I and Meiosis II. In Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and separate, reducing the chromosome number by half. Meiosis II then separates the sister chromatids, resulting in four haploid daughter cells each with a single set of chromosomes. Meiosis introduces genetic variation through independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over, providing the raw material for natural selection.