Embed presentation
Downloaded 27 times








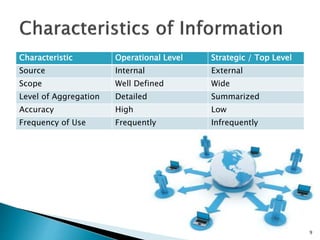



Group project members include Nayanajith, Sachith, Kavinda, Ayesha, Navinda, Lakmi, and Thilini. The document discusses information sources, distinguishing between internal sources like policies and communications within an organization, and external sources like government rules and competitor information. It also notes that organizational data is dynamic and changes over time, so information systems must verify information quality. Key characteristics of information are discussed, such as the difference between operational and strategic levels, and between formal and informal information sources.










