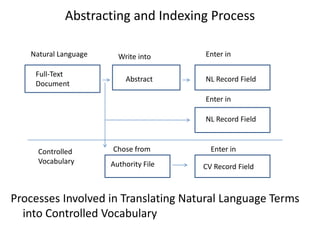
This document discusses subject indexing languages. It defines subject indexing language as a set of controlled vocabulary terms and their relationships that are used to describe the concepts in documents. There are three main types of indexing languages: natural language, which uses terms directly from the document; controlled vocabulary, which uses standardized terms from an authority list; and free indexing language, which uses any terms. The key aspects of subject indexing languages are that they allow concepts from documents to be represented in a structured way to facilitate information retrieval.