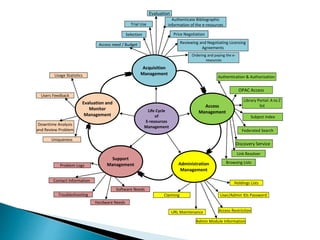
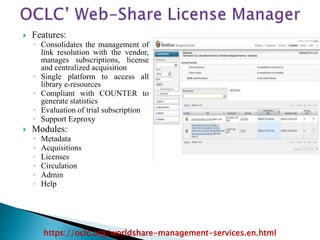
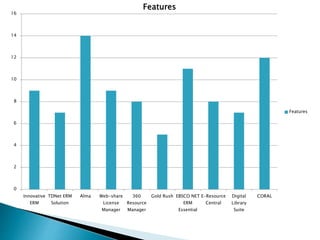
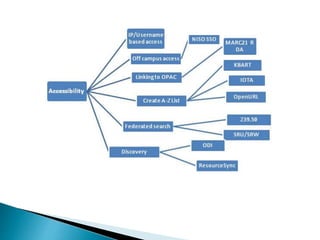
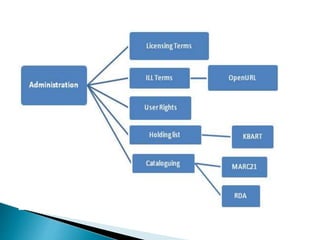
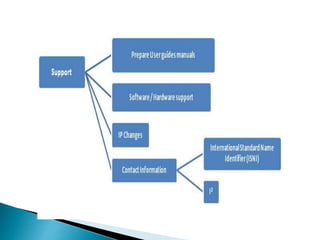
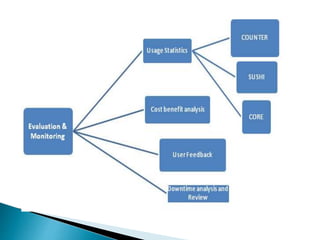
The document provides a comprehensive overview of electronic resource management (ERM), detailing its lifecycle, systems, standards, and best practices. It discusses acquisition, access, administration, support, and evaluation management, along with various ERM systems and their advantages and disadvantages. The document emphasizes the need for effective management of electronic resources in libraries, highlighting the complexities and requirements for implementation.