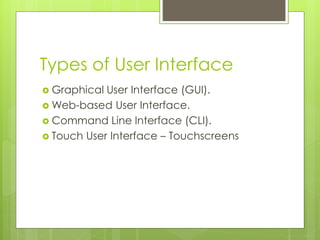
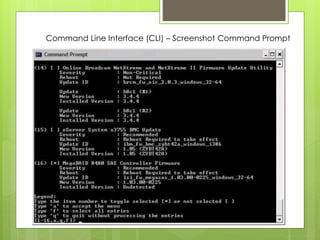
This document provides an overview of human-computer interaction (HCI) from the perspective of a student group consisting of Buwenaka, Piyumika, Thilan, Sachith, and Nuwan. It defines HCI as the discipline concerned with designing, evaluating, and implementing interactive computing systems for human use. The document discusses key aspects of HCI like the importance of understanding how humans and computers interact, defining user interfaces, principles of HCI design, the history and importance of HCI, and different types of user interfaces.