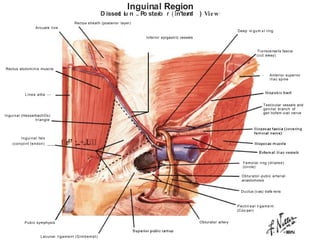
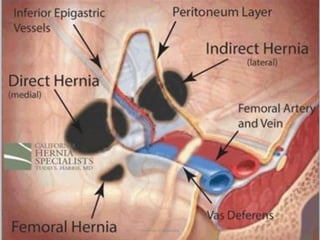
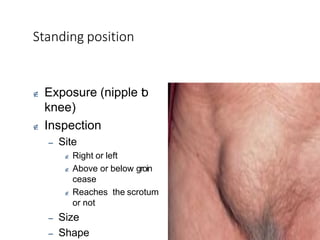
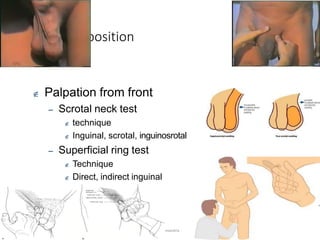
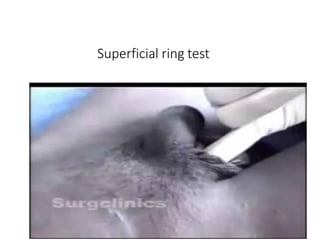
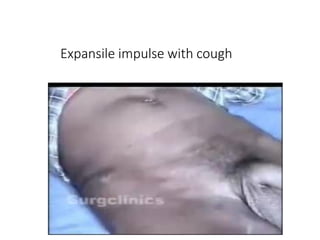
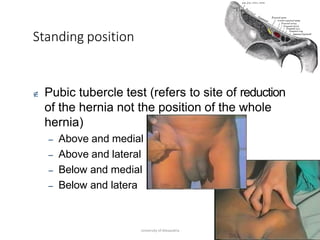
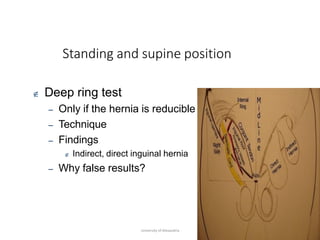
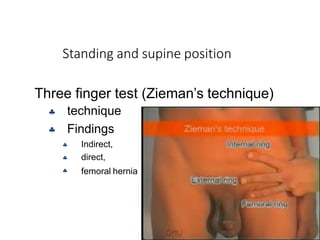
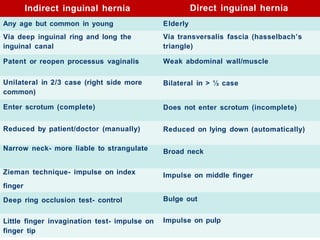
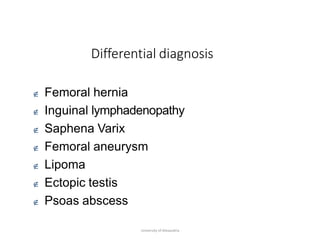
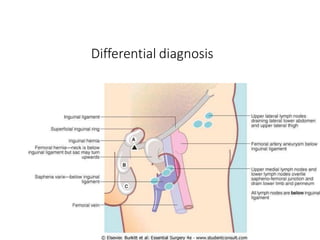
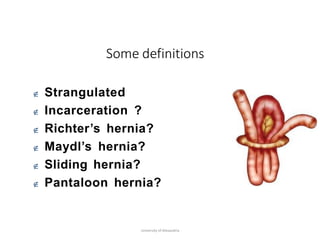
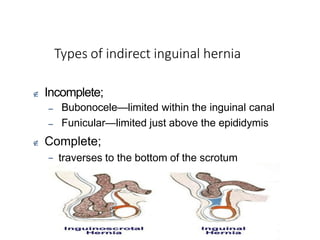
This document provides information on examining a patient with an inguinoscrotal hernia. It describes the steps of the examination including inspection, palpation, and tests to determine the type and characteristics of the hernia. The examination is done in both standing and supine positions and includes assessing the swelling, impulse, reducibility, and differentiating between direct and indirect hernias. Differential diagnoses and complications are also discussed.