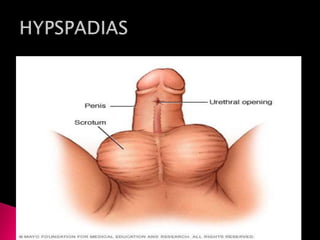
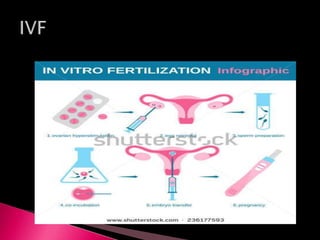
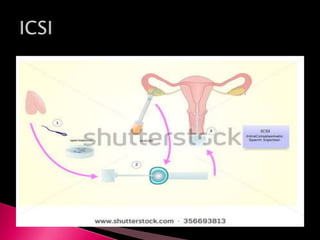
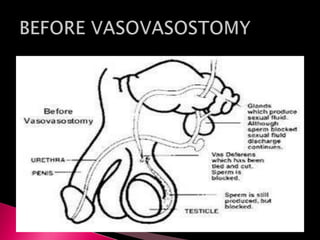
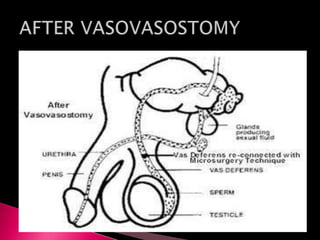
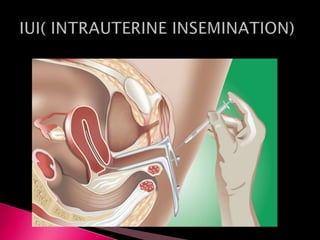
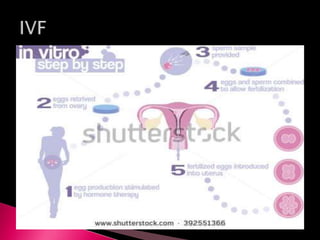
This document summarizes a seminar on male reproductive system disorders presented by Nikhil Vaishnav. It defines infertility as failure to conceive within one year of unprotected sex. There are two types of infertility - primary where couples have never conceived, and secondary where difficulty conceiving occurs after an initial conception. Infertility affects 1 in 7 couples and can be due to issues with sperm production, obstruction, ejaculation problems, or seminal fluid abnormalities in the male partner. Causes include genetic factors, infections, medications, lifestyle, and endocrine or structural abnormalities. Diagnosis involves medical history, exams, semen analysis, and hormone or genetic testing. Treatment focuses on improving general health, avoiding medications, using fertility drugs or therapies