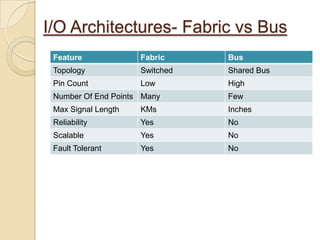
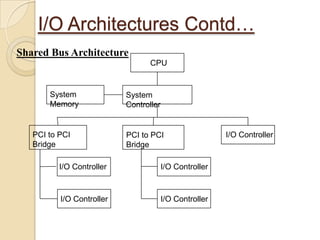
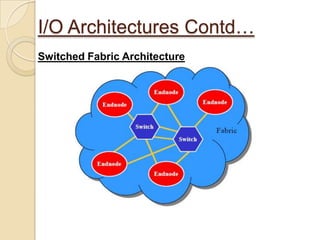
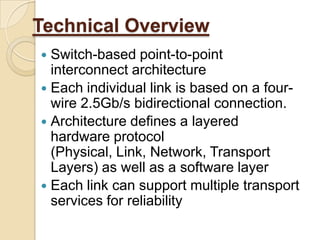
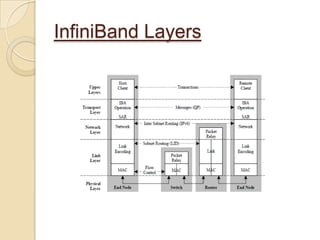
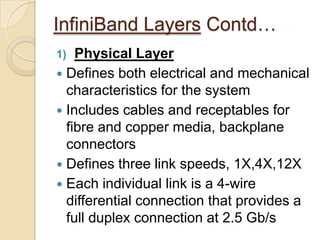
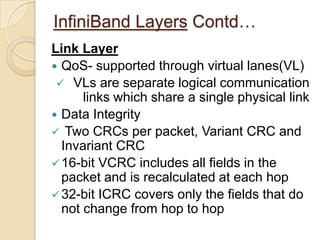
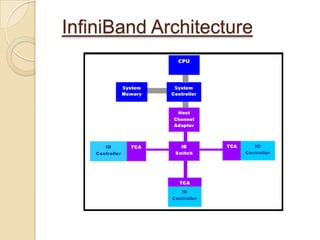
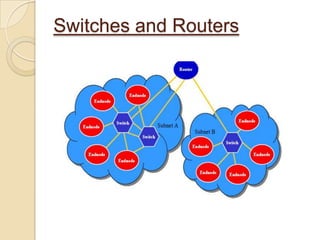
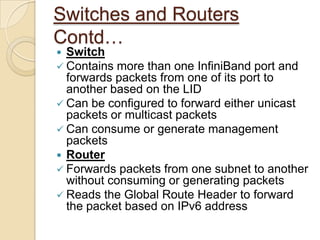
The document presents an overview of InfiniBand, a switch-based serial I/O interconnect architecture that operates at varying speeds of 2.5, 10, and 30 Gb/s while providing features like QoS and RAS. It details the architecture's layered protocol design, including the physical, link, network, and transport layers, as well as its advantages like low-latency and high efficiency, and drawbacks such as complexity and limited support. InfiniBand is positioned for markets such as application clustering, inter-processor communication, and storage area networks.