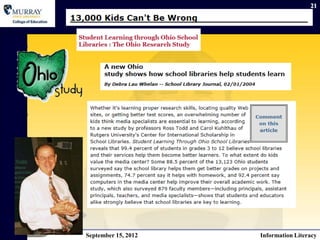
The document discusses information literacy and related concepts. It defines information literacy as the skills needed to find, understand, evaluate, and use information. These include understanding how libraries are organized, using research tools and techniques. The document also discusses related terms like information competence, which integrates additional skills. It notes the emphasis on 21st century skills and how school libraries can help develop these skills in students to prepare them for lifelong learning.






















![24
Keith Curry Lance
What Research Tells Us About the
Importance of School Libraries
• At this point . . . there is a clear consensus in
the results now [2002] available for eight
states*: School libraries are a powerful force
in the lives of America's children. The school
library is one of the few factors whose
contribution to academic achievement has
been documented empirically, and it is a
contribution that cannot be explained away
by other powerful influences on student
performance.
• White House Conference on School Libraries
• *15 states—see
Now, 20 states with New Jersey 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lib601infolit-120915205134-phpapp02/85/Information-Literacy-What-is-it-24-320.jpg)
![25
A European view
School Library and School Librarianship
• The stream of information from TV channels,
Internet, CD-ROMs, computer programmes
etc. is unending. If the students, when they
become adult citizens, are not to feel lost and
helpless in the face of such rich sources of
information, they must learn [to] devise
personal strategies for information retrieval
while they are still at school. Information
Literacy and “strategies for independent
learning skill development” are key
components of any school library.
• From a White Paper by Gert Larsen, School Library
Advisor, Albertslund, Denmark, p. 7
• Part of Project GrandSlam - General Research and New
Development in School Libraries As Multimedia Learning
Centres](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lib601infolit-120915205134-phpapp02/85/Information-Literacy-What-is-it-25-320.jpg)


