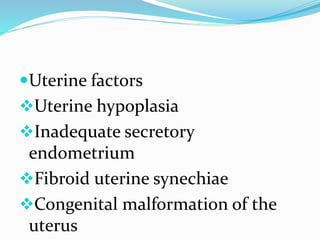
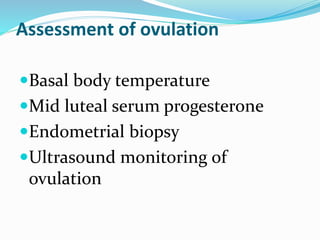
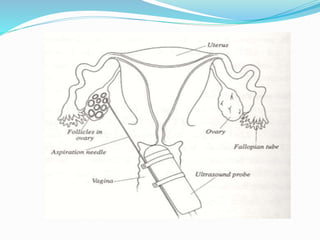
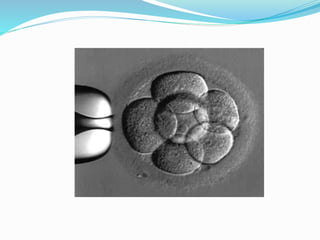
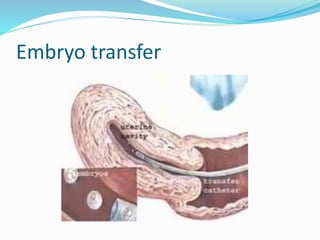
Infertility can be caused by female or male factors and is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular unprotected sex. Common causes include problems with ovulation, the fallopian tubes, sperm quality, or other issues. Treatment may include fertility drugs to stimulate ovulation, surgery to repair damaged reproductive organs, artificial insemination (IUI), in vitro fertilization (IVF), or other assisted reproductive technologies (ART) like GIFT or ZIFT. The goal of treatment is to address the underlying cause of infertility and increase the chances of conception and pregnancy.