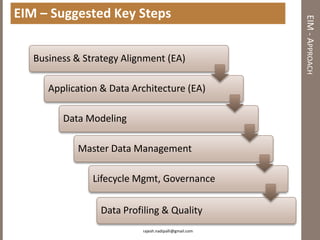
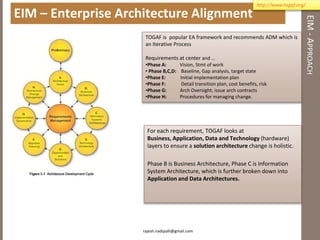
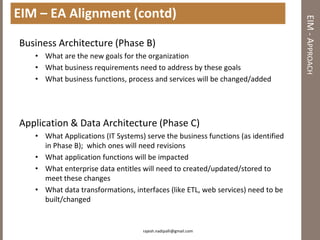
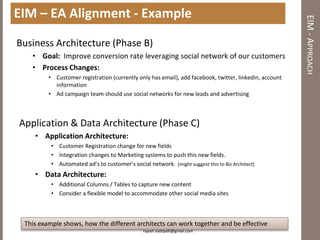
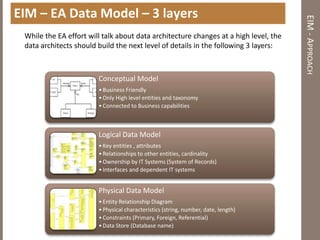
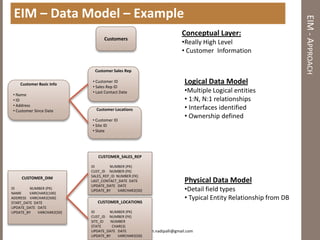
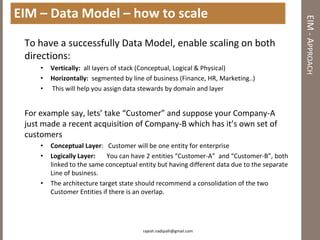
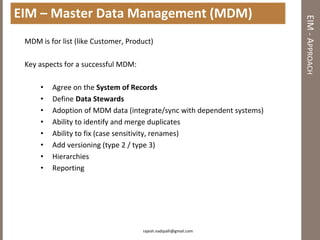
The document discusses practical enterprise information management. It describes EIM as managing data in all forms as a strategic asset. A good EIM program results in integrated, accurate and timely enterprise data through policies, frameworks, technologies and processes. These include data models, data lineage, data quality, data profiling and stewardship. The document recommends aligning EIM with enterprise architecture and developing conceptual, logical and physical data models across three layers to support the information architecture.