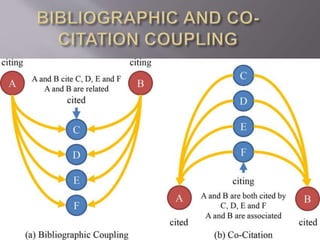
The document discusses citation analysis and its importance in measuring the quality and impact of research. Citation analysis evaluates the citations received by research papers, scientists, universities, and countries as a measure of scientific influence and productivity. Citations serve several purposes, such as acknowledging prior work, substantiating claims, and showing consideration of different opinions. Co-citation coupling and bibliographic coupling are methods to establish relationships between scholarly works based on their citations. Common citation metrics include the h-index and impact factor, which provide ways to quantify the impact of research, though they also have limitations. Overall, citation analysis through various metrics is an objective way to determine how influential and important a piece of research has been to the scientific community.